![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the fate of the paramesonephric duct in the female? In the male? |
In the female, the Mullerian duct becomes:
oviduct uterus cervix cranial vagina (nothing in male) |
|
|
What is the fate of the mesonephric duct in the female? In the male?
|
In the male, Wolffian duct becomes:
efferent ducts/ductules epididymis ductus deferens (nothing in female) |
|
|
What gene promotes male development? Where is it carried? What does it do?
|
SRY gene on Y chromosome promotes differentiation of Sertoli cells
|
|
|
What substance causes regression of the mullerian ducts? Where is it produced?
|
Mullerian inhibitory substance (produced by Sertoli cells)
|
|
|
Which is more common, male or female pseudohermaphrodites?
|
Male pseudohermaphrodite
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of male infertility?
|
Testicular degeneration (atrophy)
|
|
|
What are major causes of testicular degeneration?
|
Thermal regulation
Zn deficiencies Hormone influences Auto-immune dz Toxins Obstructions Infections |
|
|
What is a common cause of testicular hypoplasia?
|
Cryptorchidism
|
|
|
Which is more common, epididymitis or orchitis? What species is it common in?
|
Epididymitis more common;
Seen in rams and dogs |
|
|
What are important causes of epididymitis in rams? In dogs?
|
Brucella, Actinobacillus, and Histophilus in rams
E. coli and Brucella in dogs |
|
|
What are differentials for a dog with endocrine alopecia, pendulous prepuce, gyenecomastia, and enlarged testis?
|
Sertoli cell tumor (hyperestrogenism);
Cushings, hypothyroid |
|
|
What is the most common testicular neoplasm in the horse? In the dog?
|
Horse - Seminoma
Dog - Leydig cell tumor |
|
|
T or F:
Seminomas are the most common tumor of the horse and dog. |
False! Most common in horse but 2nd most common in dog.
|
|
|
What are the four tumors of the testes?
|
Sertoli cell tumor
Leydig cell tumor Teratoma Seminoma |
|
|
Leydig tumors are most common in which species? What do these tumors produce?
|
Dog and bull;
Produce androgens or estrogens |
|
|
What is the most common cause of feminization?
|
Sertoli cell tumors!
|
|
|
Which tumor is common in foal cryptorchids?
|
Teratoma
|
|
|
What effect do androgens have on the prostate? Estrogens?
|
Androgens cause hyperplasia
Estrogens interfere w/proper differentiation |
|
|
What are common bacterial causes of prostatitis?
|
E. coli
Proteus Pseudomonas Brucella |
|
|
How can prostatic hyperplasia be differentiated from neoplasia?
|
Symmetry. Adenoma/Adenocarconoma will be asymmetric.
|
|
|
Incomplete closure of the urethra is...
|
...hypospadia
|
|
|
What are some major causes of balanopostitis?
|
Herpesvirus
Habronema spp. |
|
|
What are common penile tumors and which species is prone to each?
|
SCC - horses
Fibropapilloma - bulls Papilloma - pigs, horses TVT - dogs Sarcoid - horse sheath |
|
|
What is a common neoplasm on the equine penis and prepuce?
|
SCC!!
|
|
|
What are the cell layers of the ovary and what does each produce?
|
Thecal cells - androstenedione
Granulosa cells - estrogen (from androstenedione) and Progesterone |
|
|
What are the two endocrine cells of the testis? What does each produce? What stimulates each?
|
Leydig cells (stimulated by LH to produce T)
Sertoli cells (stimulated by FSH to produce androgen binding protein among other things) |
|
|
What is strange about bitch ovaries (histologically)? What is important about this?
|
Have subsurface epithelial structures; these can become neoplastic?
|
|
|
If there is Leydig cell hypoplasia, what could be the cause?
|
Reduced LH (due to pituitary issue or GnRH issue)
|
|
|
What are the common ovarian neoplasms?
|
Sex cord stromal tumor
Epithelial tumors Dysgerminoma Teratoma |
|
|
Which species commonly get sex cord stromal tumors? In which species are these tumors prone to metastasis?
|
Cats (common metastasis)
Dogs, cows Mares (rare metastasis) |
|
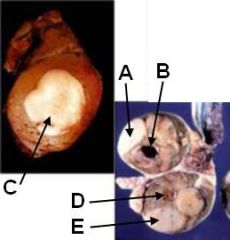
ID these testicular tumors
|
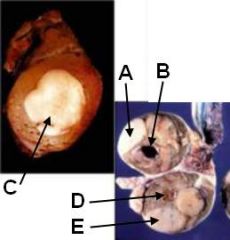
A - Seminoma
B - Sertoli cell tumor C - Seminoma D - Interstitial tumor (probably Leydig) E - Seminoma |
|
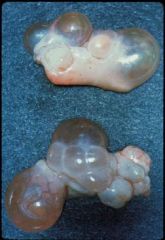
What is depicted in these ovaries? In which species is this common?
|
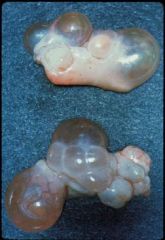
Cystic ovaries;
common in high-producing cows |
|
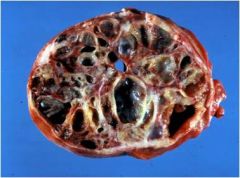
Name that tumor!!~
|
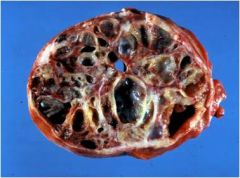
Sex cord stromal tumor (ovary)
|
|
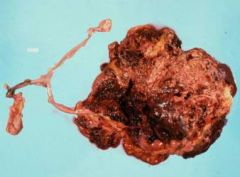
Name that tumor!
|
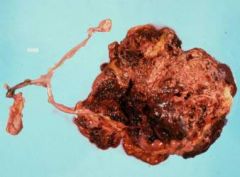
Sex cord stromal cell tumor (ovary, dog)
|
|
|
Ovarian epithelial tumors are common in which species?
|
Dogs
|
|
|
T or F:
Ovarian epithelial tumors are rarely metastatic. |
False! They are often metastatic to the abdomen.
|
|
|
Why does ascites develop in concert with ovarian tumors?
|
lymphatic blockage
|
|
|
What is the ovaries' version of the seminoma?
|
Dysgerminoma
|
|
|
What is an important cause of vulvitis in horses? In cattle, goats and horses?
|
Taylorella equigenitalis;
Herpesviruses for cattle, horses, and goats (BHV-1, EHV-3, CapHV-1) |
|
|
Why do fat old bitches get vulvitis?
|
Urine scalds
|
|
|
What are common masses found in the vagina, vulva, and cervix that are hormonally responsive?
|
Leiomyomas
Fibromatous polyps |
|
|
What are vulvar masses common to mares?
To old gray mares? |
SCC;
Melanoma |
|
|
What are some causes of uterine atrophy?
|
Anestrus
Hypopituitarism & wasting (rare) |
|
|
What condition is often a prelude to pyometra? What might cause this?
|
Endometrial hyperplasia secondary to hyperestrogenism or PG following estrogen priming
|
|
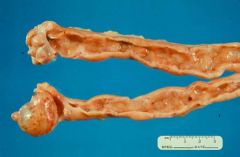
What condition is shown here?
|
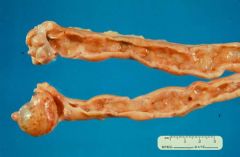
Endometrial hyperplasia (thick uterine wall with bubble-like changes)
|
|
|
What generally causes a pseudopregnancy?
|
Prostaglandan influence
|
|
|
What are common uterine masses in the bitch? In the cow?
|
Bitch (leiomyomas/sarcomas)
Cow (Lymphosarcoma) |
|
|
If you find lymphosarcoma in a cow, where else might you find it?
|
Heart
lymph nodes abomasum |
|
|
What are some differential diagnoses for equine metritis?
|
CEM (contagious equine metritis) caused by Taylorella equigenitalis;
(also S. zooepidemicus, E. coli, P. aeuriginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoniae) |
|
|
What is the post-parturitent endometritis called?
|
Lochia
|
|
|
How big of a problem is a retained placenta in a horse? In a ruminant?
|
Horse is CRISIS
Ruminant is no big deal as long as it is <12hrs |
|
|
What condition arises when a retained part of a placenta survives?
|
Subenvolution of placentocytes
|
|
|
Which species REQUIRE a CL to maintain pregnancy?
|
Cattle
Sheep Goats Pigs Horses |
|
|
How many fetuses must be present for a viable sow pregnancy?
|
4 (2 in each horn)
|
|
|
T or F:
Abortion is more common in farm animals than in cats/dogs. |
True!
Cats/dogs have a "predetermined" CL lifespan; most EED is reabsorbed or mummified |
|
|
What is the trigger inducing parturition?
|
Fetal stress! Once cortisol can be released from developed adrenals
|
|
|
When a dead fetus contaminated by putrefactive organisms it is called...
When is this common? |
Maceration is common in dystocia and first trimester deaths
|
|
|
Describe the placental type of a:
Horse Dog Cow Sheep Pig Cat |
Dog/Cat - Zonary
Horse/Pig - Diffuse Cow/Sheep - Cotyledonary |
|
|
What is the significance of squamous metaplasia on the placenta?
|
No effect on fetus
|
|
|
What are some insignificant placental lesions that may be seen?
|
Uteroverdin
Amniotic plaques (squamous metaplasia) Placental calcification Hippomane (allantoic calculi) |
|

What is going on here?
|

Uteroverdin
|
|
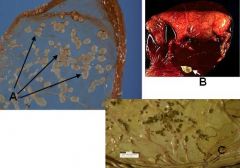
What is depicted here?
|
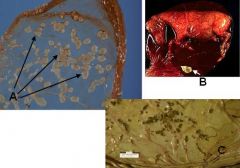
A - Amniotic plaques (squamous metaplasia)
B - Hippomane C - Placental calcification |
|
|
What are indications of placental insufficiency in ruminants?
|
Adventitial placentation
Placental wt <14% of fetal wt |
|
|
What should be examined in an equine placenta?
|
should be ~10% of fetal wt
examine avillous sites (tips of horn, cervical star, endometrial cups) umbilical cord should be 36-83cm |
|
|
What causes the majority of EED?
|
Genetics
|
|
|
What specific components of dam illness contribute to abortion/stillbirth?
|
Oxygen (anemia)
Pyrexia (fetus expelled if temp too high) Endotoxemia |
|
|
T or F:
The success rate in successfully diagnosing abortion/stillbirth causes is pretty low. |
True!
|
|
|
What are general steps in investigating abortion/stillbirth?
|
1) History
2) Dam exam 3) Serology (dam and other non-aborting dams) 4) Placental exam 5) Fetal exam 6) Estimate time of death 6) Fetal necropsy |
|
|
What is the important part of the placenta to sample?
|
Chorioallantois
|
|
|
How dead is a fetus with dehydrated eyes?
|
Really dead....72 hours
|
|
|
How dead is a fetus with cloudy corneas and blood-tinged amniotic fluid?
|
mostly dead....12 hours
|
|
|
How dead is a fetus with gelatinous fluid in subcutis (anasarca)?
|
pretty dead...36 hours
|
|
|
What tissues are sampled for bacteriology in an abortion necropsy?
|
lung, liver, stomach content
|
|
|
What samples are taken fo virology in an abortion necropsy?
|
kidney, lung, thymus
|
|
|
What serological samples are taken in an abortion necropsy?
|
2mL fetal fluid
2mL maternal serum |
|
|
What are common canine infectious agents involved in abortions?
|
Brucella canis, canine herpesvirus, neospora
|
|
|
What are common feline infectious agents involved in abortions?
|
FHV-1, calicivirus, FIV, FeLV
|
|
|
What are two important physical barriers preventing ascending infections in mammary glands?
|
Teat (streak) canal
Rosette of Furstenberg |
|
|
Which hormone promotes mammary development? Which hormone helps with milk let-down?
|
PG promotes development
PRL helps with milk let-down |
|
|
Name some mammary gland defense mechanisms against infection.
|
Normal flora
Rosette of Furstenberg/Teat canal Flushing effect of milk Lactoferrin, lysozyme, lactoperoxidase Macrophages/neutrophils/antibodies |
|
|
What are some causes of ischemic mammary necrosis?
|
Ergotism
Frostbite |
|
|
T or F:
Ascending mammary infections are more common than hematogenous. |
True
|
|
|
Which infectious mammary pathogen is an obligate inhabitant of the mammary gland?
|
Streptococcus agalactiae
|
|
|
Which infectious mammary pathogen causes watery, blood tinged milk?
|
Coliform mastitis (E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp.)
|
|
|
Which infectious mammary pathogen is associated with improper maintenance of milking machines?
|
Coliform mastitis (E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp.)
|
|
|
Which infectious mammary pathogen usually affects multiple quarters?
|
Mycoplasma bovis
|
|
|
Which infectious mammary pathogen is granulomatous and often iatrogenic?
|
Nocardia & yeasts
|
|
|
Which infectious mammary pathogen causes "blue bag" in sheep and goats?
|
Mannheimia haemolytica or Staphyloccus aureus
|
|
|
Which infectious mammary pathogen is common in sows?
|
Coliform mastitis (E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp.)
|
|
|
Which infectious mammary pathogen can affect immature or dry glands?
|
Arcanobacterium pyogenes
|
|
|
Which tumor is associated with canine mammary neoplasia in males?
|
Sertoli tumors
|
|
|
Are mammary neoplasias normally benign in dogs? In cats?
|
Dogs - half and half
Cats - usually malignant |
|
|
What is probably the most common canine mammary neoplasm?
|
Mixed mammary tumor
|
|
|
Where does neoplasia of the caudal two mammary glands metastasize to? The cranial 3?
|
Caudal - inguinal lnn
Cranial - axillary lnn |

