![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which bones constitute the foramen triosseum in birds? What fourth bone rounds-out the pectoral girdle?
|
Humerus
Scapula Coracoid (add clavicle for girdle) |
|
|
Which vertebrae are fused in the bird?
|
T2-T5;
T6-L7 |
|
|
How many cervical vertebrae do birds have?
|
variable (11 to 25)
|
|
|
What is the fastest growing bone in the bird body?
|
Tibiotarsal bone
|
|
|
Which joint is a major stress point of the bird?
|
Intertarsal joint
|
|
|
What are the two categories of birds? Which has a keel?
|
Rattites and Carinate (keeled)
|
|
|
Which birds are found in the rattite group?
|
Kiwi, Ostrich, Emu, Cassowary, and Rhea (and Moa
|
|
|
Where is most avian respiratory pathology located?
|
Dorsoposterior (due to gravity)
|
|
|
Which bird group has extensive cervical air sacs?
|
Parrots
|
|
|
What is weird about bird heart valves?
|
Right AV valve is muscular
|
|
|
What is weird about the avian hematopoetic system?
|
NO LYMPH NODES (except for ducks and geese)
|
|
|
What happens in birds if their urinary system malfunctions?
|
Gout! (uric acid buildup)
|
|
|
Which birds don't have crops?
|
Owls; fish eating birds
|
|
|
Ovary is on the ________ side in birds.
|
LEFT
|
|
|
T or F:
Birds have no diaphragm to divide their thoracic and abdominal cavities. |
Bad question!
They have no diaphragm AND have no abdominal or thoracic cavities! They just have a coelomic cavity! |
|
|
Characterize the avian inflammatory response.
|
Intense granulomatous reaction (within 12h);
Basophils NOT eosinophils involved in acute response |
|
|
What is a common pathogen affecting the skin of birds?
|
Pox viruses
|
|
|
Fowl Cholera is caused by...
|
Pasturella multocida
|
|
|
What is an important rule-out for Newcastle Disease?
|
Fowl Cholera (P. multocida)
|
|
|
Which respiratory disease is caused by a herpesvirus, is reportable in some states, and mainly affects young chickens with up to 50% mortality?
|
Infectious laryngotrachitis
|
|
|
What is a major cause of fungal pneumonia in birds?
|
Aspergillus spp.
|
|
|
Infectious bursal disease is caused by which viral family?
|
Birnavirus
|
|
|
What viral family causes Marek's disease?
|
Herpesvirus
|
|
|
What are two categories of lymphoid neoplasia in chickens? What causes each?
|
Marek's disease (herpesvirus)
Lymphoid leukosis (retrovirus) |
|
|
Lymphoid leukosis causes a ____ cell neoplasm while Marek's disease causes a ________ cell neoplasm.
|
B for Lymphoid;
T for Marek's |
|
|
What are important protozoal diseases of chickens?
|
Coccidiosis (esp. Eimeria spp.);
Histomoniasis (black-head) |
|
|
What causes hemorrhage and/or fibrin exudates of the cecum or small intestine?
|
Coccidiosis
E. tenella (cecum) E. necatrix (small intestine) |
|
|
Black head is caused by...
|
Histomonas infections
|
|
|
What are lesions found in histomoniasis in chickens?
|
Black head;
Enteritis (typhlitis and fibrin casts) Target lesions in the liver |
|
|
How is histomoniasis transmitted?
|
Round worms transmit the protozoans
|
|
|
Slippage of the gastrocnemius is called...
|
...Perosis
|
|
|
What is a common condition in laying hens?
|
Hepatic lipidosis;
also carcinomatosis |
|
|
Failure of cartilage resorbtion can cause...
|
...Tibial dyschondroplasia
|
|
|
What are the two most important causes of mortality in baby chicks?
|
Retarded and don't know how to eat and then starve
Yolk sac infections |
|
|
What is a common condition in fast growing chickens? What exacerbates this?
|
ASCITES SYNDROME
R-sided heart failure when put on weight too fast; Exacerbated by high altitude (low pressure and O2) |
|
|
What is an important rule-out in diagnosing carcinomatosis in old laying hens?
|
Avian tuberculosis
|
|
|
Fowl plague is known as...
|
avian influenza
|
|
|
What viral family causes avian flu? What is the reservoir?
|
Orthomyxoviridae:
Waterfowl reservoir |
|
|
What is the major clinical sign of HPAI? What is a great place to spread avian influenza?
|
Respiratory distress;
spread in bird markets! |
|
|
What are gross lesions found with HPAI?
|
Necrosis of cecal tonsils
Cyanosis of extremities Hemorrhage in duodenum |
|
|
What are important differentials when considering HPAI?
|
Newcastle disease
Fowl cholera Infectious laryngotracheitis Other respiratory diseases |
|
|
How can HPAI diagnosis be confirmed? Is this a reportable disease?
|
Yes its reportable, dumbass!
COnfirm via pcr of serum, tracheal or cloacal swabs. Histo of tissues too. |
|
|
What are some important causes of oral and crop lesions (white to yellow plaques) in birds?
|
Infectious laryngotracheitis
Fowl pox Thrush (candidiasis) Trichomoniasis Salmenellosis Capillaria Hypovitaminosis A (squamous metaplasia) |
|
|
Bumblefoot is caused by...
|
Staph aureus infection
|
|
|
What causes psitticosis in humans?
|
Chlamydia
|
|
|
What are lesions associated with avian chlamydophilosis?
|
Fibrin on liver
lung hemorrhage perhaps necrosis of liver |
|
|
How can chlamydophilosis be diagnosed histologically? Clinically?
|
Positive acid-fast stain shows organisms in cytoplasm;
Clinical tests include PCR and ELISA |
|
|
What avian multisystemic disease is caused by a herpesvirus? How is it transmitted?
|
Pacheco's disease;
orofecal transmission |
|
|
How can Pacheco disease be treated? How can it be diagnosed?
|
Acyclovir and quarantine;
dx via PCR, pharyngeal or cloacal swabs |
|
|
Which highly fatal viral disease is seen just prior to fledgling?
|
Avian polyoma virus
|
|
|
What are two avian diseases spread via feather dander?
|
Marek's Disease
Beak and Feather Disease |
|
|
Beak and Feather Syndrome is caused by which family of virus?
|
Circovirus
|
|
|
Which bird species is most affected by beak and feather syndrome? When does it usually strike?
|
Cockatoos;
usually <3yrs |
|
|
Macaw wasting disease is also known as....
What causes this disease? |
Proventricular dilation syndrome;
caused by a Bornavirus |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of Macaw wasting syndrome?
|
Bornavirus attacks sympathetic nervous system, causes proventricular ileus (dilation)
|
|
|
Which avian viral diseases are characterized by a lymphocytic proliferation of nervous tissue? What viral familes are these from?
|
Proventricular dilation syndrome (bornavirus)
Marek's disease (herpesvirus) |
|
|
What is the cause of scaly face? How is it treated?
|
Knemidocoptes mutans (mites);
Treat w/ivermectin |
|
|
What is a major cause of lameness in budgies?
|
Renal carcinomas (push on nerve roots)
|
|
|
Budgies get lots of neoplasms. What are they commonly?
|
Lipomas
Renal carcinomas Pituitary adenomas |
|
|
Oral or cloacal lesions on an Amazon are usually...
|
Papillomas
|
|
|
What virus family is responsible for Newcastle Disease?
|
Paramyxovirus
|
|
|
Which avian viral diseases may exhibit neurotropisms? What family for each?
|
Newcastle disease (Paramyxovirus);
Proventricular Dilation syndrome (Bornavirus); Pacheco's Disease (herpesvirus) Avian flu (Orthomyxovirus); Mareck's dz (Herpesvirus) |
|
|
What are major routes of Newcastle disease transmission?
|
Direct contact (feces/respiratory);
Fomites |
|
|
T or F:
Newcastle disease causes no disease in humans. |
False!
Causes conjunctivitis and mild respiratory disease. |
|
|
Newcastle disease signs resemble what other viral disease?
|
Avian flu
|
|
|
What are the three types of newcastle disease and what are the characterics of each?
|
Neurogenic (paralysis, torticollis, opisthotonus, depression)
Viscerotropic (conjunctivitis, coughing, gasping) Lentogenic (long incubation) |
|
|
T or F:
Respiratory signs of Newcastle disease are often more pronounced in poultry as compared to psittacines. |
True!
|
|
|
What are some gross lesions of Newcastle disease?
|
Often none (esp. if neurotropic);
Hemorrhages anywhere in GI tract or trachea (cecal tonsils) |
|
|
What samples are taken to diagnose Newcastle disease?
|
Tracheal/cloacal swabs
Lung Spleen Brain |
|
|
What are some differentials for Newcastle disease?
|
Fowl cholera
Avian flu ILT Fowl pox Pacheco's disease Chlamydophilosis Also cormorant paramyxovirus in Oregon |
|

What oral med should be given to this poor kid?
|

Ivermectin! Treats the mites in scaly face!
|
|
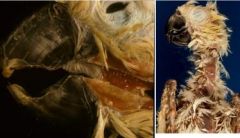
Family of virus causing this disease?
|
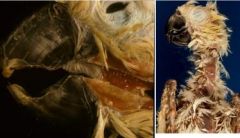
Circovirus (Beak and Feather Disease)
|
|
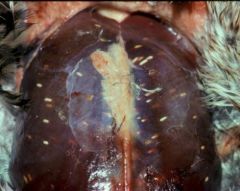
Diagnosis?
|
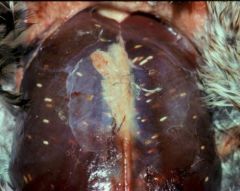
Sarcocystis
|
|
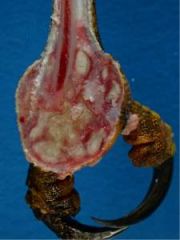
Causative agent?
|
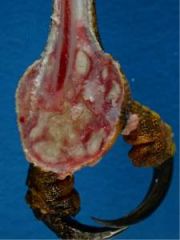
Staph aureus (bumblefoot)
|
|

Differentials?
|

Infectious Laryngotracheitis (ILT)
Fowl pox Candidiasis (thrush) Salmenellosis |
|
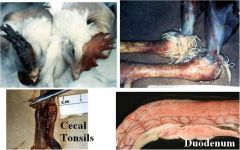
What are these lesions indicative of?
|
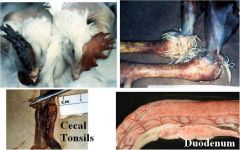
Avian flu (also rule-out Newcastle dz)
|
|
|
What is the oncogenic virus family responsible for lymphoid leukosis and avian myelocytomatosis?
|
Retroviruses
|
|
|
What are the three forms of gout in birds?
|
Visceral
Renal Joint |
|
|
What can cause typhlitis and hepatitis in some birds?
|
Histomonas
|
|
|
Common term for psittacine disease caused by herpes virus and typically features multifocal hepatic necrosis.
|
Pacheco's disease
|
|
|
What are two important differentials for hemorrhagic enteritis in birds?
|
HPAI
Newcastle disease |
|
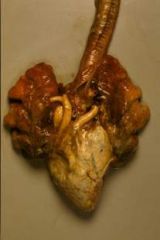
What gives with this bird heart?
|
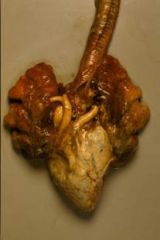
Visceral gout
|
|
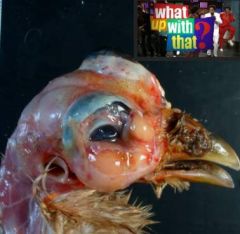
Oooooooooh-wheeeeeeee......what up with that?
|
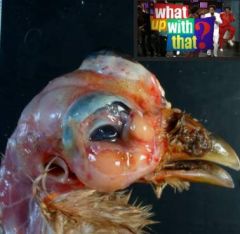
Mycoplasm infection
|
|
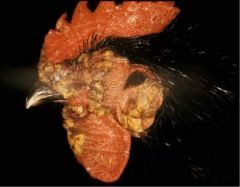
Disease?
|
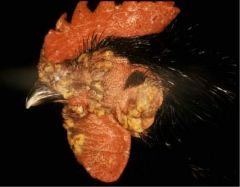
Fowl pox
|

