![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many teeth do puppies have? What is the dental formula for them?
|
2 (I 3/3, C 1/1, P 3/3) = 28 teeth
|
|
|
How many teeth do dogs have? What is the dental formula for them?
|
2 (I 3/3, C 1/1, P 4/4, M 2/3) = 42 teeth
|
|
|
How many teeth do kittens have? What is their dental formula?
|
2 (I 3/3, C 1/1, P 3/2) = 26
teeth |
|
|
How many teeth do cats have? What is their dental formula?
|
Permanent - 2 (I 3/3, C 1/1, P 3/2, M1/1) = 30 teeth
|
|
|
Compared to dogs, cats are missing:
a) both upper and lower 1st premolars b) both upper and lower 2nd molars c) lower 2nd premolar and 3rd molar d) a and b e) a and c f) a, b, and c |
f) a, b, and c
missing upper and lower P1 missing upper and lower M2 missing lower P2 and M3 |
|
|
Which tooth is 307 in the dog? In the cat?
|
Lower left P3 in both!
|
|
|
Using the tridian numbering system, identify the carnassial teeth in the dog.
|
108, 208, 309, 409
(Upper P4s and lower M1s) |
|
|
Using the tridian numbering system, what are the first teeth encountered distal to the upper canines in the cats? First teeth distal to the lower canines in cats?
|
106/206
307/407 |
|
|
Which teeth have 3 roots in the dogs? The cat?
|
Upper 8s, 9s, and 10s (dog)
Upper 9s (cat) |
|
|
T or F:
The periodontal ligament is visible via radiography? |
False (kinda)
The ligament is radiolucent, thus you can "see" its absence |
|
|
Which teeth in dogs have one root? Cats?
|
Incisors and canines in both
Dogs (PM1 and maybe lower M3) Cats (Upper PM2, upper M1) |
|
|
Toward the tongue =
Toward the cheek = Toward midline = Away from midline = |
Toward the tongue = LINGUAL
Toward the cheek = BUCCAL Toward midline = MESIAL Away from midline = DISTAL |
|
|
T or F:
Canines and incisiors are labial while molars and premolars are buccal. |
True!
|
|
|
When should all canine deciduous teeth be in wear? Feline?
|
10 weeks (puppy)
6 weeks (kitten) |
|
|
When should all canine permanent teeth be in? Cats?
|
6-7 months (dogs)
6 mos (cats) |
|
|
What are some oral anatomical aspects that must be taken into consideration in the dog? Cat?
|
Infraorbital artery, parotid duct, zygomatic duct (both)
add lingual molar gland in cat |
|
|
What are the three major positioning techniques for dental radiography?
|
Parallel (film is parallel to tooth root)
Bisecting angle Extraoral |
|
|
What is a radiographic issue in cats? What technique is used in this case?
|
Zygomatic arch; use extraoral technique
|
|
|
In terms of tooth disease, dogs get _____________ while cats get _____________.
|
Dogs = periodontal disease
Cats = gingivitis/stomatitis complex and resorptive lesions |
|

What gives in this? What animal?
|
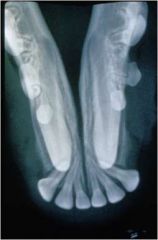
Dog missing canines!
|
|
|
What etiologies may contribute to feline gingivitis/stomatitis complex?
|
FeLV/FIV
Lymphoplasmacytic stomatitis Atopy? Calici virus Bartonella? |
|
|
What is the etiology of feline tooth resorptive disease? What is the pathogenesis?
|
Nobody really knows...
Pathogenesis involves odontoclast resorption from the outside in |
|
|
Choose type 1 or type 2 tooth resorption...
...localized gingivitis |
Type 2
|
|
|
Choose type 1 or type 2 tooth resorption...
...intact tooth roots |
Type 1
|
|
|
Choose type 1 or type 2 tooth resorption...
...gingivitis/stomatitis association. |
Type 1
|
|
|
Choose type 1 or type 2 tooth resorption...
...treated with crown removal. |
Type 2
|
|
|
Choose type 1 or type 2 tooth resorption...
...often symmetrical. |
Type 2
|
|
|
Choose type 1 or type 2 tooth resorption...
...involves root removal. |
Type 1
|
|
|
What are some sequellae to incomplete tooth removal?
|
Draining tracts and lytic bone
|
|

Which radiograph (left or right) requires treatment by crown removal? What type of tooth resorption is it?
|

Left is Type 2; just need to remove crown.
|
|
|
What is the common signalment for periodontal disease?
|
Small, older (>6yrs) dogs
|
|
|
Choose gingivitis or periodontal dz...
...inflammation of the gingival tissues. |
gingivitis...DUH
|
|
|
Choose gingivitis or periodontal dz...
...a visual diagnosis. |
gingivitis
|
|
|
Choose gingivitis or periodontal dz...
...a radiographic diagnosis. |
periodontal dz
|
|
|
Choose gingivitis or periodontal dz...
...classified by stage. |
periodontal dz
|
|
|
Choose gingivitis or periodontal dz...
...classified by index. |
gingivitis
|
|
|
How much attachment loss does stage 4 periodontal disease exhibit? Stage 2?
|
Stage 4 >50%
Stage 2 <25% |
|
|
T or F:
Stage 1 periodontal disease shows <10% attachment loss and mild gingivitis. |
False!
Gingivitis with NO ATTACHMENT LOSS. |
|
|
How long does it take for plaque to form into calculus?
|
72 hrs!
|
|
|
What makes dog breath STANKY when they have plaque?
|
Volatile sulfur compounds
|
|
|
What two antibiotics are good for gingivitis/periodontal disease?
|
Clindamycin and clavamox
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of pocket formation and bone loss? How are these differentiated radiologically?
|
Suprabony (horizontal bone loss)
Infrabony (vertical bone loss) |
|

What type of bone loss is featured in A? In B?
|

A = infrabony (vertical)
B = suprabony (horizontal) |
|
|
What is the treatment for the following:
a) loss of >50% of tooth attachment b) 3-5mm pocket c) 5-7mm pocket d) loss of <50% of attachment |
a) EXTRACT
b) clean and allow to resolve c) Use Doxyrobe gel d) clean and allow to heal |
|

What is the index and stage of these teeth?
|

A - Gingivitis Index 1; Stage 1 periodontal disease
B - GI 2-3; Stage 2 (note - we technically can't do the periodontal stage without radiography) |
|

What is the stage/index of these teeth?
|

A - Gingivitis Index 3; Stage 4 perio
B - GI 3; Stage 3 perio (need rads for perio technically) |
|
|
Name 5 indications for extraction
|
Persistent deciduous teeth
Crowded supernumerary teeth Crowded/malpositioned teeth Tooth crown fracture with pulp exposure Deep crown-root fractures Root fracture >50% bone loss perio dz infected/abscessed tooth Severe root exposure or furcation tooth resorption advanced caries |
|
|
What are the major nerve blocks available facilitating dental procedures in the dog and cat?
|
Mental
Mandibular Infraorbital Palatine Maxillary |
|
|
Which nerve block(s) could be used when performing a procedure on 205?
|
Left infraorbital or
Left maxillary |
|
|
Which nerve block(s) could be used when performing a procedure on 109?
|
Right maxillary +
Right palatine |
|
|
Describe the approach to a maxillary block in cats and brachycephalic dogs?
|
Insert needle at medial canthus of eye just rostral to globe and perpendicular to the last molar.
|
|
|
Where is the infraorbital canal located?
|

Infraorbital canal is dorsal to distal root of maxillary PM3.
|
|
|
Where is the mental foramen located?
The mandibular foramen? |

Mental foramen is ventral to mesial root of 2nd premolar.
Mandibular foramen is btw angle of mandible and 311/411. |
|
|
Which tooth on the cat do you need to take extra care in sectioning?
|

Lower M1
|
|
|
How does blood help with extractions?
|
Hydraulic activity
Collagenase activity |
|
|
Describe the tools and procedure for developing a gingival flap.
|
Use scalpel to make vertical releasing incisions past mucogingival jxn
Elevate flap w/periostal elevator Remove buccal bone to 1/3 of root |
|
|
What is the goal of extraction repair? What suture is preferred?
|
Close the hole w/tension free sutures and remove dead space;
Use 5-0 to 4-0 simple interrupted vicryl rapide (maybe monocryl) |
|
|
Which tooth in dogs has a weird mesial root that must be sectioned with care?
|
Upper PM4
|
|
|
What are the most common causes for malocclusion? Which is #1 cause?
|
Genetics (#1 pimp daddy)
Retained deciduous Fractured deciduous Missing teeth Extra teeth Tight lip (Shar Pei) |
|
|
Where are retained deciduous incisors usually? Retained deciduous canines?
|
Incisors on labial aspect
Upper canines behind permanent Lower canines in front of permanent canines |
|
|
What is the treatment for retained deciduous teeth?
|
Extract 'em
|
|
|
What is a good treatment for a dog with canine teeth that are directed medially?
|
Play with a ball > moves teeth laterally
|
|
|
When should maloccluded teeth be clipped?
|
NEVER! If deciduous are maloccluded, remove or correct w/orthodontics
|
|
|
Missing teeth is called...
|
...oligodontia
|
|

ID the bite abnormality
|

NORMAL BITE!
note scissor bite, dental interdigitation lower canine midway btw upper 3rd incisor and upper canine |
|

ID the bite abnormality
|

Class 1 malocclusion
Canine growing medially; normal jaw relationship |
|

ID the bite abnormality
|

Class 1 - anterior crossbite
Reverse scissor Normal jaw relationship |
|
|
Class 3 malocclusion is "normal" in which breeds?
|
Lhasa, Shih Tzu, Pekinese, Bull dogs
(underbite; lower jaw too long) |
|
|
What is a class 2 malocclusion?
|
Overbite (maxilla too long or mandible too short)
|
|
|
T or F:
Class 2, 3, and 4 malocclusions are always genetic. |
False!
2 and 3 nearly always are; class 4 is usually due to trauma or congenital. |
|
|
What is a lance canine?
|
When the canine erupts very mesially
|
|
|
Which breeds are predisposed to supranumary teeth?
|
Boxers, mastiffs, bostons
|

