![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
103 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an important zoonotic ascarid associated with dogs?
|
Toxocara canis
|
|
|
T or F:
Toxocara canis eggs are not immediately infectious once released into the environment. |
True! They embryonate once released.
|
|
|
T or F:
There is no transmammary or transplacental transmission of T. canis. |
False! There is both transmammary and transplacental transmission.
|
|
|
Describe the migration of T. canis after ingestion of infective eggs by an older dog.
|
Larvae hatch, penetrate gut wall, and encyst in various tissues.
|
|
|
Describe the migration of T. canis after ingestion of infective eggs by a puppy.
|
Larvae hatch, penetrate gut wall, undergo tracheal migration, then develop into adult worms in small intestine.
|
|
|
T or F:
Older male dogs never excrete T. canis eggs. |
False!
It is rare, however. Only way that this can happen is for a male dog to eat encysted larvae when consuming a paratenic host. |
|
|
Which dogs commonly shed T. canis eggs (think sex and life stages) via the feces?
|
Lactating bitch
Puppies |
|
|
Why do male dogs not shed T. canis eggs?
|
No adults in their intestine
Females have adults since pregnancy reactivates encysted larvae. |
|
|
What are the two main presentations for T. canis infection in humans?
|
OLM (ocular larva migrans)
VLM (visceral larva migrans) |
|
|
How does T. canis kill puppies?
|
intestine rupture
|
|
|
T or F:
Heartworm preventive protects against T. canis. |
True!
|
|
|
What are the 4 transmission pathways that can result in adult T. canis? What age/sex of dog is associated with each?
|
Oral (usually only young dogs)
Transplacental (bitch to pup) Transmammary (bitch to pup) Ingestion of paratenic host (any age but probably not puppies) |
|
|
Which worm group typically has an insect intermediate host?
|
Spirurids (also Filirial worms)
|
|
|
What is the intermediate host for the Spirocerca lupi? The paratenic host? The definitive host?
|
Dogs – definitive
Paratenic – lizards, birds, rodents Beetles – intermediate |
|
|
T or F:
Spirocerca lupi does not undergo tracheal migration within the definitive host. |
True! It penetrates stomach, migrates in arteries to thoracic artery then to esophagus.
|
|
|
What is a worm that can cause sarcomas in dogs?
|
Spirocerca lupi
|
|
|
Which worm has "paperclip" eggs?
|
Spirocerca lupi (also Physaloptera)
|
|
|
What are two common pathologies resulting from infection by Spirocerca lupi?
|
Esophageal nodules and cancer
Aortic stenosis or rupture |
|
|
What is the eye worm? What is the intermediate host for this worm?
|
Thelazia californiensis;
Face fly is intermediate host |
|
|
What is the cause of "summer sores" on horses?
|
Equine stomach worms (Habronema or Drashia)
|
|
|
T or F:
Habronema skin infections are dead-ends. |
True!
|
|
|
When/where do equine stomach worms become infective L3?
|
Mature inside maggot, becoming L3 when adult fly emerges from pupa
|
|
|
How do equine stomach worms get from the intermediate host (fly) into the stomach?
|
Larvae deposited by fly on lips, nostrils and wounds as they feed. If horse licks and swallows L3, then they mature in the stomach.
|
|
|
Which spiurid infects cougars? What are the intermediate hosts?
|
Physaloptera spp.
Beetles/cockroaches |
|
|
What is the Greek-y name for flatworms? For tapeworms? For flukes?
|
Platyhelmenthes (flatworms)
Cestodes (tapeworms) Digenea (flukes or trematodes) |
|
|
Why is the planarian sometimes called a "pseudoparasite"?
|
Because it likes poop and owners might find one on a pile and think that it's a parasite!
|
|
|
What flatworm is a parasite of salmon?
|
Monogenea
|
|
|
What is the free-swimming stage of a Digene known as?
|
Cercaria
|
|
|
T or F:
Only the adult cestodes have no gut or mouth. |
Nope! No gut or mouth at ALL stages!!!
|
|
|
What is the segment of a cestode called?
|
proglottid
|
|
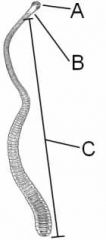
ID these regions of the tapeworm
|
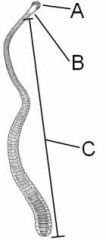
A - scolex
B - neck C - strobila |
|
|
How many pairs of posterior hooks are present on cestode larvae?
|
3 paris
|
|
|
What organs are found in each mature (but not yet gravid) segment of a cestode?
|
ovary, vagina, testes, seminal vesicle --> HERMAPHRODITIC ORGANISM
|
|
|
T or F:
A gravid cestode segment contains both ovary and testes. |
False!
Ovary and testes disappear; uterus branches and fills with eggs |
|
|
What stage of cestode development is always eaten by the intermediate host?
|
Oncosphere
|
|
|
What is the cestode stage that is infective to the definitive host?
|
metacestode
|
|
|
What structure is always visible in the embryonated cestode egg?
|
oncosphere (also called hexacanth embryo)
|
|
|
How does the metacestode infect the definitive host?
|
Definitive host eats intermediate host
|
|
|
What is the most important cestode group for veterinary medicine?
|
Cyclophyllidea
|
|
|
What is the name of the sheep tapeworm? What is its intermediate host?
|
Moniezia expansa
Mite is intermediate host |
|
|
What is the horse tapeworm? What is its intermediate host?
|
Anoplocephalid spp (A. perfoliata and A. magna); mite is intermediate host
|
|
|
Which horse tapeworm can cause colic?
|
Anoplocephala magnus
|
|
|
What species is most affected by Diplyidium caninum? What type of parasite is this?
|
Dog tapeworm; mainly affects CATS!!!
|
|
|
What is the intermediate host of Diplyidium caninum?
|
Fleas and biting lice
|
|
|
What is the intermediate host of the Mesocestoides tapeworms?
|
Usually mouse; dog can be infected by larvae too
|
|
|
Which group of tapeworms can be found in dogs as a definitive or intermediate host? Where would the larval forms be found?
|
Mesocestoides
Larval forms found in the viscera |
|
|
Humans are the definitive host for which cestodes? What is the intermediate host for each?
|
Taenia saginata (beef tapeworm)
Taenia solium (pork tapeworm) |
|
|
Which is worse, ingesting a Taenia solium egg or larva?
|
Egg! It develops in the brain in humans!
|
|
|
Where does the Taenia solium metacestode develop in pigs? In humans?
|
Pigs - in muscle
Humans - brain |
|
|
Which cestodes have the dog as the definitive host? What is the intermediate host for each?
|
Mesocestoides (mouse)
Taenia ovis (sheep muscle) T. hydatigena (sheep viscera) T. multiceps (sheep brain) T. pisiformis (rabbit viscera) Echinococcus granulosus (humans/sheep) |
|
|
Which cestodes have the cat as the definitive host? What is the intermediate host for each?
|
Taenia taeniaformis (rodent viscera)
|
|
|
Which cestode has tiny adult worms consisting of only a scolex, neck, and 2 segments?
|
Echinococcus granulosus
|
|
|
What is remarkable about the life cycle of Echinococcus granulosus?
|
Oncosphere hatches, penetrates GI, encysts in organs and undergoes ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
|
|
|
What is a pathogenic sequelula to Echinococcus multilocularis infection? How is this treated?
|
Metastatic cancer-like hepatic cyst
Remove by injecting formalin (or patient's bile) into cyst then removing |
|
|
T or F:
All of the digenes use 2 or more hosts. |
True!
|
|
|
What is the most common obligate 1st intermediate host of flukes?
|
Mollusks (snails)
|
|
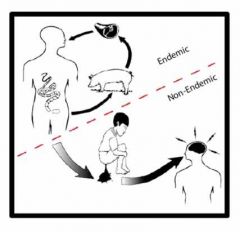
What tapeworm does this make you think of?
|
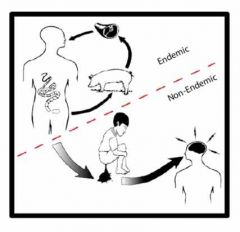
Taenia solium
|
|
|
Describe a generalized fluke in terms of its gut morphology, attachment structures, and sex.
|
Blind gut
attach w/suckers (oral and ventral) Mostly hermaphroditic |
|
|
T or F:
Flukes are hermaphroditic and frequently self-mate. |
False! They don't frequently self-mate!
|
|
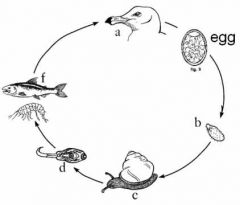
What are the names for the life cycle stages in a, b, d, and f?
|
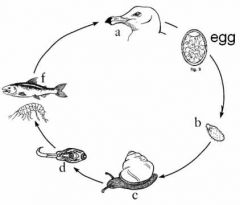
a - adult
b - miracidium d - cercaria f - metacercaria |
|
|
What is an important fluke in Oregon that infects sheep? dogs?
|
sheep - Fasciola hepatica
dogs - Nanophyetes salmincola |
|
|
T or F:
Fasciola hepatica does not cause a lot of damage on a per-worm basis. |
False! Lots of per-worm damage!
|
|
|
T or F:
Fasciola hepatica can infect cows. |
True
|
|
|
If F. hepatica inhabits the liver and bile ducts, how do its eggs get into the feces?
|
Eggs pass into bile, into gut, then into feces
|
|
|
When is "fluke season" normally? When were the snails infected? When will eggs be detected?
|
June is fluke season!
Snails infected Mar/Apr Eggs detected in the fall |
|
|
T or F:
F. hepatica does not lay a lot of eggs and instead relies on the asexual reproduction of the miracidium in the first intermediate host to multiply. |
False!
Up to 20k eggs/day may be shed. Also, there is asexual reproduction in the snail (about 600x) |
|
|
What are the intermediate hosts for Fasciola hepatica (be specific)?
|
Lymnaea humilis
Pseudosuccinea columella (both snails....jeez who cares...like he's gonna be this specific!) |
|
|
What condition arises in cattle infected with Fasciola hepatica? What is the pathogenesis of this condition?
|
"Pipe Stem Liver" caused by immune response
|
|
|
What fluke is benign in deer but BAD NEWS for sheep and cattle?
|
Fascioloides magna
|
|
|
T or F:
Paramphistome flukes are generally thought to have little pathogenic effects. |
True (for the adults; juveniles can cause severe enteritis)
|
|
|
What is the lung fluke of cats and dogs? What is the first intermediate host? The second?
|
Paragonimus kellicotti
Snail intermediate then aquatic crustaceans |
|
|
Which fluke is commonly found in pairs when encysted in tissues?
|
Lung fluke (Paragonimus kellicotti)
|
|
|
Which fluke uses "mind control" of ants?
|
Dicrocoelium dendriticum (lancet liver fluke)
|
|
|
T or F:
The lung fluke is the only fluke to undergo a tracheal migration. |
False! None of the flukes do this! The lung fluke gets to the lungs by tunneling through the stomach, liver, and diaphragm!
|
|
|
What are the three groups of Enoplids?
|
Filarids
Trichuroids Dictyocaulus |
|
|
Whipworms are from which genus?
|
...Trichuris spp.
|
|
|
T or F:
Whipworms have a high degree of host specificity. |
True!
|
|
|
Where do Trichuroids embed in the GI tract?
|
Embed in cecum and lower intestine
|
|
|
Which whipworms undergo a tracheal migration?
|
NONE OF THEM! No extraintestinal migration!
|
|
|
T or F:
Puppies (dogs <6mos) have a higher incidence of Trichuris vulpis infection than do older dogs. |
False! Older dogs are more infected!
|
|
|
Which form causes disease in a Trichinella spiralis infection? Larvae or adults?
|
Larvae
|
|
|
T or F:
Trichenella spp. have a broad host specificity. |
True!
|
|
|
Briefly describe the life cycle of Trichinella spiralis.
|
Encysted larvae eaten
Emerge and become adults in intestine Females release larvae (ovoviviparity) Larvae migrate to heart, lungs, etc (in same host) Encyst in skeletal muscle as L1 |
|
|
Which species do capillarids commonly infect and what tissues are targeted?
|
Cats/dogs (urinary bladder)
Cattle (small int) Poultry (intestine) Mammals (liver) |
|
|
Describe the route of infection of a capillarid from the GI to the bladder in a dog or cat.
|
Ha ha...trick question! The route is UNKNOWN!!!
|
|
|
What is the intermediate host for capillarid infection in dogs and cats?
|
earthworm
|
|
|
When are the eggs released in a Calodium (Capillaria) hepatica infection?
|
When host dies
|
|
|
After a carnivore feeds on the carcass of a Calodium (Capillaria) hepatica infected animal, where do the ingested eggs end-up?
|
Eggs become embryonate in the primary host and are passed through the feces without infecting the primary host.
|
|
|
T or F:
The only way to acquire a Calodium (Capillaria) hepatica infection is to eat dead tissues containing C. hepatica eggs. |
False!
The primary host does eat the tissue but there is no infection. Infection comes from the soil (egg embryonates in primary host then is passed via feces into soil) |
|
|
Which tissues to filarial worms target?
|
Heart
Lymphatics Blood Vessels |
|
|
What is the first stage larva of a filarial worm called?
|
Microfilaria
|
|
|
T or F:
Filarial worms always use an arthropod vector. |
True! Usually a dipteran.
|
|
|
T or F:
Arthropods are the definitive host for filarial worms. |
False!
Arthropods are intermediate hosts. |
|
|
Dog heartworm is more specifically known as...
|
...Dirofilaria immitis
|
|
|
T or F:
D. immitis is an important pathogen of dogs and cats. |
True! Definitive host is dog; abnormal host is cat.
|
|
|
T or F:
The mosquito is a paratenic host in the D. immitis life cycle. |
False!
Intermediate host - develops from L1 to L3 in mosquito. |
|
|
T or F:
Adult D. immitis release eggs directly into bloodstream. |
False!
They release microfilaria! |
|
|
What are techniques for D. immitis diagnosis? Any drawbacks for each?
|
Knott's test (direct microfilaria observation - tough to see)
Antigen against female (males can cause occult infection) Necropsy (um, you gotta be dead) Radiology (disease must have progressed for morphological changes) |
|
|
What would be seen radiographically in a dog with chronic Dirofilariosis?
|
Enlarged main pulmonary artery
Enlarged R. heart |
|
|
Which has a more severe reaction to D. immitis infection, cats or dogs?
|
Cats! Only 1-3 worms can cause disease!
|
|
|
T or F:
Knott's test is the preferred method for diagnosing D. immitis infection in cats. |
False! Microfilaria are not usually produced in cats.
|
|
|
What is a common sequela to using adulticides in dogs with Dirofilariosis? How about in cats?
|
Thromboembolism (dogs);
Probably the same in cats although there is NO APPROVED ADULTICIDE FOR CATS |
|
|
Which group of roundworms is characterized by cutaneous microfilariae? What is the vector?
|
Onchocerca delivered by Culicoides (black fly, no-see-ums)
|

