![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the dermis of the hoof called?
|
Corium
|
|
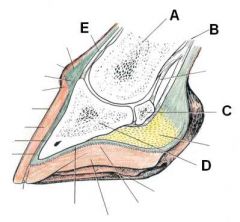
ID these hoof regions
|
A - Second phalanx
B - Flexor tendon C - Navicular bone D - Distal phalanx (coffin bone) E - Extensor tendon |
|
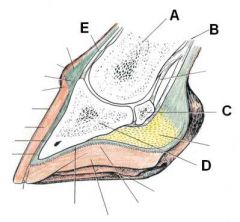
ID these hoof structures
|
A - Perioplic corium
B - Perioplic epidermis C - Coronary corium D - Coronary epidermis E - White line |
|
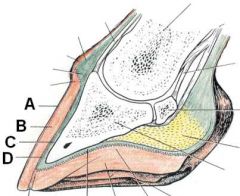
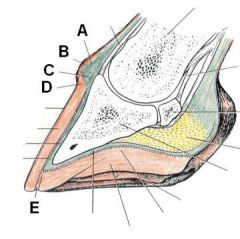
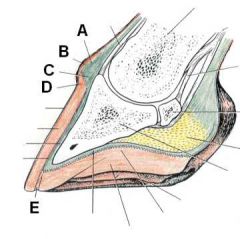
ID these hoof regions
|
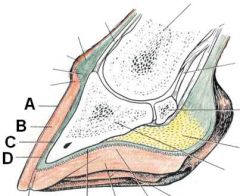
A - Stratum tectorium (extension of perioplic epidermis)
B - Stratum medium (extension of coronary epidermis) C - Lamellar corium D - Lamellar epidermis |
|
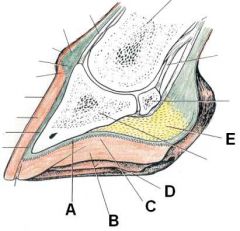
ID these hoof parts
|
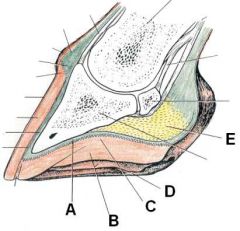
A - Sole corium
B - Frog C - Sole epidermis D - Bar E - Digital cushion |
|
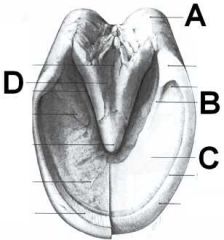
ID these hoof regions. which touch the ground?
|
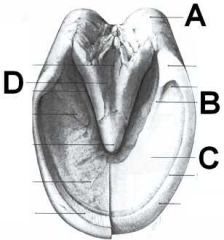
A - Heel
B - Bar C - Sole (doesn't touch ground) D - Frog |
|
|
What are the regions of the hoof wall?
|
Perioplic
Coronary Laminar |
|
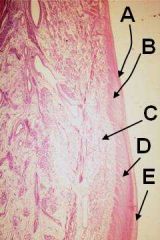
ID these hoof layers
|
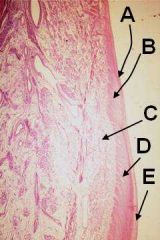
A - Perioplic epidermis
B - Perioplic corium C - Coronary corium D - Coronary epidermis E - Stratum tectorium |
|
|
Which layer forms the bulk of the hoof wall? What kind of horn is this made of?
|
Stratum medium (extension of coronary epidermis) is made of tubular and intertubular horn
|
|
|
What layer(s) does the stratum medium lack?
|
No stratum lucidum or stratum granulosum
|
|
|
From whence does the tubular horn of the stratum medium arise?
|
From germinal epithelium covering lateral and distal parts of the dermal papillae
|
|
|
From whence does the intertubular horn of the stratum medium arise?
|
From germinal epithelium in the depths of the epidermal pegs
|
|
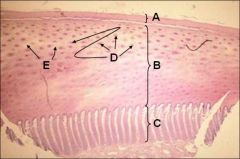
ID or FAIL!!!
|
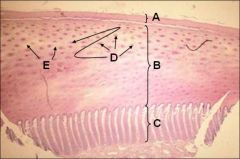
A - Stratum tectorium
B - Stratum medium C - Stratum internum D - Tubular horn E - Intertubular horn |
|
|
Which is stronger - tubular or intertubular horn?
|
Intertubular....totally
|
|
|
What are the proximal and distal boundaries of the laminar epidermis?
|
Extends from the deep edge of the coronary region to the sole
|
|
|
What do the primary and secondary epidermal laminae interdigitate with?
|
Primary and secondary laminar corium
|
|
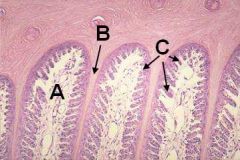
ID these. Which are dead.
|
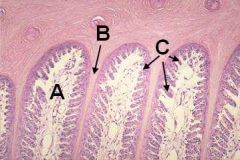
A - Laminar corium
B - Primary lamina (dead) C - Secondary laminae |
|
|
What is the composition of the secondary laminae?
|
Stratum germinitavum (basale?) of the epidermis
|
|
|
T or F:
If the primary laminae are ripped-out, the hoof can still regrow. |
True! The germinal cells are not damaged in this case.
|
|
|
Where does hoof growth primarily occur?
|
Coronary band
|
|
|
What is the rate of hoof growth?
|
6mm/month
Takes 9-12mos for toe to grow out |
|
|
What is the junction of the laminar and sole epidermis known as?
|

White Line!
|
|
|
What is the water content of the wall, sole, and frog?
|
25%
33% 50% |
|
|
What is the function of the frog?
|
Shock absorber
|
|
|
Which has longer papillae - the frog or the sole?
|
Sole, brotha!
|
|
|
What is the composition of the digital cushion? What is its function?
|
Fibroelastic CT and Adipose tissue
Shock absorber |
|
|
What is the difference between the claws/horns of equids vs. artiodactyl ungulates?
|
Equids - primary and secondary laminae; single hoof contacts ground
Artiodactyls - only primary laminae; well developed heel bulbs (no frogs) |
|
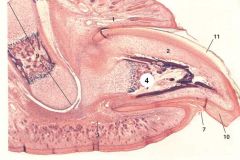
ID 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 10, and 11
|
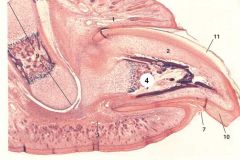
1. Claw fold
2. Dermis 3. Digital pad 4. Distal phalanx 7. Limiting furrow 10. Sole 11. Wall |

