![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Yo, what are the main genital organs in this bitch!?
|
Ovaries
Uterine tubes Uterus Cervix Vagina Vulva Mammary glands |
|
|
What are the endocrine and exocrine functions of the ovaries?
|
Endocrine - Estrogen, progesterone, androgens
Exocrine - female gametes |
|
|
What are the functions of the female reproductive system?
|
Production of oocytes
Transport of male and female gametes Capacitation of sperm accomodation of developing embryo/fetus Parturition Hormone production |
|
|
What are the two main regions of the ovary? What does each contain? Which is deepest (and what species has these swapped)?
|
Medulla - deepest; contains blood vessels
Cortex - superficial, contains developing oocytes Switched around in horses |
|
|
What is the ovarian capsule called?
|
Tunica albugenia of the ovary
|
|
|
What is the histological makeup of the ovarian cortex?
|
Follicles
Corpora lutea Interstitial cells Stromal elements |
|
|
What is the function of corpora lutea?
|
Produce progesterone
|
|
|
What is the histological makeup of the medulla of the ovary?
|
Vessels, lymphatics, nerves
Loose CT |
|
|
What is the process of creating oocytes called?
|
Oogenesis
|
|
|
Where do primordial germ cells form? When do they become oogonia?
|
Yolk sac
When they migrate to the gonadal ridge |
|
|
T or F:
The maturing oocyte arrests as a secondary oocyte before or shortly after birth. |
False! They arrest as Primary Oocytes and mature (and arrest) as Secondary Oocytes at puberty.
|
|
|
What are the five levels of follicular development?
|
Primordial follicle
Unilaminar primary follicle Multilaminar primary follicle Antral (secondary) follicle Mature (tertiary) follicle |
|
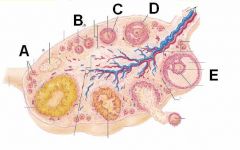
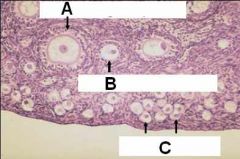
ID these stages of follicular development
|
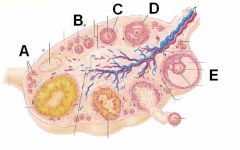
A - Primordial follicle
B - Unilaminar primary follicle C - Multilaminar primary follicle D - Antral (secondary) follicle E - Mature (tertiary) follicle |
|
|
What cells surround the primordial follicle?
|
Stromal cells
|
|
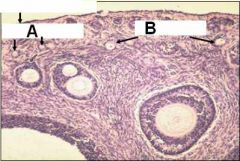
ID the follicles in A and B
|
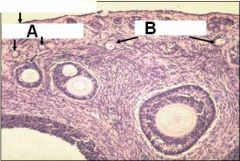
A - primordial
B - Primary follicles |
|
|
What cell type surrounds the unilaminar primary follicle? What initiates this change from the primordial follicle?
|
Cuboidal or columnar ovarian follicular cells.
Growth stimulated by FSH |
|
|
What are the cells surrounding the primary oocyte in the multilaminar primary follicle?
|
membrana granulosa cells
|
|
|
T or F:
The zona pellucida develops at the secondary or antral follicular stage. |
False! This develops at the multilaminar primary stage. The CORONA RADIATA develops at the antral stage.
|
|
|
T or F:
The oocyte and the granulosa cells secrete the zona pellucida. |
False! Only the oocyte secretes this
|
|
ID these stages of follicular development
|
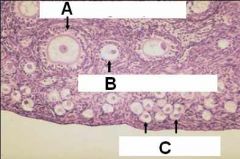
A - Multilaminar primary follicle
B - Unilaminar primary follicle C - Primordial follicle |
|
|
What two layers do the multilaminar primary follicle stromal cells differentiate into. Which produces androgens and what is the signal for androgen production?
|
Theca folliculi externa
Theca folliculi interna - produce androgens |
|
|
What differentiates the multilaminar primary follicle from the antral (secondary) follicle?
|
Follicular antrum filled with liquor folliculi
|
|
|
What is the best part of follicular development?
|
CUMULUS OOPHORUS!!!
|
|
|
What secretes the liquor folliculi? What hormone is liquor folliculi high in?
|
Granulosa cells
Estrogen |
|
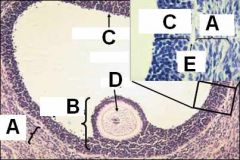
ID these regions of the antral follicle
|
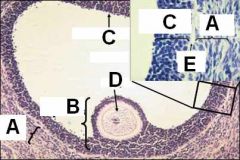
A - Theca folliculi
B - Cumulus oophorus C - Membrana granulosa D - Oocyte E - Basement membrane |
|
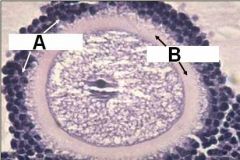
What are these?
|
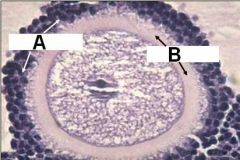
A - Corona Radiata
B - Zona Pellucida |
|
|
T or F:
Atresia may occur at any point in the developmental sequence. |
True!
|
|
|
Where is the point of rupture from a follicle?
|
Follicular stigma
|
|
|
What structure forms after ovulation? How long does this structure last?
|
Corpus hemmorhagicum
<1day |
|
|
What does the corpus hemmorhagicum eventually form?
|
Corpus luteum
|
|
|
Which cells proliferate/invade the corpus hemmorhagicum and what do they become?
|
Granulosa cells form granulosa lutein cells
Stromal cells become theca lutein cells |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the corpus luteum and which cells secrete them?
|
Progesterone - granulosa lutein cells and theca lutein cells
Androgens - theca lutein cells |
|
|
What happens to the corpus luteum if fertilization does not occur? What happens if fertilization does occur?
|
degenerates and is replaced by corpus albicans
persists for a variable time during pregnancy |
|
|
Which are the main hormones involved in the ovarian cycle?
|
FSH
LH GnRH (releases both of these; indirect effect) |
|
|
What is the effect of GnRH on the ovary? On the pituitary?
|
Ha ha fooled ya! GnRH ONLY acts on the pituitary! It triggers the basophils to release FSH and LH.
|
|
|
What is the function of FSH and LH on the ovary (both individually and combined)?
|
LH - follicle rupture, ovulation, development of corpora lutea and oocytes
FSH - growth and maturation of follicles and stimulates estrogen secretion Both - regulate cyclical activity of ovary |
|
|
What are the components of the oviduct?
|
Infundibulum
Ampulla Isthmus |
|
|
What are the functions of the uterine tube? Where does fertilization occur?
|
Fxn - transport of gametes, capacitation of sperm, and fertilization area (in ampulla)
|
|
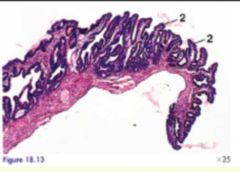
Which structure of the oviduct is this?
|
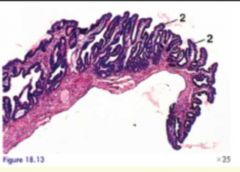
Infundibulum
|
|
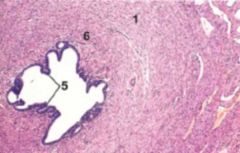
Where in the oviduct is this?
|
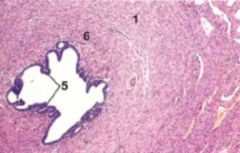
Isthmus
|
|
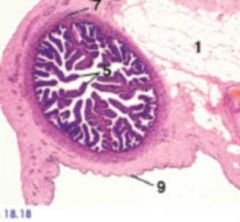
Where in the oviduct is this?
|
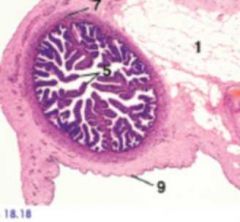
Ampulla
|
|
|
T or F:
There is no muscularis mucosa in the oviduct? |
True!
|
|
|
What is the epithelium of the oviduct?
|
Simple/Pseudostratefied columnar epithelium with intermittent cilia.
|
|
|
What are some functions of the uterus?
|
Semen deposition
Spermatozoa transport Development of embryo/fetus |
|
|
What are the layers of the uterus?
|
Endometrium
Myometrium Stratum vasculare Perimetrium |
|
|
Which region of the endometrium is devoid of glands? What is the function of this region?
|
Caruncles
Placental attachment |
|
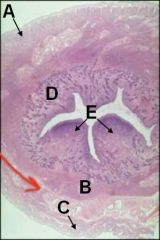
ID these layers of the uterus. What lies between B and C?
What structure is indicated by E? |
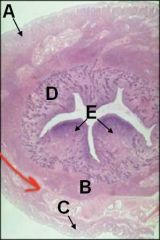
A - Perimetrium
B - Myometrium (inner circular layer) C - Myometrium (outer longitudinal layer) Stratum vasculare between B and C D - Endometrium E - Caruncles |
|
|
What distinguishes a bovid cervix from a carnivore cervix histologically?
|
Bovid cervix has complex folded cervical mucosa
|
|
|
What is the vaginal epithelium?
|
Stratefied squameous epithelium (nonglandular)
|
|
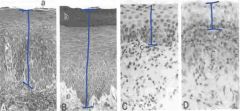
Classify A - D by stage of estrous.
|
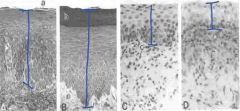
A - Proestrous
B - Estrous C - Mesestrous D - Diestrous (anestrous) |
|
|
T or F:
A bitch in heat has cornified stratefied squameous epithelium in her vagina. |
True!
|
|
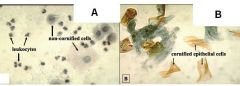
Which of these smears shows an anestrous bitch?
|
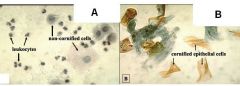
The one on the left.
|
|
|
What is unique about the epithelium of the duct in a teat?
|
Bistratefied columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What are the secretory components of milk? How is each component secreted?
|
Fat - apocrine
Protein and carbohydrates - merocrine |
|
|
What is the gland morphology of mammary glands?
|
Compound tubuloalveolar glands
|
|
|
Describe the alveoli in a lactating mammary gland? In a non-lactating gland?
|
Lactating - distinct alveoli with blebs; interlobular ducts present, secretory product present
Non-lactating - no lobules, indistinct alveoli |

