![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
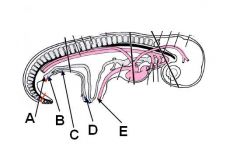
ID these regions of the developing embryo
|
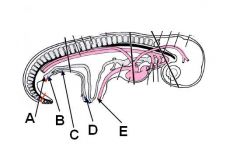
A - Cloacal membrane
B - Cloaca C - Urogenital sinus D - Urachus E - Umbilicus |
|
|
Where do gonads arise from? What specific cells form this?
|
Intermediate mesoderm (gonadal ridge); formed by coelomic epithelium and mesenchymal cells
|
|
|
List the stages in undifferentiated embryonic reproductive development.
|
Gonadal ridge forms
Primitive sex cords form Primordial germ cells migrate to gonadal ridge Genital ducts develop Paramesonephric duct fuses w/wall of urogenital sinus Undifferentiated external genitalia forms |
|
|
What is the primitive kidney called? Where are the gonads located with respect to this?
|
Gonads are ventromedial to mesonephric kidney
|
|
|
What are the two types of genital ducts?
|
Mesonephric (Wolffian) ducts
Paramesonephric (Mullerian) ducts |
|
|
What are the 3 stages of kidney development? Where does each stage develop?
|
Pronephros - cervical
Mesonephros - thoracic Metanephros - lumbar |
|
|
T or F:
The metanephric kidney develops segmentally. |
False! This describes the pronephritic and mesonephric kidneys
|
|
|
T or F:
The pronephric duct extends caudally to the cloaca. |
True!
|
|
|
Which duct becomes the uterus? What feature of this duct determines the extent of the body?
|
Paramesonephric duct septum determines body extent.
|
|
|
What separates the gonad from the coelomic epithelium in male development?
|
Tunica albuginea
|
|
|
What do the primitive sex cords become in the male? In the female?
|
Testis cords become seminiferous tubules and rete testes in the male but disappear in the female.
|
|
|
What is the most important hormone secreted by the sustentacular cells during male embryonic development? What do the interstitial cells secrete?
|
Antimullerian hormone
Testosterone |
|
|
What structures does the mesonephric duct form?
|
Efferent ductules, ductus epididymis, ductus deferens, and some accessory sex glands
|
|
|
What causes regression of the paramesonephric ducts in the male?
|
Antimullerian hormone (remember that the eponymous name for the paramesonephric ducts are Mullerian ducts)
|
|
|
What forms the accessory sex glands?
|
Mesonephric duct or urethra
|
|
|
What hormone influences male external genitalia development?
|
Testosterone
|
|
|
Describe testicular dexcent.
|
Gubernaculum (from mesenchyme) attaches testis to scrotum.
Gubernaculum shortens, pulls testis into scrotum. |
|
|
What happens after primitive sex cords disappear during female development?
|
Surface epithelium gives rise to cortical cords that surround primordial germ cells - these are now oogonia
|
|
|
What is the fate of the cortical cord cells?
|
They become follicular cells
|
|
|
T or F:
Estrogen causes the paramesonephric ducts to disappear in female development. |
False! Estrogen causes the Mullerian ducts to form uterine tube, uterus, and cervix
|
|
|
T or F:
The presence of estrogen and lack of testosterone causes the mesonephric ducts to regress in female development |
True!
|
|
|
What is the embryological origin of the broad ligament in female development?
|
Fusing of paramesonephric ducts
|
|
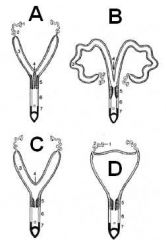
Match the junk with the species:
Sow, Mare, Human, Rabbit, Cow |
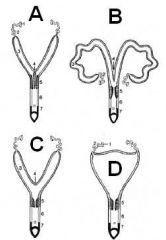
A - Rabbit
B - Sow, Cow (not the ice skating jump) C - Mare D - Human |
|
|
What is the embryologic origin of the vagina?
|
Mesoderm and endoderm
|
|
|
What is the fate of the genital tubercle in males and females?
The Urethral folds? |
Tubercle - glans penis and clitoris
Fold - phallus (body of penis) and labia |
|
|
What are symptoms of gonadal hypoplasia?
|
Lack germ cells
Small genital organs |
|
|
What commonly causes cryptorchidism?
|
Problem with gubernaculum development
|
|
|
Abnormal development of the paramesonephric duct in white shorthorn cattle results in...
|
White heifer disease
|
|
|
Failure for urethral folds to close in the male is called...
|
Hypospadia
|
|
|
What is the difference between hermaphrodites and pseudohermaphrodites?
|
Pseudo have gonads of one sex but external appearance of other.
Hermaphrodites have ambiguous genitalia |
|
|
What genitalia will a female pseudohermaphrodite have? How does this happen?
|
Male genitalia
Due to adrenal hyperplasia overproducing androgens |
|
|
What genitalia will a male pseudohermaphrodite have? How does this happen?
|
Female genitalia (internal and external)
Reduced androgens and antimullerian hormone |
|
|
What happens if antimullerian hormone is present but no testosterone response occurs? How would this manifest externally?
|
Androgen insensitivity syndrome; look externally female.
|

