![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How can the optic nerve be tested?
|
Direct light reflex
Consensual light reflex Menace response |
|
|
Which reflexes test the oculomotor nerve?
|
Direct light reflex
Consensual light reflex |
|
|
Describe the reflex arc of the direct light reflex.
|
Afferent = rods/cones > optic n. > optic chiasm > optic tract
Efferent = Preganglionic parasym. fibers in CNIII > ciliary ganglion > postganglionic fibers to spinchter pupillae mm. |
|
|
Describe the reflex arc of the consensual light reflex.
|
Afferent = rods/cones > optic n. > optic tract
Efferent = preganglionic parasym. in CNIII > ciliary ganglion > postganglionic fibers to spinchter pupillae mm. |
|
|
How can the Opthalmic n. be tested? Which nerve is tested at the same time?
|
Corneal reflex
Palpebral reflex Same reflexes for Facial n. |
|
|
How can the Facial n. be tested?
Which reflex uses the facial n. for both afferent and efferent pathways? |
Anything causing motor action in the face (palpebral, corneal, muzzle reflex, and ear twitch reflex)
Ear twitch uses facial for in and out. |
|
|
T or F:
The palpebral reflex can be used to test all three major branches of the trigeminal nerve. |
False. Only Maxillary and Opthalmic can be tested in this way.
|
|
|
Where would you touch a dog to discern if there was damage to the zygomatic n.?
|
Palpebral reflex
(superiolateral/inferiolateral) |
|
|
What nerve does the superior muzzle reflex test? The inferior muzzle reflex?
|
Superior - Maxillary (infraorbital)
Inferior - Mandibular (Mental) |
|
|
Which reflex test ONLY tests the trigeminal nerve? Which specific branch is this testing?
|
Jaw reflex
Tests mandibular n. |
|
|
How can the glossopharyngeal n. be tested? What other nerve or nerves may be tested as well?
|
Carotid sinus reflex
Gag/swallowing reflex Vagus n. is tested in both in the efferent arc. |
|
|
Failure of the tongue to retract after pulling on it involves which nerve(s)? What is the name of this reflex?
|
Hypoglossal n.
Hypoglossal reflex dummy! |
|
|
What does the ear twitch reflex test?
|
CNVII for both in and out (if tested in the pinna)
C2 for other areas of the ear |
|
|
What is dysfunction of CNI known as? CNII?
|
Anosmia
Anopia (blindness) |
|
|
What are four dysfunctions of the oculomotor nerve?
|
Lateral strabismus
Ptosis Mydriasis Cycloplegia |
|
|
Which muscle controls the third eyelid and how?
|
Abducens; retractor bulbi mm. contraction causes retrobulbar fat to push 3rd eyelid into position
|
|
|
A dog with dry eyes may have a lesion involving which cranial nerve?
|
CNVII - GVE to the lacrimal gland
|
|
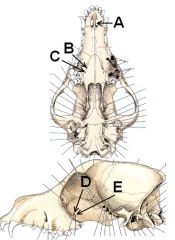
Identify the holes!
What structure(s) pass through each foramen? |
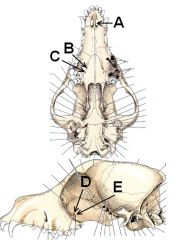
A. Palatine fissure (opening to vomeronasal organ)
B. Major palatine foramen C. Minor palatine foramen (Major palatine a., v., and n. for both) D. Sphenopalatine foramen (sphenopalatine a. and caudal nasal n.) E. Caudal palatine foramen (Major palatine a., v., and n.) |
|
|
What courses through the optic canal?
|
CN II (optic nerve) and external opthalmic a.
|
|
|
What structures does the trigeminal nerve (CN V) course through in the dog? In the cat?
|
Orbital fissure
Rostral alar foramen (dog only) Round foramen Oval foramen |
|
|
Name the structures coursing through the orbital fissure.
|
External opthalmic a.
Oculomotor n. (CN III) Opthalmic division of trigeminal n. (CN V) Abducens n. (CN VI) |
|
|
What courses through the rostral alar foramen?
|
Maxillary a. and maxillary division of trigeminal n. (CN V)
|
|
|
What courses through the caudal alar foramen? The alar canal?
|
Maxillary a. for both
|
|
|
What courses through the round foramen?
|
Maxillary division of trigeminal n. (CN V)
|
|
|
What courses through the oval foramen?
|
Middle meningeal a. and mandibular division of trigeminal n. (CN V)
|
|
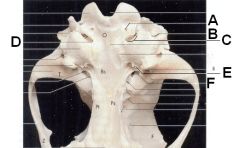
Identify the holes. What passes through each?
|
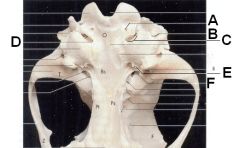
A. Hypoglossal canal (hypoglossal n. CN XII)
B. Stylomastoid foramen (Facial n. CNVII) C. Tympano-occipital fissure (Internal carotid a., glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX), vagus n. (CN X), accessory n. (CN XI), sympathetic nn. from cranial cervical ganglion) D. Jugular foramen E. Musculotubal canal (Bony enclosure of auditory tube which courses between the nasopharynx and middle ear) F. Foramen lacerum (internal carotid a.) |
|
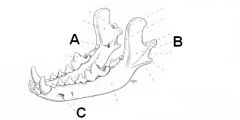
ID the area or the holes and what courses through them.
|
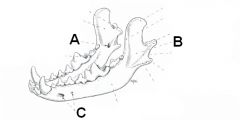
A. Mandibular foramen (inferior alveolar a. and n.)
B. Masseteric fossa (insertion of masseter m.) C. mental foramina (mental aa. and nn.) |

