![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the wavelength range for x-rays?
|
0.01 to 10nm
|
|
|
T or F
Wavelength has no effect on x-ray energy. |
False. Shorter wavelengths afford greater energy.
|
|
|
What three things modulate x-ray absorption in a tissue?
|
Tissue density (eg: bone vs fat)
Atomic # of elements in the tissue Thickness of tissue |
|
|
What are the 5 radiodensities?
|
1 - air
2 - fat 3 - water (soft tissue) 4 - bone 5 - metal |
|
|
What are the main parts of a radiograph machine?
|
Generator
Control panel Tube (anode + cathode) |
|
|
What parameters can usually be controlled at the control panel of a radiograph?
|
on/off
mA (current in milliamperes) kVp (energy in peak kilovolts) s (time in seconds) |
|
|
The total number of electrons crossing the tube describes the_________ parameter.
|
mA (current)
|
|
|
Increased x-rays is a result of increasing which parameters?
kVp mA mAs s |
Any one of these will increase x-rays
|
|
|
Increased median x-ray energy is a result of increasing which of the following parameters?
kVp mA mAs s |
kVp
|
|
|
What components are necessary to produce x-rays?
|
source (cathode)
accelerating device target (anode) |
|
|
What material comprises the source in most medical radiograph machines? What material comprises the target?
|
Source (cathode) = W
Target (anode) = W on top of Cu (for heat dissipation) |
|
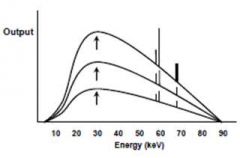
This graph depicts an increase in which of the following parameters:
kVp mA mAs s |
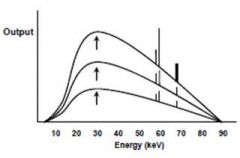
mA
|
|
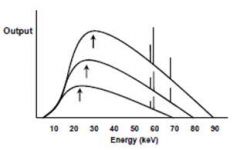
This graph depicts an increase in which of the following parameters:
mA mAs kVp s |
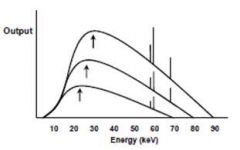
kVp
|
|
|
What are the two main types of x-ray radiation?
|
Bremsstrahlung radiation
Characteristic radiation |
|
|
Choose characteristic or Bremsstrahlung radiation...
...characterized by discrete energy peaks. |
Characteristic radiation
|
|
|
Choose characteristic or Bremsstrahlung radiation...
...energy produced by the deceleration by a second charged particle. |
Bremsstrahlung radiation
|
|
|
Choose characteristic or Bremsstrahlung radiation...
...radiation in a continuous background spectrum. |
Bremsstrahlung radiation
|
|
|
Choose characteristic or Bremsstrahlung radiation...
...energy released when electrons from an outer energy level drop to a lower energy. |
Characteristic radiation
|
|
|
Match the kVp value (low, medium, high) to the part being radiographed.
Fast moving structure Distal extremity Shoulder region Pelvic region Thorax Slow or non-moving structure |
Fast moving structure - high
Distal extremity - low Shoulder region - medium Pelvic region - medium Thorax - high Slow or non-moving structure - low |
|
|
What is the range for low kVp? Medium? High?
|
low = 45-60
med = 65-75 high = >80 |
|
|
What are two major problems with scattered radiation in radiography?
|
Safety concern
Reduced image quality |
|
|
What are some techniques used to minimize scatter in order to achieve better image quality?
|
Reduce area of tissue irradiated
Add Pb layer under cassette Use a grid Use higher kVp |
|
|
What unit denotes the absorbed dose of radiation? What is this unit equal to?
|
Gray (Gy) = 1 joule/kg
|
|
|
What unit denotes the rate of radioactive decay? What is this unit equal to?
|
Becquerel (Bq) = 1sec^-1;
also a Curie |
|
|
What unit denotes the ability of radiation to ionize air? What is this unit equal to?
|
Roentgen (R) = 2.58E^(-4) C/kg
|
|
|
What unit measures the dose equivalent? What is this unit equal to?
|
Sievert (Sv) = Gray x q.f. = 100rem
|
|
|
Which of the following are sources of radiation?
a) Cosmic radiation b) Background radiation in food c) Xe gas d) Medical radiographs e) Weapons fall-out; nuclear reactor accidents f) Old orange fiestaware |
All of the above are EXCEPT for the Xe gas...try Rn gas instead!
|
|
|
What is the non-occupational exposure legal radiation limit?
What is the occupational exposure legal radiation limit? Occupational limit if pregnant? |
non-occupational < 100 mem/yr
occupational < 5 rem/yr occupational/preggo < 500 mrem/yr |
|
|
What are the 3 sources of radiation in radiology?
|
Scattered radiation
Primary Beam Leakage from x-ray tube |
|
|
What are the 2 ways of monitoring radiation exposure?
|
Film badges
TLD (thermoluminescent detector) |
|
|
What is the ALARA principle?
|
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
|
|
|
Which are ways to minimize radiation exposure to the radiographer?
a) use barriers b) use lead body shielding c) stand far away d) manually restrain patient to minimize necessary exposures |
A B and C are correct
|
|
|
What is contained inside the cassette?
|
screen + film
|
|
|
What information should be entered in pre-processing of radiographs?
|
Name of owner
Name of animal Date Marker (L vs. R) Clinic Vet/vet tech |
|
|
What information should be entered in post-processing of radiographs?
|
NONE! post processing is NOT ok!
|
|
|
What term describes the degree of blackening of the film?
Which parameter has the MOST effect on this? |
Radiographic density; mA (or mAs)
|
|
|
What term describes the range of gray shades on a film? Which parameter has the MOST effect on this?
|
Contrast; kVp
|
|
|
The amount of detail in a radiograph is known as...
|
...resolution
|
|
|
What are the three types of radiography?
|
Conventional
Fluoroscopy Digital |
|
|
What are the 2 types of digital radiography?
|
computerized and direct
|
|
|
T or F:
In computerized radiography, there is no need for a film cassette. |
False! This describes direct digital radiography.
|
|
|
What is the universal diagnostic imaging file format extension?
|
.dicom
|
|
|
What are the 6 Rotengen signs?
|
Number
Position Size Shape Opacity Margination (architectural pattern) |
|
|
What is the minimum number of views that should be taken?
|
2
|
|
|
Doubling the mAs is equivalent to what change in kVp?
|
increasing kVp by 15%
|
|
|
Decreasing kVp by 27.75% (2 15% reductions) is equivalent to what change in mAs?
|
decreasing mAs by 3/4
|
|
|
What will be the impact on latitude, blackness, and contrast when...
...increasing kVp by 15% and decreasing mAs by 50%? |
latitude - increase
blackness - no change contrast - decrease |
|
|
T or F:
Increasing kVp increases contrast. |
False! It decreases contrast (reduces the shades of gray)
|
|
|
What will be the impact on latitude, blackness, and contrast when...
...decreasing kVp by 15% and increasing mAs 100%? |
Latitude - decrease
Blackness - no change Contrast - increase |
|
|
When should a grid be used (ie, what is the cutoff thickness)?
|
>11cm
|
|
|
T or F:
Photographic film is very sensitive to x-ray exposure. |
False!
Actually, only ~10% of film exposure is due to directly to x-rays. |
|
|
T or F:
There is no way to discern if a structure is above or below another structure in a single radiograph. |
True (mostly)...
This is why you need 2 views. You can, however, use the magnification effect to determine which structures are farther from the film. |
|
|
What are the four common radiographic views of the equine carpus?
|
DP
Lateromedial Medial oblique Lateral oblique |
|
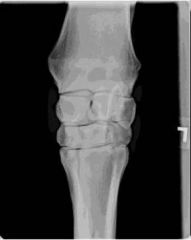
ID this radiographic view of the equine carpus.
|
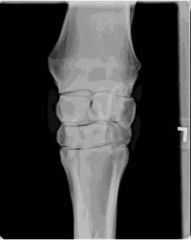
Dorsopalmar
|
|
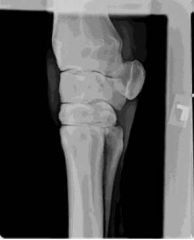
ID this radiographic view of the equine carpus.
|
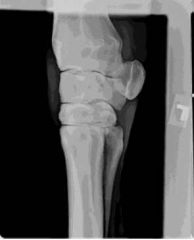
Medial oblique
|
|
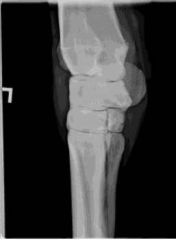
ID this radiographic view of the equine carpus.
|
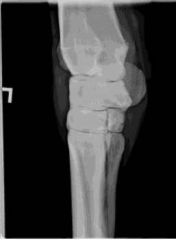
Lateral oblique
|
|
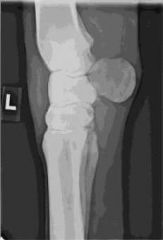
ID this radiographic view of the equine carpus.
|
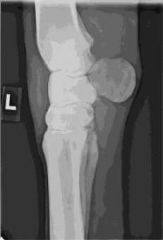
Lateromedial
|

