![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Refrative power of a lens is measured in
|
Diopters
|
|
|
Diopters is equal to
|
Reciprocal of focal distance in Meters
|
|
|
Emmetropia
|
Normal; light focuses on retina
|
|
|
Hypertropia
|
Farsighted; light focuses behind the retina
|
|
|
Hypertropia is corrected with
|
Convex lens
|
|
|
Myopia is
|
Nearsighted; light focuses in front retina
|
|
|
Myopia is corrected with
|
Biconcave lens
|
|
|
Astigmatism is
|
Irregular Curvature of the lens
|
|
|
Astigmatism is corrected with
|
Cylindric lens
|
|
|
Presbyobia is a result of
|
Loss of accomodation power of the lens occur with aging
|
|
|
In presbyopia, the near point moves and corrected with
|
further from the eye
Convex lens |
|
|
Pigment layers of the retina absorb
|
Stray light and prevent scatter of light
|
|
|
Layer that converts 11-cis retinal to all trans retinal
|
Pigment epithelial layer
|
|
|
Rods and cones are not present on
|
The optic disk; ie blind spot
|
|
|
The ______ cells synapse on bipolar cells; the bipolar cells then synapse on _______
|
Rods and cones cells
Ganglion cells |
|
|
The basis for high acuity and low sensitivity of cones is
|
Few cones synapse on single bipolar cells
|
|
|
Where is the highest visual acuity and what is the ratio?
|
The fovea; ratio 1:1 bipolar:cones
|
|
|
What is the reason for less acuity and and greater sensitivity seen in the rods?
|
Many rods synapse on single bipolar cell; light striking any one of the rods will synapse on the bipolar
|
|
|
Are the output cells of the retina
|
Ganglion cells
|
|
|
What form the optic nerve?
|
Ganglion cells' axons
|
|
|
In presbyopia, the near point moves and corrected with
|
further from the eye
Convex lens |
|
|
Pigment layers of the retina absorb
|
Stray light and prevent scatter of light
|
|
|
Layer that converts 11-cis retinal to all trans retinal
|
Pigment epithelial layer
|
|
|
Rods and cones are not present on
|
The optic disk; ie blind spot
|
|
|
The ______ cells synapse on bipolar cells; the bipolar cells then synapse on _______
|
Rods and cones cells
Ganglion cells |
|
|
The basis for high acuity and low sensitivity of cones is
|
Few cones synapse on single bipolar cells
|
|
|
Where is the highest visual acuity and what is the ratio?
|
The fovea; ratio 1:1 bipolar:cones
|
|
|
What is the reason for less acuity and and greater sensitivity seen in the rods?
|
Many rods synapse on single bipolar cell; light striking any one of the rods will synapse on the bipolar
|
|
|
Are the output cells of the retina
|
Ganglion cells
|
|
|
What form the optic nerve?
|
Ganglion cells' axons
|
|
|
Axons of the ganglion cells for the optic tract and end in the
|
Lateral geniculate body of thalamus
|
|
|
What fibers of the cross in the optic chiasm and what fibers remain ipsilateral?
|
The nasal hemiretina cross while the temporal fibers remain ipsilateral
|
|
|
The right optic tract is composed of _____ and synapse in the ______ tract
|
Left nasal hemiretina and
Right temporal hemiretina Synpase in Right lateral genicualte |
|
|
What is the geniculocalcarine tract?
|
Fibers from the lateral geniculate that pass posterior to the occipital lobe of the cortex
|
|
|
Cutting the optic nerve causes
|
Blindness on the same side
|
|
|
Cutting the optic chiasm causes
|

Heteronymous bitemporal hemianopia
|
|
|
Axons of the ganglion cells for the optic tract end in the
|
Lateral geniculate body of thalamus
|
|
|
What fibers of the cross in the optic chiasm and what fibers remain ipsilateral?
|
The nasal hemiretina cross while the temporal fibers remain ipsilateral
|
|
|
The right optic tract is composed of _____ and synapse in the ______ tract
|
Left nasal hemiretina and
Right temporal hemiretina Synpase in Right lateral genicualte |
|
|
What is the geniculocalcarine tract?
|
Fibers from the lateral geniculate that pass posterior to the occipital lobe of the cortex
|
|
|
Cutting the optic nerve causes
|
Blindness on the same side
|
|
|
Cutting the optic chiasm causes
|
Heteronymous bitemporal hemianopia
|
|
|
Visual Aide
|
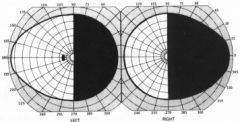
Homonymous Contralateral Hemianopia; results from a lesion in optic tract
|
|
|
Visual
|

|
|
|
Rhodopsin belongs to what family of receptors?
|
G-protein coupled receptors
|
|
|
Rhodopsin is
|
the photosensitive element; opsin = protein and retinal = aldehyde of Vit.A
|
|
|
Light in the retinal converts ____ to ____.
|
11-cis retinal to all-trans retinal
|
|
|
Thru a series of steps ______ product is formed which activates trasnducin
|
Metarhodopsin II
|
|
|
Why is vit. A necessary for the visual pathway?
|
Regeneration of 11-cis retinal.
|
|
|
Metarhodopsin II signaling:
|
Metarhodopsin activates G-protein transducin which then activates phospodiesterase
|
|
|
Phosphodiesterase role in the visual pathway is
|
1.Catalyzes the conversion of cGMP to 5'GMP; decreases cGMP.
2. ↓cGMP causes closure of Na+ channels; causing hyperpolarization 3.Hyperpolarization, leads to DECREASED RELEASE OF EITHER EXCITATORY OR INHIBITORY NEUROTRANSMITTERS |
|
|
Increasing light intensity causes an increase
|
hyperpolarization
|
|
|
Three cotrical cell type are involved in shape and orientation and they are:
|
Simple cells
Complex cells Hypercomplex cells |
|
|
The Simple cells of visual cortex are involved in
|
Correct position and orientation
|
|
|
The complex cells of the visual cortex are involved in
|
moving bars or edges of light with correct orientation
|
|
|
The hypercomplex cell of the visual cortex respond to
|
Lines of length and curves and angles
|
|
|
An opacity that forms in the lens
|
Cataracts
|
|
|
Tx for Cataracts
|
Removal of lens and artificially implant a lens
|
|
|
Intraocular pressures are extremely high which can lead to optic nerve compression
|
Glaucoma
|

