![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Action |
An action is:-An assembly of concentrated or distributed mechanical forces acting on a structure (direct actions),or -The cause of deformations imposed on the structure or constrained in it (indirect actions) Action1. Direct action- load2. Indirect |
|
|
Classification of action according to the variation of their magnitude with time: |
-Permanent action which is likely to act continuously throughout a given reference period and for which variationsin magnitude with time are small compared with the mean value -Variable action, for which the variation in magnitude with time is neither negligible in relation to the mean value nor monotonic. -Accidental action which is unlikely to occur with a significant value on a give en structure over a given reference period |
|
|
Examples of action |
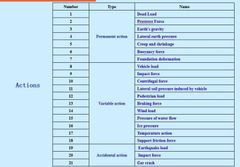
|
|
|
Permanent action |
Including: structural gravity, prestressing, soil gravity, soil latera pressure,concrete shrinkage and creep effect, and the role offoundation deformation and so on.The weight of the structure itself and the external gravity of the bridge deck pavement, ancillary facilities, etc. belong to the structural gravity, which can be calculated by multiplying the actual volume of the structure or the designed volume by the bulk density of the material. |
|
|
Examples of permanent action |
1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V 2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete * The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance. 1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete* The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance.Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other.4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. 1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete* The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance.Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other.4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. 1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete* The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance.Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other.4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. 1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete* The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance.Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other.4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. 1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete* The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance.Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other.4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. 1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete* The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance.Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other.4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. 1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete* The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance.Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other.4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. 1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete* The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance.Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other.4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. 1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete* The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance.Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other.4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. 1.Dead load*Dead load on a structure is the result of the weight of the permanent components. *These components will produce the same constant 'dead' load during the lifespan of bridges. *Dead loads are exerted in the vertical plane.*Dead load =volume of member x unit weight of materials*G=r.V2. Shrinkage Creep and shrinkage of concrete are two physical properties of concrete* The volumetric changes of concrete structures due to the loss of moisture *It is a time-dependent deformationImmediate which reduces the volume of concrete without the impact of external forces. 3.Pre-stressed structure*The prestressing force should be used as a permanent load to calculate its Primary and secondary effect at normal use limit state design; *In the design of the structure bearing capacity limit state, pre-stressing is not a load, and the prestressed reinforcement as part of the structural resistance.Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other.4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. Principle of pre-stressing*Pre-stressing is a method in which compression force is applied tothe reinforced concrete section.*The effect of pre stressing is to reduce the tensile stress in thesection to the point till the tensile stress is below the cracking stress *Thus the concrete does not crack.It is then possible to treat concrete as a elastic material*The concrete can be visualized to have two compressive forcei.Internal pre-stressing force. ii . External forces (d.l , l.l etc )*These two forces must counteract each other. 4. Creep*Creep can be defined as the elastic and long-term deformation ofconcrete under a continuous load. *Generally, a long term pressure changes the shape ofconcrete structure and the deformation occurs along the direction of the applied load. |

