![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Normal Breast Anatomy & Histology
|
twenty lobes, segmental & sub segmental ducts. rest is skin, nipple, areola, subcutaneous fat. "milk line" from axilla to inguinal may contain ectopic tissue subject to inflammation & disease
|
|
|
|
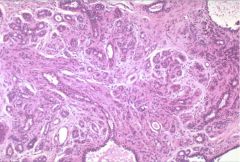
Sclerosing Adenosis
|
Fibrocystic change mimicking carcinoma. proliferation of small ducts within fibrous stroma.
histo: lobular architecture, myoepithelial cells present |
|
|
intraductal papilloma
|
localized benign papillary epithelial hyperplasia in large duct, no atypia = not pre-malignant (need to excise to exclude). presents w/ discharge "papillomatosis"
|
|
|
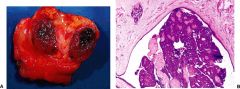
Fibroadenoma
|
Painless, moveable lump, young women. benign tumor made up of fibrous and/or myxoid stroma & glandular epithelium. NO risk of malignancy. similar to Phyllodes (less cellular & less atypia)
|
|
|
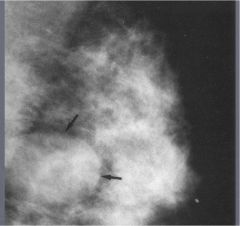
fibroadenoma
|
Painless, moveable lump, young women. benign tumor made up of fibrous and/or myxoid stroma & glandular epithelium. NO risk of malignancy. similar to Phyllodes (less cellular & less atypia)
|
|
|
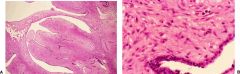
Phyllodes Tumor
|
epithelial & stromal components (more cellular & atypical than fibroadenoma). can be massive, may be malignant
|
|
|
Breast Cancer Epidemiology
|
increasing incidence 30% of diagnoses result in death from the dz. incidence increases w/ age & plateaus at 60. lifetime risk is 1:8 of developing 1:30 mortality
|
|
|
|
Breast Cancer Risk Factors
|
Genetic (5-10% from germline mutations), hormonal, diet (high fat)?, environmental (more common in western world)?, Viral?
|
|
|
|
Breast Cancer Genes
|
BRCA1 (17q21) >50% develop before 50y/o. Responsible for 50% of inherited breast cancers. new tx w/ PARP inhibitors
BRCA2 (13q) men & ashkenazi jewish women |
|
|
|
Breast Cancer Classification
|
Ductal In situ/Invasive
Lobular In situ/Invasive Special types |
|
|
|
Prognostic factors
|
Stage (TNM), histologic grade (degree of differentiation), ER/PR status, molecular markers
|
|
|
|
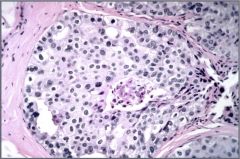
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
|
Neoplastic cells within dilated duct, confined by basement membrane. Graded by growth pattern & cytologic appearance. typically not palpable. Untreated 25% develop invasive carcinoma in 10yrs
Tx: surg, rad, hormonal (if ER/PR +) |
|

|
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
|
Neoplastic cells within dilated duct, confined by basement membrane. Graded by growth pattern & cytologic appearance. typically not palpable. Untreated 25% develop invasive carcinoma in 10yrs
Tx: surg, rad, hormonal (if ER/PR +) |
|
|
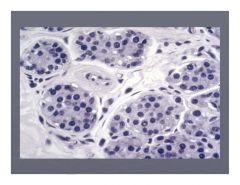
Lobular Carcinoma in Situ
|
clinically silent, not palpable (no microcalcification or stromal fibrosis), incidental finding on biopsy. 25% bilateral.
Considered to be an indicator of increased risk |
|
|
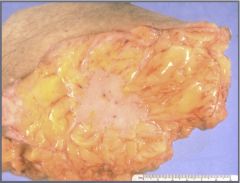
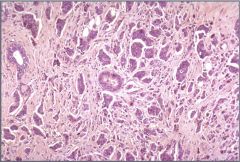
Carcinoma of the breast (ductal?)
|
|
|
|
(invasive?) ductual carcinoma
|
|
|

|
Paget's Disease
|
typically associated w/ underlying ductal carcinoma. neoplastic cells spread to epidermis of the nipple. prognosis depends on nature of underlying lesion
|
|

|
HER2/neu overexpression in invasive ductal carcinoma & FISH identification of HER2/neu
|
|
|
|
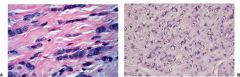
Lobular Carcinoma in Situ (L)
Signet Ring Carcinoma (R) |
clinically silent, not palpable (no microcalcification or stromal fibrosis), incidental finding on biopsy. 25% bilateral.
Considered to be an indicator of increased risk Signet Ring Carcinoma |
|
|
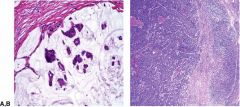
colloid (mucinous) carcinoma
medullary carcinoma (not in syllabus) |
|

