![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anterior spinal artery Syndrome
|
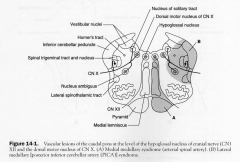
- medial medullary syndrome
1. CsT; contralateral spastic hemiparesis 2. ML; contralateral loss of tactile, vibration 3. CNXIIn. Ipsilateral flaccid hemiparalysis of tongue |
|
|
PICA syndrome or
Lateral Medullary Syndrome |
- dissociated sensory loss
1. vestibular n.; i.e nystagmus, n/v & vertigo 2. Inferior cerebellar peduncle. Ipsilateral cerebellar signs (e.g dystaxia, dysmetria, dysdiadochokinesia) 3. NA. ipislateral... 4. IX nerve roots 5. Vagal Nerve roots 6. SptT contralateral 7. Sp V n & T. Ipsilateral (facial hemianesthesia) 8. Descending sympathetic tract. Ipsilateral horners |
|
|
Medial Inferior Pontine Syndrome
|
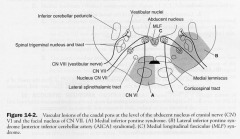
- occlusion of paramediam branches of the basilar a.
1. CsT contralateral 2. ML contalateral 3. CNVI roots. ipsilateral |
|
|
Lateral Inferior Pontine Syndrome
|
AICA
1. VIIn and intraaxial nerve fibres; ipsilateral 2. Cochlear n & intraaxial fibres 3. vestibular nuclei and intraaxial nerve fibres 4. Spinal trigeminal nucleus & tract. ipsilateral 5. Middle & inferior cerebellar peduncles. ipsilateral limb & gait dystaxia 6. SpT 7. Descending Sympathetics |
|
|
MLF Syndrome aka
Internuclear Opthalmoplegia |
fibres from contralateral CNVI that project via MLF to the ipsilateral CNIII (medial rectus nuclei)
CAUSES; - MR palsy on attempted lateral conjugate gaze & nystagmus in the abducting eye - convergence remains intact - often seen in MS |
|
|
Facial Colliculus Syndronme
|
Causes; pontine glioma or vascular
- the internal genu of CNVII & nucleus of CN VI 1. facial nerve ipsilateral facial paralysis 2. LR; medial strabismus, horizontal diplopia |
|
|
Dorsal Midbrain (Parinaud's Syndrome)
|
Causes; pinealoma or germinoma
1. Superior colliculus and pretectal area. Paralysis of upward & downward gaze, pupillary disturbances & absence of convergence 2. Cerebral Aqueduct. compressioon causing non-communicating hydrocephalus |
|
|
Paramedian midbrain (benedikt) syndrome
|
1. CNIII roots
2. dentatothalamic fibres. contralateral cerebellar dystaxia with intention tremor 3. ML |
|
|
Medial Midbrain (weber) Syndrome
|
1. CNIII roots
2. CsT 3. CbT. contralateral weakness of lower face (VII), tongue (XII), palate (CNX), uvula and pahrygeal wall pulled towards normal side (X) |
|
|
Acoustic Neuroma
- SCHWANNOMA |
- benign tumour of schwann cells affecting CNVIII
- in posterior fossa inside the IAM - can often compress VII - can impinge on the pons affecting SpV tract - more often in females A. Cochlear n B. vestibular N. C. VII D. Spinal trigeminal tract E. Neurofibromatosis type 2 |
|
|
Jugular Foramen Syndrome
|
IX, X, Xi
|
|
|
Locked In Syndrome
|
lesion in base of pons due to
- infarction, trauma, tumor, demyelination 1. CsT & CbT bilaterally 2. CNII & IV are not injured |
|
|
Central Pontine Myelinolysis
|
lesion @ base of pons affects CsT & CbT
- CAUSES 75% are alcoholism or rapid correction of hyponatremia - may become locked in syndrome |
|
|
Top of the Basilar Syndrome
|
embolic occlusion of rostral basilar a.
- optic ataxia - psychic paralysis of fixation of gaze - ectopic pupils - somnolence - cortical blindness |
|
|
Subclavian Steal Syndrome
|
thrombosis of left subclavian aa. proximal to vertebral a. blood shunted retrograde down the left verterbral a & into the left subclavian
- clinical signs transient weakness & claudication of left arm on exercise & vertebrobasilar insufficiency (i.e vertigo & dizziness) |
|
|
Cerebellopontine angle
|
junction between medulla, pons & cerebellum (CNVII & VIII)
- 5 common brain tumours - SAME (mneumonic) - schwannoma (75%) - arachnoid cyst (1%) - meningioma (10%) - Ependymoma (1%) - EPidermoid (5%) |
|
|
Coma
|
BRF
|
|
|
Cerebellar signs
|
cerebellar peduncles
|
|
|
Nystagmus, vertigo, nausea
|
Vestibular Nuclei
- fast phase towards lesion side |
|
|
Speech
|
NA (X)
|
|
|
Vomit
|
BRF vomit centre
Area posterima |
|
|
Motor Loss
|
Corticospinal tract
|
|
|
Sensory Loss
|
Trigeminal nuclei
Spinothalamic tract - specific to brainstem injury - loss sensation on one side of face and opposite side of the body CARDINAL SIGNATURE |
|
|
Cortical Innervations
|
Corticobulbar Tract
- most are bilateral EXCEPT VII (Upper face is lower face isnt) and XII (contralateral) |

