![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the structures of the BRAIN STEM
|
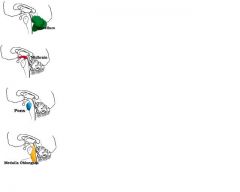
Listed superiorly:
Midbrain Pons Medulla Oblongata The Cerebelum is not part of the brain stem; it is located above the brain stem |
|
|
What is the function of the cerebellum?
|
-Coordination and Voluntary motor movements
-Balance and equilibrium -MS tone |
|
|
What are the Dysfunctions if the Cerebellum is damaged?
|
Person seems like s/he is drunk!
-ATAXIA: Inability to coordinate MS movements, Ataxic gait, ataxic speech -Intention Tremors -Hypotonia -Nystagmus -Dysmetria: Inability to judge distance -adiadochokinesia- inability to perform quick alternating movements |
|
|
Where is the midbrain?
|
-Top most structure of the brain stem
-Gradual transition to SC through Foramen Magnum |
|
|
What are the functions of the Midbrain?
|
-Eye movement AND Vision
-Hearing -Body movement |
|
|
Where is the Pons?
|
Continuous w/and below the midbrain; directly in front of the cerebellum
|
|
|
What are the functions of the pons
|
-Consciousness
-Arousal -Movement -Posture -Sleep |
|
|
Where is the Medulla Oblongata? and what goes through it?
|
-Lower most portion of the brain stem, and makes gradual transition to SC at the Foramen Magnum
-Crossing of the motor tracts |
|
|
What are the functions of the Medulla Oblongata?
|
-Breathing (Resp center)
-Heart rate (Cardiac center) -Blood pressure (Vasomotor center) -Reflex Center for gag, vomit, swallow |
|
|
What is the Reticular Activating System (RAS)?
|
It is the reticular formation and its connections (afferent axons from diff sources)
|
|
|
Where is the Reticular formation located?
|
it is a group of nuclei scattered throughout the brain stem
|
|
|
What is the RAS function?
|
Involved with the sleep/wake cycle
"The reticular formation has four functions: behavioral arousal, regulation of muscular reflexes, coordination of autonomic functions (like breathing and heartbeat) and the modulation of pain sensations." |
|
|
What is the stimuli for the RAS?
|
-sudden light
-cold water splashed on face |
|
|
What is the result of a damaged Reticular formation?
|
COMA
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of a brain stem injury?
|
-decreased capacity in breathing
-impaired speech -difficulty with swallowing food/water (dysphasia) -difficulty w/orginzational/perception of the environment -problems w/bal & movement -dizziness & nausea -sleeping disorders (insomnia, sleep apnea) -CAN CAUSE DEATH |

