![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe what is seen in acute neuronal injury.
|
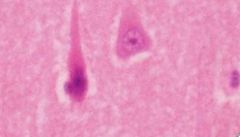
Red neurons
body shrinks nisl disappears pyknotic nucleus absent nucleolus |
|
|
When is neuronal atrophy/ degeneration seen?
What takes place during neuronal atrophy/degeneration? |
progressive neurologic disease
neoronal cell loss and reactive gliosis |
|
|
What can be seen in the cell body pathologically when an axon is injured
|
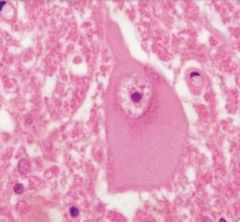
cell body changes:
disersed nissl substance enlargement peripheral nucleus with enlarged nucleolus and a central neuronal cell body |
|
|
What are neuronal inclusions?
Cause? Location? Composition? |
Nueronal inclusions are substances visable in neurons that are not normally seen
aging, infection, degenerative/metabolic diseases intranuclear cytplasmic axonal viral particles, proteins, etc. |
|
|
What is seen in lipofuscin neuronal inclusions?
When is it seen? |
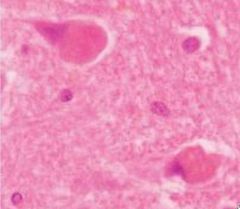
intracytoplasmic lysosomal accumulation of orange-brown granules
complex lipids/lipoproteins often seen in aging |
|
|
What is seen in spheroid neuronal inclusions?
|
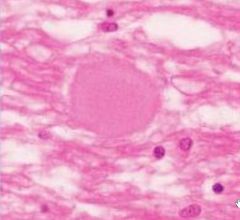
eosinophillic axonal swellings
neurofilaments, organelles, transport material accumulates focally when axon is damaged |
|
|
What is seen in lewy bodies?
What disease causes these? |
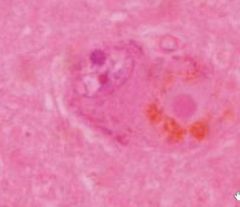
hylaine eosinophillic cores with pale halos
cytoplasmic inclusions (cytoskeletal proteins) seen in parkinsons |
|
|
What is seen in neurons with cytomegalovirus?
|
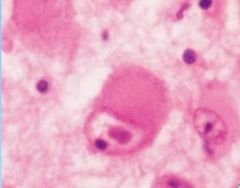
eosinophillic intranuclear inclusions
CMV viral particles |
|
|
What is seen in Tay Sachs Ganglioside neurons?
|
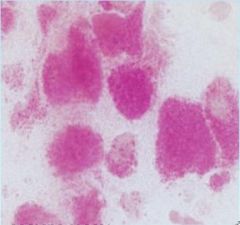
PAS positive gaglioside storage granules
accumulate in teh cytoplasm of neurons |
|
|
What are the glial reactions involving astrocytes?
|
Cellular swelling due to acute insult (hypoxia)
fibriallary gliosis (nospecific reation to injury) Cavitation (end result of CNS injury) Alzheimer type 2 astrocytes astrocytic inclusions (rosenthal fibers) corpora amylacea (degenerative change) |

