![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Notochord |
Notochord induce neural plate (which is above) to change. neural plate starts to thicken. |
|
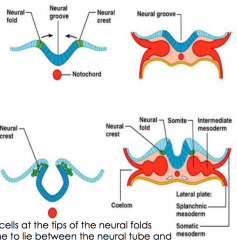
|
On edge of fold, neural crest cells. These migrate |
|
|
Secondary neurulation |
Formation of spinal cord: mass of cells form a tube |
|
|
Neural Crest Cells form... |
sensory neurons parts of the autonomic NS Schwann cells Satellite cells of the PNS |
|
|
Sulcus Limitans |
Separates sensory and motor areas of spinal cord and brain stem Opposing concentration gradients of singling molecules 1) ectoderm near what will become dorsal surface of neural tube 2) mesodermal notochord near ventral surface separate dorsal half and ventral half separate alar plate and basal plate BRAINSTEM AND SPINAL CORD (sonic hedgehog) |
|
|
Alar plate (Dorsal half) |
Sensory processing (posterior horn) spinal cord and brainstem |
|
|
Basal Plate (Ventral half) |
Motor processing (anterior horn) spinal cord and brainstem |
|
|
Pontine Flexure |
pulls walls of neural tube apart, forming the floor of the 4th ventricle. alar and basal plate spread across floor of 4th ventricle. Sensory neurons lateral to motor neurons (midline) Split alar plate. Brainstem |
|
|
Primary Vesicles |
Prosencephalon (forebrain) Mesencephalon Rhombencephalon (hindbrain) B/w Mesen and Rhomb: cephalic flexure B/w Rhomb and Spinal Cord: Cervical flexure |
|
|
Secondary Vesicle |
Telencephalon Diencephalon Mesencephalon Metencephalon Myelencephalon |
|
|
Telencephalon |
Cerebral hemisphere (Lateral ventricle) Two hemispheres Lamina terminalis is midline to whole thing |
|
|
Mesencephalon |
Midbrain |
|
|
Metencephalon |
Pons, cerebellum |
|
|
Myelencephalon |
medulla (fourth ventricle, central canal) |
|
|
Pontine Flexure |
third flexure that occurs in metencephalon flexure division of flexure |
|
|
Diencephalon |
Thalamus, hypothalamus, retina, structures (third ventricle) |
|
|
Cerebellum Formation |
Opening of alar plate, see rhomic lip: where future cerebellum |

