![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Map the primary vesicle development onto
secondary vesicle development, and onto adult brain regions. (ie. Which embryonic structures lead to which adult regions?) |
Embryo at 4 Weeks
1. Prosencephalon – forebrain 2. Mesencephalon – midbrain 3. Rhombecephalon – hindbrain Embryo at 5 weeks 1. Telecephalon – forebrain 2. Diencephalon – forebrain 3. Mesencephalon – midbrain 4. Metencephalon – hindbrain 5. Myelencephalon – hindbrain Adult 1. Cerebrum – forebrain 2. Epithalamus – forebrain 3. Thalamus – forebrain 4. Hypothalamus – forebrain 5. Cerebral peducles – midbrain 6. Superior colliculi – midbrain 7. Interior colliculie – midbrain 8. Pons – hindbrain 9. Cerebellum – hindbrain 10. Medulla oblongata - hindbrain |
|
|
Know the order (depth) of the 3 meninges.
|
1. Dura mater
2. Arachnoid 3. Pia mater |
|
|
Know the order (depth) of the 3 meninges:
What are the functions of the meninges (all together)? |
They are 3 connective tissue layers that separates the soft tissue of the brain from the bones of the cranium, enclose and protect blood vessels that supply the brain, and contain and circulate cerebrospinal fluid.
|
|
|
What are the functions of the dural septa?
|
Partition parts of the brain and provide stabilization and support
|
|
|
What are the functions of the dural septa?:
Venous sinuses? |
Large veins that drain blood from the brain into the internal jugular.
|
|
|
What are the ventricles of the brain filled with?
|
Cerebrospinal fluid
|
|
|
What are the ventricles of the brain filled with? :
What is the purpose of this fluid? |
1. Buoyancy
2. Protection 3. Environmental stability |
|
|
What are the ventricles of the brain filled with?
What is the purpose of this fluid? : Name the ventricles. |
1. Lateral ventricle
2. Lateral ventricle 3. Third ventricle 4. Fourth ventricle |
|
|
How does the brain keep unwanted chemicals out?
|
Blood-Brain Barrier
|
|
|
What is the major structure that connects the cerebral hemispheres?
|
Corpus callosum
|
|
|
Name the general functions of the five lobes of the cerebrum.
|
1. Frontal lobe - head quarters (hightes function area: personality, consintration..ect)
2. Parietal lobe - somatosensory info processes. e.i. touch, pain, vibrations 3. Temporal lobe - process hearing, smell 4. Occipital lobe - visual info process 5. Insula - memory, taste, links emotion to vercera |
|
|
Know the specific locations of the primary motor and somatosensory cortices.
|
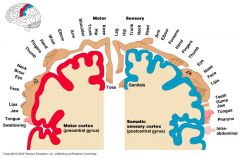
Left to Right: MOTOR CORTEX; swallowing, tongue, jaw, lips, face, eye, brow, neck, thumb, fingers, hand, wrist, elbow, arm, shoulder, trunk, hip, knee, toes. SOMATIC SENSORY CORTEX; genitals, leg, hip, trunk, neck, head, arm, elbow, forearm, hand, fingers, thumb, eye, nose, face, lips, teeth, gums, jaw, tongue, pharynx, intra-abdominal.
|
|
|
What defines a primary sensory area?
|
First cortical region activated by a given sense.
|
|
|
The functions and locations of Broca’s area vs Wernicke’s area.
|
Broca’s area is in the Left Frontal Lobe and deals with speaking.
Wernicke’s area recognizes and compreheneds spoken and written language (listening) in the Left Temporal Lobe |
|
|
What are the 3 components of the dienchephalon.
|
• Thalamus
• Hypothalamus • Epithalamus |
|
|
Name several functions of the hypothalamus.
|
• Secretes 2 hormones:
o Anti-Diurentic Hormone ADH o Oxytocin • Controls secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland o Negative feedback o Positive feedback |
|
|
What are the 3 regions of the brainstem?
|
1. Mesencephalon
2. Pons 3. Medulla oblongata |
|
|
Which of the mesencephalon structures are involved in Parkinson’s disease?
|
Substantia nigra
|
|
|
Which of the mesencephalon structures are involved in Parkinson’s disease?:
how does the BBB impact treatment? |
Astrocytes blocks dopamine from the bloodstream, Levodopa can be take to supple the brain of dopamine which bypass astrocytes.
|
|
|
What is the function of the tectum?
|
2 sensory nuclei
• Tectal plate o Superior colliculi Visual reflex center (tracking) o Inferior colliculi Auditory reflex center (tracking) |
|
|
Pons
|
• Autonomic respiratory centers
• Cranial never nuclei |
|
|
Where does motor output decussate?
|
Pyramids
|
|
|
Medulla Oblongata
|
All communication between the brain and spinal cord involves tracts that ascend or descend through.
|
|
|
Medulla Oblongata: Important Autonomic nuclei
|
• Cardiac center - heart rate and strength of contractions
• Vasomotor center - blood pressure • Respiratory center - breath rate • Other nuclei - are involved in coughing, sneezing, swallowing, salivation, gagging, vomiting. |
|
|
What is the function of the cerebellum?
|
Coordinates and fine-tunes skeletal muscle movements via feedback loops
|
|
|
What is the function of the limbic system?
|
Collectively process and experience emotion
|
|
|
What are the structures within the limbic system?
|
Cerebral and Diencephalic Structures
• Cingulated gyrus • Hippocampus • Olfactory bulbs, tracts, cortex • Fornix |

