![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
144 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
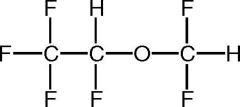
Name this structure.
|
Desflurane
|
|
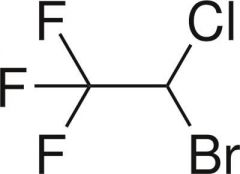
Name this structure.
|
Halothane
|
|
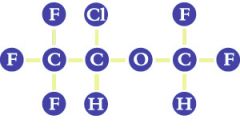
Name this structure.
|
Isoflurane
|
|
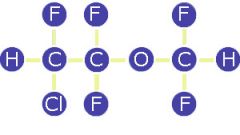
Name this structure.
|
Enflurane
|
|
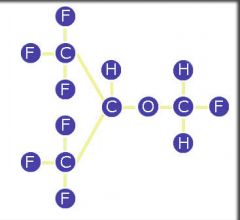
Name this structure.
|
Sevoflurane
|
|

Who wants some gas????
|
Take a deep breath.....
|
|
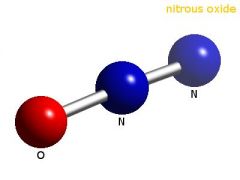
Name this structure.
|
Nitrous-oxide
|
|
|
What two inhalation gases are isomers to each other?
|
isoflurane and enflurane
|
|
|
N2O is a -------- at room temperature and a ------- under pressure.
|
gas
liquid |
|
|
Volatiles are ------- at room temperature but readily evaporate.
|
liquid
|
|
|
The birth of modern anesthesia dates back to the public use of ether by Wm. Morton in Boston on Friday, October 16 ------.
|
1846
|
|
|
Ether was earlier used by who in 1842.
|
Crawford Long
|
|
|
Who used nitrous oxide successfully in dental anesthesia in 1844?
|
Horace Wells
|
|
|
True or False
most of the modern volatile anesthetics are direct descendants of ether. |
True
|
|
|
What is the name of the new gas that is not in general use and is a gas at room temperature?
|
Xenon
|
|
|
The solubility of inhalational anesthetics in blood is indicated by their blood --- --------- -----------.
|
gas partition coefficient
|
|
|
What does gas partition coefficient determine?
|
the speed of onset and the rate of recovery of a gas
|
|
|
True or False
Relatively insoluble agents act more rapidly. |
True
|
|
|
Why does insoluble agents act more rapidly?
|
a smaller quantity is removed by dissolving in blood. This leaves a higher alveolar concentration to facilitate induction.
|
|
|
True or False
Solubility in blood is the inhalation equivalent of volume distribution. |
True
|
|
|
What are the four physical properties of inhalational anesthetic agents ( for our purposes)?
|
Solubility in blood
Lipid solubility Vapor pressure Structure |
|
|
What indicates the solubility of an inhalational anesthetic in lipids?
|
Oil:Gas partition coefficient
|
|
|
True or False
The Meyer-Overton relationship suggests that volatile anesthetics act on a hydrophilic target. |
FALSE--- it suggests that they act on a hydroPHOBIC target.
|
|
|
What does the oil:gas partition coefficient correlates to?
|
with volatile anesthetic potency according to the Meyer-Overton relationship.
|
|
|
What is the structure of Halothane?
|
a halongenated alkane
|
|
|
What structure are of Enflurane,Isoflurane,Desflurane, and Sevoflurane ?
|
They are halogenated methyl ethers.
|
|
|
What are the name of the two volatile agents that are structural isomers to each other?
|
Isoflurane and Enflurane
|
|
|
What is the difference in the structure of Desflurane and Isoflurane?
|
You substitute the Cl atom in Isoflurane with a F atom in Desflurane
|
|
|
Does the length of the molecule have an effect on the anesthetic effect? If so What is the effect?
|
Yes.. if a chain is over 5 carbons long it will loose some anesthetic effect.
|
|
|
True or False
Halothane is more potent then Desflurane due to it being a heavy molecule? |
True
|
|
|
Does the lipid solubility of a volatile gas make it more potent? If so , Why? If not, why?
|
YES... the more lipid soluble the more potent because it can get through the cell lipid bilayer easier.
|
|
|
Why did we use to use Halothane for children?
|
Because it smells good
|
|
|
What is a common cardiac side effect of Halothane?
|
cardiac arrhythmia's
|
|
|
What are two major side effects of Enflurane?
|
Nephro Toxic
seizures |
|
|
True or False
Desflurane smells good, and a patient will easily breath it in. |
FALSE .... Des smells bad and will cause a patient to hold their breath and cough.
|
|
|
Does the length of the molecule have an effect on the anesthetic effect? If so What is the effect?
|
Yes.. if a chain is over 5 carbons long it will loose some anesthetic effect.
|
|
|
Does the length of the molecule have an effect on the anesthetic effect? If so What is the effect?
|
Yes.. if a chain is over 5 carbons long it will loose some anesthetic effect.
|
|
|
Why is Isoflurane used more in 3rd world countries, and veteran hospitals?
|
it is cheaper
|
|
|
What is the name of the special vaporizer used for
Desflurane? |
TEC-6
|
|
|
True or False
Halothane is more potent then Desflurane due to it being a heavy molecule? |
True
|
|
|
True or False
Halothane is more potent then Desflurane due to it being a heavy molecule? |
True
|
|
|
What is Desflurane heated with the TEC-6?
|
boils at room temperature
help to control amount of gas given, if not heated you can give a hypoxic mixture. |
|
|
Does the length of the molecule have an effect on the anesthetic effect? If so What is the effect?
|
Yes.. if a chain is over 5 carbons long it will loose some anesthetic effect.
|
|
|
Does the lipid solubility of a volatile gas make it more potent? If so , Why? If not, why?
|
YES... the more lipid soluble the more potent because it can get through the cell lipid bilayer easier.
|
|
|
Does the lipid solubility of a volatile gas make it more potent? If so , Why? If not, why?
|
YES... the more lipid soluble the more potent because it can get through the cell lipid bilayer easier.
|
|
|
Does the length of the molecule have an effect on the anesthetic effect? If so What is the effect?
|
Yes.. if a chain is over 5 carbons long it will loose some anesthetic effect.
|
|
|
True or False
Halothane is more potent then Desflurane due to it being a heavy molecule? |
True
|
|
|
Does the lipid solubility of a volatile gas make it more potent? If so , Why? If not, why?
|
YES... the more lipid soluble the more potent because it can get through the cell lipid bilayer easier.
|
|
|
True or False
Halothane is more potent then Desflurane due to it being a heavy molecule? |
True
|
|
|
Why did we use to use Halothane for children?
|
Because it smells good
|
|
|
Why did we use to use Halothane for children?
|
Because it smells good
|
|
|
Why did we use to use Halothane for children?
|
Because it smells good
|
|
|
Does the lipid solubility of a volatile gas make it more potent? If so , Why? If not, why?
|
YES... the more lipid soluble the more potent because it can get through the cell lipid bilayer easier.
|
|
|
What is a common cardiac side effect of Halothane?
|
cardiac arrhythmia's
|
|
|
What is a common cardiac side effect of Halothane?
|
cardiac arrhythmia's
|
|
|
What is a common cardiac side effect of Halothane?
|
cardiac arrhythmia's
|
|
|
Why did we use to use Halothane for children?
|
Because it smells good
|
|
|
What are two major side effects of Enflurane?
|
Nephro Toxic
seizures |
|
|
What are two major side effects of Enflurane?
|
Nephro Toxic
seizures |
|
|
What are two major side effects of Enflurane?
|
Nephro Toxic
seizures |
|
|
What is a common cardiac side effect of Halothane?
|
cardiac arrhythmia's
|
|
|
True or False
Desflurane smells good, and a patient will easily breath it in. |
FALSE .... Des smells bad and will cause a patient to hold their breath and cough.
|
|
|
What are two major side effects of Enflurane?
|
Nephro Toxic
seizures |
|
|
True or False
Desflurane smells good, and a patient will easily breath it in. |
FALSE .... Des smells bad and will cause a patient to hold their breath and cough.
|
|
|
True or False
Desflurane smells good, and a patient will easily breath it in. |
FALSE .... Des smells bad and will cause a patient to hold their breath and cough.
|
|
|
Why is Isoflurane used more in 3rd world countries, and veteran hospitals?
|
it is cheaper
|
|
|
Why is Isoflurane used more in 3rd world countries, and veteran hospitals?
|
it is cheaper
|
|
|
True or False
Desflurane smells good, and a patient will easily breath it in. |
FALSE .... Des smells bad and will cause a patient to hold their breath and cough.
|
|
|
Why is Isoflurane used more in 3rd world countries, and veteran hospitals?
|
it is cheaper
|
|
|
What is the name of the special vaporizer used for
Desflurane? |
TEC-6
|
|
|
Why is Isoflurane used more in 3rd world countries, and veteran hospitals?
|
it is cheaper
|
|
|
What is the name of the special vaporizer used for
Desflurane? |
TEC-6
|
|
|
What is the name of the special vaporizer used for
Desflurane? |
TEC-6
|
|
|
What is Desflurane heated with the TEC-6?
|
boils at room temperature
help to control amount of gas given, if not heated you can give a hypoxic mixture. |
|
|
What is the name of the special vaporizer used for
Desflurane? |
TEC-6
|
|
|
What is Desflurane heated with the TEC-6?
|
boils at room temperature
help to control amount of gas given, if not heated you can give a hypoxic mixture. |
|
|
Why is Desflurane heated with the TEC-6?
|
boils at room temperature
help to control amount of gas given, if not heated you can give a hypoxic mixture. |
|
|
What is Desflurane heated with the TEC-6?
|
boils at room temperature
help to control amount of gas given, if not heated you can give a hypoxic mixture. |
|
|
What gas is used now a days with kids instead of Halothane and why?
|
Sevoflurane... smells good
|
|
|
Which gas has a higher vapor pressure because it's boiling point is closer to room temperature?
|
Desflurane
|
|
|
TEC-6 is used with Desflurane because a conventional vaporizer would not be able to cope with the large changes in ----- -------- resulting from small variations in ambient temperature, and would be unable to supply sufficient ---- for the evaporation of an adequate amount of Des.
|
vapor pressure
heat |
|
|
What should you do if you are using Desflurane and the power goes out?
|
switch to a different gas, because the TEC-6 vaporizer is not working ( it needs an electrical current to evaporate the agent which is then metered as a gas)
|
|
|
True or False
The vaporizer dial setting does not necessarily reflect the concentration in the breathing circuit, alveoli, blood or brain. |
TRUE
|
|
|
What is the definition of MAC ( Minimum alveolar concentration)?
|
is the concentration necessary to abolish response( movement to incision) in 50% of the patient population ( relative potency)
|
|
|
What does ED50 mean?
|
is the 50% effective dose
|
|
|
What is the ED95 mean?
|
the alveolar concentration necessary to abolish movement in 95% of the population
|
|
|
What is the MAC dos of ED95?
|
1.2 to 1.5 MAC
|
|
|
Name some factors that decrease MAC.
|
a2 Agonists
barbiturates benzodiazepines opioid analgesics other anesthetics increasing age hypothermia hypoxia pregnancy hypotension |
|
|
What factors that increase MAC?
|
CHRONIC ETOH use
young age hyperthermia |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
Lower MAC values indicate a more potent volatile anesthetic. |
TRUE
|
|
|
Is MAC inversely related to potency?
|
yes
|
|
|
What kind of medication can you use with a volatile agent to decrease the MAC of the volatile agent?
|
a Narcotic
|
|
|
What major side effect can all of the halogenated volatile agents trigger in susceptible individuals?
|
Malignant hyperthermia
|
|
|
What is the only absolute contraindication to the use of halogenated volatile agents?
|
a patient who is susceptible to Malignant hyperthermia
|
|
|
What volatile agent undergoes the most metabolism? and what % ?
|
Halothane 20%
|
|
|
What volatile agent undergoes the least metabolism? and what %?
|
Desflurane 0.02%
|
|
|
In the presence of extremely dry soda lime, what can be produced by desflurane,enflurane, and isoflurane?
|
Carbon monoxide
|
|
|
What does soda lime degrade sevoflurane into?
|
Compound A
|
|
|
Compound A is nephrotoxic in rats at concentrations of --------.
|
50 parts per million (ppm)
|
|
|
What has been associated with a higher compound A production than soda lime?
|
Baralyme
|
|
|
How many segments does the right and left lung have?
|
Right has 10 segments
Left has 8 segments |
|
|
How many lobes does the right and left lung have?
|
right has 3 lobes
left has 2 lobes |
|
|
The terminal respiratory unit is distal to the terminal bronchiole and consists of a respiratory bronchiole branching into.........
|
alveolar ducts
atria alveolar sac alveoli |
|
|
Alveolar ducts are short and branch into 1-3 atria each leading to --- or ---- alveolar sacs and their alveoli.
|
1 to 3
|
|
|
There are about 300 million alveoli in the 2 lungs, each alveolus has an average diameter of what?
|
0.12-0.25 mm in diameter
|
|
|
How does Guyton describe the alveolar walls, due to them being very thin and are vascularized by a network of capillaries?
|
" sheet of flowing blood"
|
|
|
Where does gas exchange begin?
|
in the partially alveolarized respiratory bronchioles
|
|
|
What is the total surface of the respiratory membrane ( the membrane through which gas exchange occurs)?
|
70 square meters
|
|
|
What are the 5 cellular layers that make up the respiratory membrane?
|
surfactant layer
alveolar epithelium epithelial basement membrane capillary basement membrane capillary endothelial membrane |
|
|
What is the name of the fluid lipoprotein layer of the respiratory membrane that lines the alveolus and what is its function?
|
Surfactant layer which reduces the surface tension which reduces the work required to expand the alveoli
|
|
|
What are some factors that affect the rate of gas diffusion through the respiratory membrane?
|
the thickness of the membrane, (an increased in thickness can decrease the rate of diffusion)
The surface area of the membrane ( a decrease in surface area will decrease diffusion) the diffusion coefficient of the gas in the substance of the membranes the pressure difference between the two sides of the membrane. |
|
|
Define dead space.
|
ventilation without perfusion
|
|
|
What are the two types of dead space?
|
anatomic and physiologic
|
|
|
What is anatomic dead space?
|
it represents the amount of air or volume of air present within the nose,mouth larynx and other structures above the terminal respiratory unit.
|
|
|
What is physiologic dead space?
|
the sum of the anatomic dead space and alveolar dead space
|
|
|
What is alveolar dead space?
|
the volume of alveolar gas that does not take part in gas exchange or diffusion
|
|
|
In patients with moderate to severe COPD, the alveolar dead space is --------- due to destruction of alveolar septa.
|
increased
|
|
|
In patients with a pulmonary embolism physiologic dead space is ----------.
|
increased
|
|
|
What is the percentage of cardiac output that is not oxygenated called?
|
shunt
|
|
|
What is known as the increase in the partial pressure of the inhalational anesthetics in the alveoli?
|
wash in
|
|
|
What is the additive sum of the expiratory reserve volume in the lungs and the residual volume (2300ml) called?
|
functional residual capacity(FRC)
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
Denitrogenation via pre oxygenation prior to induction of anesthesia replaces the the nitrogen within the FRC with oxygen. |
true
|
|
|
If you have a decrease in FRC how does it effect wash in?
|
it will increase, more rapid wash in
|
|
|
Does cardiac output effect the uptake of inhalant anesthetics from the lung?
|
yes, the movement of the anesthetic across the alveolar capillary membrane and its removal by the blood transversing the pulmonary capillaries is due to cardiac output
|
|
|
The introduction of a certain concentration of drug into the system is the development of the inspired concentration is known as what abbreviation?
|
FI-- inspired concentration
|
|
|
The uptake of the drug into the lungs is development of the alveolar concentration, known as what abbreviation?
|
FA-- alveolar concentration
|
|
|
What is the time required for 63% wash in of a new gas to the lungs called?
|
time constant
|
|
|
What is the time constant of a normal lung with VA of 4 L/M and FRC of 2 liters ?
|
0.5 min
|
|
|
What are the three factors which determine the anesthetic uptake by the blood?
|
solubility
cardiac output alveolar mixed venous blood partial pressure difference of drugs |
|
|
What is the MAC, b/g,oil/gas of Halothane?
|
0.77 mac
2.3 b/g 224 oil/gas |
|
|
What is the biotransformation percentage of Halothane?
|
18%
|
|
|
What is the MAC, b/g, oil/gas and % of biotransformation of Enflurane?
|
MAC= 1.7
b/g= 1.9 oil/gas= 98 3% |
|
|
What is the MAC, b/g, oil/gas, and % of biotransformation of Isoflurane?
|
MAC= 1.15
b/g= 1.4 oil/gas= 92 1% |
|
|
Which gas is an ether-first synthesized in 1963 by Terrell, and is no longer used in the USA?
|
Enflurane
|
|
|
Which gas is a hydrogenated alkane and first synthesized in 1951 by Suckling and introduced into clinical practice by Johnstone in 1956?
|
halothane
|
|
|
What is the MAC, b/g, oil/gas and % of biotransformation of Sevoflurane?
|
MAC= 2.05%
b/g = 0.6 oil/gas = 53 3.5% |
|
|
What gas is an ether and first synthesized by Wallin et al int eh early 1970's?
|
Sevoflurane
|
|
|
What is the MAC, b/g, oil/gas, and % of biotransformation of Desflurane?
|
MAC= 6 for age 30-65, 7.25 % for 18-30 year old
b/g= 0.42 oil/gas=19 1% |
|
|
What gas is an ether, an analog of forane with an additional F- replacing the CL- on the ether alpha carbon atom and was introduced into clinical practice in 1992?
|
Desflurane
|
|
|
What is the MAC,b/g, oil/gas, of Nitrous Oxide?
|
MAC= 104%
b/g=0.46 oil/gas= 1.4 |
|
|
What gas is extensively metabolized, its major metabolite is trifluoroacetic acid via P450?
|
halothane ( CF3-CHBrCL )
|
|
|
What gas is slowly metabolized by the hepatic mixed function oxidase system, releases F- by oxidative dehalogenation?
|
Enflurane ( CHF2-O-CF2-CHCIF)
|
|
|
What gas is very slowly metabolized, and what little metabolism there is results from oxidation of the a-carbon?
|
isoflurane ( CHF2-O-CHCI-CF3)
|
|
|
Why is the wake time for desflurane about 50% less than observed with isoflurane?
|
this is principally attributable to a blood/gas partition coefficient.
|

