![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is used for clean tissue management of subgingival margins?
|
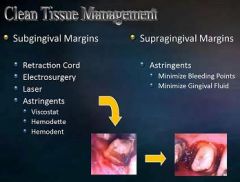
Retraction Cord
Electrosurgury Laser Astringents (viscostat, Hemodent, Hemodette) |
|
|
What is used for clean tissue management of supragingival margins?
|
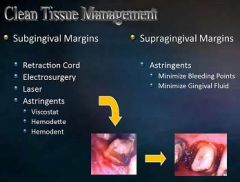
Astringents (minimize bleeding points and gingival fluid)
|
|
|
What are astringements used for?
|
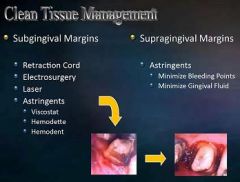
Both subgingival and supragingival margins.
Minimize bleeding points and gingival fluid. |
|
|
What are some problems with stock trays?
|

Cannot Confine and Control
No Tissue Stops Possible |
|
|
When should you fabricate custom trays?
|

Multiple units
When No posterior stop on unprepared tooth structure |
|
|
What considerations should you contemplate when using Triple Trays?
|

Single units
Must have rigid, fast-setting material to form tray for wash Less information = more error |
|
|
What are the most commonly used Final impression materials?
|
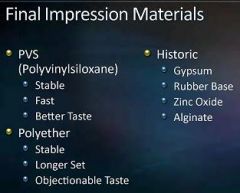
PVS & Polyether
(historic: Gypsum, Rubber base, Zinc Oxide, Alginate) |
|
|
What are the general properties of PVS?
|
Stable
Fast Better Taste |
|
|
What are the general properties of Polyether?
|
Stable
Longer Set Objectionable taste |
|
|
What is the Chroma of something?
|

Chroma = Amount (saturation) of color
|
|
|
What is the Hue of something?
|

Hue = Color
|
|
|
What is the Value of something?
|
Whiteness
Light/Dark |
|
|
How do you increase the value of something?
|
Value can be increased by the addition of light or white
|
|
|
What does the following do to the value?
Inadequate reduction Excessive opaque layer Hypersmooth texture Inadequate facial anatomy |
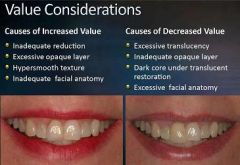
Increases the Value
|
|
|
What does the following do to the value of something?
Excessive translucency Inadequate opaque layer Dark core under translucent restoration Excessive facial anatomy |
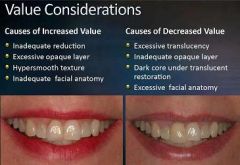
Decreases Value
|
|
|
What are four commonly used cements?
|

Zinc Phosphate
Resin Ionomer Glass Ionomer Resin |
|
|
Which cement has a long set and is exothermic, water soluble over time, technique sensitive
|

Zinc Phosphate
|
|
|
Which cement has fluoride release, not water soluble, easy cleanup, and is less technique sensitive?
|

Resin ionomers
|
|
|
Which cement is water soluble, more forgiving of environment, and has HIGH fluoride release?
|

Glass Ionomers
|
|
|
Which cement is extremely technique sensitive, has high bond strength, multiple steps, and isolation is critical?
|

Resin
|
|
|
What are the two key factors in final adjustment?
|
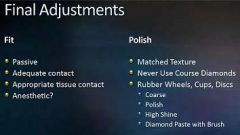
Fit and Polish
|
|
|
What properties are desireable when determining the fit?
|
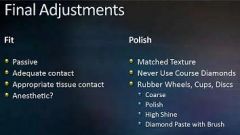
Passive
Adequate Contact Appropriate Tissue Contact Anesthetic |
|
|
What features should you look for when evaluating the polish?
|
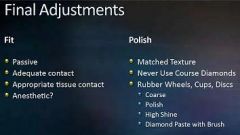
Matched texture
Never use course diamonds Rubber wheels, cups, discs |
|
|
What should you check when verifying and confirming the seat of a restoration?
|

Proximal contacts
Marginal integrity Axial contour Occlusion |
|
|
What should be accomplished when trying in the restoration?
|

Isolate field & control fluids
Application of Throat Pack Patient Position Familiarize yourself with the path of insertion and removal Verify and confirm the seat |
|
|
What are some potential problems associated with improper cementation?
|

Premature occlusion
Pulpitis Lack of Retention Fractures of abutment or restoration Recurrent Caries |
|
|
When should you attempt to remove the excess cement?
|
Allow the cement to reach a final set prior to attempting to clean away any excess
|
|
|
T/F
Appropriate and adequate seating force is crucial to ensure a complete seat when cementing a restoration. |
True
|
|
|
What types of cement are used for provisionals?
|

Zinc oxide Eugenol
Zinc oxide Non-Eugenol |
|
|
What steps should you take prior to cementation?
|

Isolate the field
Verify path of insertion Complete ALL polishing BEFORE cementation Ensure that abutment is clean (prep scrub & Oil-free pumice) |
|
|
What are the KEYS to Cementation Success?
|
Complete removal of excess material is vital to soft tissue rebound
Positive Seat |
|
|
What can you use to clean the excess cement once it has reached a final set?
|
Explorer or scaler
Knotted floss through interproximal pontic region |
|
|
Acid etch and bonding agen are added to the _____.
|
Abutment
|
|
|
Primer, catalyst, air abrasion is accomplished on the ______.
|
Restoration
|
|
|
How should you mix the cement?
|
Mix material according to manufacturer's directions on the appropriate mixing pad
|
|
|
A thin layer of cement should be applied to the _______ surface or the ______ with the _____
|
A thin layer of cement should be applied to the INTAGLIO surface or the RESTORATION with the CEMENT SPATULA
|
|
|
How should you mix cement?
|
USE MANUFACTURERS GUIDELINES
|
|
|
What is the primary source of retention?
|
The parallelism of the walls
|
|
|
T/F
a thin layer of cement provides retention |
True
|

