![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Outline the advantages and disadvantages of AI
|
ADVANTAGES
• Genetic progress and increased production – Use of estimated breeding values enables producers to select sires which can confer production advantages compared to the average animal • Greater selection pressure – only elite sires bred to elite cows are used to produce bulls & then only a minority of these are found to be suitable as sires • Disease control – Venereal diseases can be eliminated (provided that semen is collected from disease free bulls) • Wider choice of sires available • Safety – can eliminate or reduce the need for bulls • Improves record keeping – encourages producers to maintain up to date records DISADVANTAGES • Cost – relatively more expensive in beef herds c/f dairy herds • Requires good management to facilitate the process and to ensure cows are in their optimum condition to maximise pregnancy rates • Requires skill to achieve satisfactory pregnancy rates • Increase the frequency undesirable traits within the population. Inappropriate bull selection can lead to dystocia, & introduction of physical traits that are undesirable • Can reduce reproductive performance in some circumstances. Poor semen quality, semen handling or AI technique can lead to poor reproductive performance and delay conception. Increased pregnancy loss if pregnant cows are inseminated. |
|
|
Describe the rectovaginal technique for AI in cows.
|
Insert the AI gun through the cervix
Stop when the tip of the gun just penetrates the cervix. The tip of your finger can be used to judge the distance Deposit all semen in body of uterus. Tip: As soon as the tip passes through the internal os of the cervix, check with your finger, keep gun straight and deposit semen If the gun is more than 1 inch through the cervix, all the semen will be deposited into only one horn and pregnancy rates will be reduced |
|
|
Outline the recommended thawing technique for bovine semen
|
• Site of thawing: sheltered, clean, dry, warm, away from direct sunlight
• Equipment: clean, dry and preferably warm • Thawing: Place in a water bath (32 to 38 oC for 30 to 60 sec) • Use a thermometer that is tested as accurate and maintain water temperature within the optimum range throughout the day • Separate straws on insertion into water bath to facilitate thawing (prevent them from freezing together) • Ambient temperature < 20oC – maintain in water bath until ready to AI or keep loaded guns warm • Keep AI equipment clean, dry and warm |
|
|
How soon should a frozen-thawed dose of semen be used after
thawing? |
• Interval between removing from N2 tank and AI should be <15 min
|
|
|
What is the temperature of semen stored within liquid nitrogen?
|
Frozen semen must be maintained at a temperature of <-
100oC. Liquid nitrogen tanks maintain temperatures of -196oC Warming of frozen semen above -100 oC & recooling will result in recrystalisation with damage to sperm membranes. |
|
|
Outline the factors that can affect pregnancy rates to artificial
insemination. |
• Timing of AI in relation to onset of oestrus
• Semen storage • Semen handling • Dose of semen • Sire • Insemination technique • Poor records • Fertility of cows |
|
|
What is the min. standard required post thawing?
|
30% of sperm should be alive,
with 30% of live sperm progressively motile |
|
|
While you are pregnancy testing cows one day a farmer
comments that he is a little confused about when he should AI his cows to achieve optimum pregnancy rates as he has heard different recommendations. He mentions that he records those cows he notices in heat at the time of the morning and evening milking. Outline your response to his question and what would you recommend regarding when he should AI his cows after detecting them in heat. |
Optimum time for AI: 4 to 14 h post onset of oestrus. • Recommendation: Where onset of oestrus is not
known accurately: Cows should be inseminated when detected in oestrus as you don’t know at what stage of oestrus the cow is at. |
|
|
You analyse a herds reproductive performance and
calculate that first service conception rates were 28%, which is lower than you expect in this herd. Outline your approach to trying to determine the cause of low conception rates. |
Question appropriate storage of semen, semen handling and thawing
Did the famer split straws? What sire(s) did the semen come from (quality and suitability for freezing & thawing) Question proper insemination technique Check record keeping Check factors that could affect cow fertility (bredd, nutrition, BC, age, disease, reproductive health, calving interval,...) Check environmental factors eg heat stress |
|
|
The optimum time to inseminate cows after the onset of oestrus is:
a) 0 h b) 4 to 14 h c) 14 to 24 h d) 24 to 34 h e) 34 to 44 h |
b
|
|
|
The temperature at which frozen bovine semen is
stored at within liquid nitrogen is: a) 0oC b) -35oC c) -80oC d) -165oC e) -196oC |
e
|
|
|
O d ff i th d dl dd
Review questions Once a dose of frozen semen is thawed and loaded within an AI gun it is recommended that it be deposited within the uterus of a cow within a) 10 minutes b) 30 minutes c) 1 hour d) 2 hours e) 3 hours |
a
|
|
|
Explain conception rate
|
Conception rate: literally it means the % of oocytes during
oestrus that are fertilised and develop into a zygote after insemination. This is usually in excess of 90%. Conception rate = no. of inseminations that resulted in pregnancy x 100/ no. of inseminations |
|
|
Pregnancy rate
|
Pregnancy rate: Refers to the total number of cows that are diagnosed as
pregnant for the group being analysed. For example, this could be the whole herd, the group of animals that were given a particular treatment, or the group of cows that were inseminated or bred. Thus it can be easily confused with conception rate. When reading a report check what the definition of the terms is that is being used by the authors as each author may have a different definition for the same term cows diagnosed pregnant/ total no of cows |
|
|
In-calf rate
|
the percentage of
animals within a herd or group being analysed that are diagnosed pregnant after a specific duration of breeding eg 6 wks or 100d |
|
|
Non-return rate
|
• Non rate = % of cows that are not detected oestrus
Non-return in following insemination • Correlated with conception rate • Non-return cows are assumed to be pregnant • Used by semen suppliers to assess conception rates of different bulls and AI technicians where pregnancy rate data may not be available |
|
|
Factors affecting pregnancy rates to AI
|
• Timing of AI in relation to onset of oestrus
• Semen storage • Semen handling • Dose of semen • Sire • Insemination technique • Poor records • Fertility of cows |
|
|
Steps in cryopreservation
|
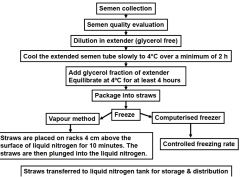
|

