![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the physiological events associated with the development of a follicular wave in cows.
|
• A rise in FSH concentrations occurs at the time of follicular
emergence (“emergence”) • As concentrations of FSH decline a single follicle will become larger than others in the developing cohort (“selection”) • This follicle becomes the largest (“dominant”) follicle • A reduction in LH pulse frequency during development of dominant follicles (negative feedback of P4 and E2 on LH secretion) can lead to atresia of the dominant follicle as it is “starved” of LH support. Secretion of E2 and inhibin from the dominant follicle will decrease, an increase in FSH secretion will occur & a new wave will start. This process occurs when concentrations of P4 >1 ng/mL. • Luteolysis results in an increase in LH pulse frequency and amplitude, an increase in concentrations of E2, positive feedback of E2 on secretion of GnRH and release of LH, resulting in an LH & FSH surge and ovulation. A secondary rise in FSH will occur 24 h after the LH surge and stimulate emergence of the first follicular wave of the next cycle |
|
|
Within what time after birth do you expect the placenta to normally be expelled?
|
<12h
|
|
|
Which one of the following endocrine changes occurring within the peripheral circulation of a cow best describes changes that occur around parturition?
a) An increase in concentrations of cortisol, a decline in plasma concentrations of progesterone, an increase in plasma concentrations of oestrogen, PGF2α and relaxin b) An increase in plasma concentrations of cortisol progesterone and cortisol, oestrogen and a decrease in concentrations of PGF2α and relaxin c) A decline in plasma concentrations of cortisol, progesterone, oestrogen, PGF2α and relaxin d) An increase in plasma concentrations of cortisol, progesterone, and oestrogen and an increase in concentrations of PGF2α and relaxin e) A decline in plasma concentrations of cortisol and oestrogen, an increase in plasma concentrations of progesterone, PGF2α and relaxin |
a)
• Parturition initiated by the foetus • Increase in foetal ACTH secretion which intern stimulates foetal cortisol production • Increase in concentrations of oestrogens prepartum • P4 decreases in last week of gestation • As oestrogen concentrations increase, stimulates release of PGF2α from uterus, & myometrial oxytocin receptors regression of CL and secretion of relaxin – softening of cervix and relaxation of pelvic ligaments • Increased PGF2α stimulates release of maternal oxytocin from posterior pituitary gland which in turn stimulates further PGF2α release by the uterus and uterine contractions |
|
|
• On average luteolysis in the bovine occurs around
which day of the oestrous cycle? a) Day 8 b) Day 10 c) Day 13 d) Day 17 e) Day 24 |
d) Day 17
|
|
|
How many follicluar waves do you normally expect to see in an oestrous cycle in a cow?
|
2 to 4 waves of follicular
development/cycle |
|
|
What is the average duration of oestrous cycles in
cows (days)? |
21 days (17 to 25), heifers often slightly shorter ie 20
days |
|
|
What is the average interval from onset of oestrus to
ovulation (hours) |
Ovulation 24 to 30 h after onset of oestrus
|
|
|
What is the expected interval from the LH surge to
ovulation (hours)? |
24 to 28 h
Onset of oestrus coincides with surge of LH and FSH |
|
|
What is the duration of oestrus in the average cow & modern dairy cow
(hours)? |
Traditionally: 18 h (12 to 30 h).
In modern dairy cow appears to be shorter averaging around 10h Tend to be shorter in cows under greater nutritional stress or with higher dry matter intakes and milk yield |
|
|
How long following calving does it normally take for uterine involution to occur in the cow?
|
30 days
|
|
|
When do cows normally resume oestrous cycles
postpartum? |
Usually within 40 days from
calving. Can be extended in certain circumstances |
|
|
The fertility of cows generally peaks at what interval
postpartum? |
60 to 90 days
|
|
|
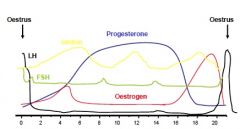
Draw an outline of the endocrine changes that occur:
a) during the oestrous cycle, and b) during pregnancy in the cow |
|

