![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gravel
|
76 mm - 2.0 mm
|
|
|
Sand
|
2.0 mm - 0.05 mm
|
|
|
Silt
|
0.05 mm - 0.002 mm
|
|
|
Clay
|
< 0.002 mm
|
|
|
Best agricultural soil is?
|
Loam
|
|
|
Composition of Loam...
|
roughly silt (40%)
sand (40%) clay (20%) No Rocks! |
|
|
How do nutrients enter plants?
|
Via the soil
|
|
|
Methods by which minerals travel into plants
|
Osmosis / Transpiration
Active transport |
|
|
Essential Elements...how many are considered essential?
|
Only 17
|
|
|
Criteria to be essential
|
Complete life cycle
Part of essential molecule Show deficiency symptoms in absence |
|
|
deficiency symptoms
|
Chlorosis Wilting Tips, Margins, interveinal Necrosis Stunting Roots or Leaves
Curling |
|
|
Macronutrients:
|
100mg per kg of dry weight of plant
>0.5% of dry weight of plant Nine elements H,C,O = 6-45% dry tissue! |
|
|
Name all nine macronutrients
|
Hydrogen (H)
Carbon (C) Oxygen (O) Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Magnesium (Mg) Sulfur (S) Potassium (K) Calcium (Ca) |
|
|
Micronutrients:
|
< 100mg per kg of dry weight of plant < 0.5% of dry weight of plant
Eight elements (7-9) |
|
|
name 8 of the micronutrients
|
Manganese (Mn)
Chlorine (Cl) Copper (Cu) Nickel (Ni) Iron (Fe) Zinc (Zn) Boron (B) Molybdenum (Mo) |
|
|
Mobility of Elements
Mobile = moved easily through plant |
Mostly transported by xylem, some phloem
Mg,P,K,N If deficient, symptoms appear where? |
|
|
mmobile = Not moved easily in plants
|
B, Fe, Ca
If deficient, symptoms appear where? |
|
|
where do elements not labeled as mobile, or immobile fall under
|
Rest of the elements lie somewhere in between with mobility
|
|
|
•Parts of cell structures / cell physiology:Calcium
|
Cell walls, membrane permeability
|
|
|
Parts of cell structures / cell physiology:Potassium
|
osmosis, opening / closing stomata
|
|
|
Parts of necessary molecules:Sulfur
|
Amino acids, disulfide bonds
|
|
|
Parts of necessary molecules: Phosphorus
|
ATP, ADP, Nucleic Acids
|
|
|
Parts of necessary molecules: Mg
|
Chlorophyll
|
|
|
Parts of necessary molecules: Nitrogen
|
Amino acids, proteins, chlorophyll
|
|
|
Magnesium / Potassium
|
enzyme activator
|
|
|
Calcium
|
regulates enzyme activity
|
|
|
Nickel, Copper, Zinc
|
activators or regulators
|
|
|
Mycorrhizae*
|
*fungus that is associated with roots
75% of plant species involved in a mycorrhizal association Mutualism . .. |
|
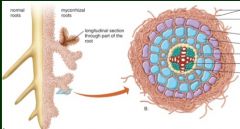
Whats happening
|
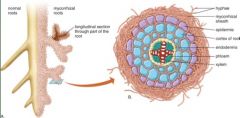
Whats happening
|
|
|
How bacterial mutualism works in roots
|
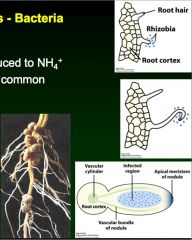
|
|
|
Regulation of Transpiration
|
Guard cells open / shut
Turgor pressure Moist surface for CO2 diffusion BUT Evaporation occurs too |
|
|
Environmental factors affect transpiration
|
Environmental factors affect transpiration
•Humidity : inverse •Air temperature : 2x every 10oC „til 30-35oC •Wind : similar •Light intensity : photosynthesis •Transpiration is greatest when ... Hot (but not too hot), windy, low humidity |
|
|
Plant Adaptations to Transpiration
|
-Time of stomata closure
-Leaf position -Trichomes -Reduced leaf area -Thick cuticle / epidermis -Sunken stomata -Leaf abscission |
|
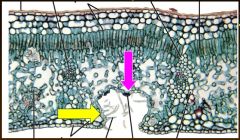
Xerophyte‟s Leaves – Extreme Adaptation to Transpiration
|
―Desert Loving‖
Reduced leaves Trichomes Sunken stomata Thick cuticle & epidermis |
|
|
•Transpiration is greatest when...
|
Hot (but not too hot), windy, low humidity
|
|
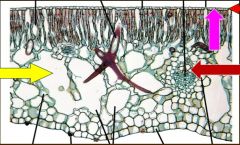
Hydrophyte‟s Leaves – Extreme Adaptation to Little Transpiration
|
―Water Loving‖
Modifications for readily-available water Large air spaces Stomata on top – if present Thin / Absent cuticle Reduced xylem |
|
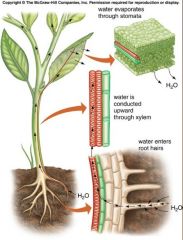
Watah turahnsporttt
|
Oh yeah
|
|
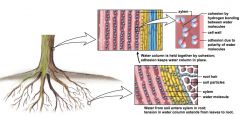
H2O molecules are slightly polar
H20 molecules adhering to xylem walls (adhesion) & each other (cohesion) = tension |
oh yeahhh
|
|

|
water molecules are slightly polar
|
|
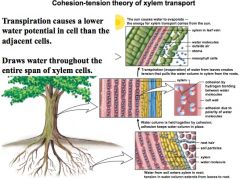
Get that shit
|
no big deal just go out and get yours
|
|
|
Transport of Organic Solutes
|
-Sugars move into assimilate stream in phloem
-Move from the source to the sink -Examples of source cells -Examples of sink cells |
|
|
Pressure-Flow Hypothesis
|
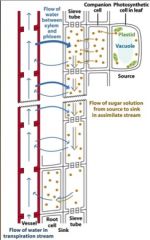
•Phloem Loading (ATP)
•Decrease H2O potential •H2O via osmosis from xylem •Passively carried •Unloaded (ATP) •Increase H2O potential •H2O via Osmosis |
|
|
What is photosynthesis?
|
Changing light energy to biochemical energy in the bonds between atoms of carbohydrates.
3CO2 + 6 H20 light---->C3H6O3 + 3O2 + 3H20 |
|
|
Light-dependent reactions (LDR)
|
-Light energy to chemical energy as ATP & NADPH
|
|
|
Light-independent reactions (LIR)
|
-Use ATP & NADPH to fix & reduce Carbon and to synthesize sugars via Calvin cycle
|
|
|
Energy of a photon is inversely/directly proportional to
wavelength of light (pick one) |
Energy of a photon is inversely proportional to
wavelength of light Greater the # of nm = Longer wavelength = less energy |
|
|
Light and Pigments
|
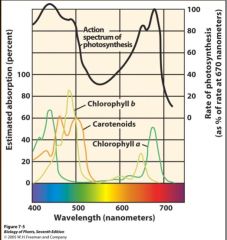
Pigments absorb some & Reflect others
Absorption Spectrum Action Spectrum Why green plants? |
|
|
Chlorophyll a
|
Ring of carbon & nitrogen
Magnesium ion Long hydrocarbon chain ALL photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms and cyanobacteria 430nm and 663nm Appears as what color? |
|
|
Chlorophyll b
|
COH not CH3
Most plants, green algae, euglenoid algae •453nm and 642nm •Appears as what color? |
|
|
Pigments in plants;Accessory pigments;Carotenoids Group
|
•All eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms &some cyanobacteria
•460 to 550nm •Carotenes Reddish-yellow Xanthophylls Yellow-brown |
|
|
Chloroplasts
|
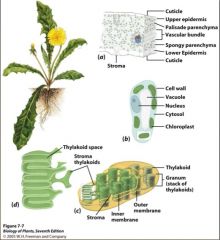
Double membrane
Stroma Grana Thylakoids •LDR occur across the thylakoid membrane •LIR occur outside the grana in the stroma |
|
|
Light-Dependent Reactions
|
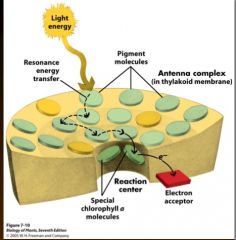
Light-Dependent Reactions
Photosystem? Thylakoid membrane 250-400 pigments -Antenna complex = pigments act as funnel -Reaction center = proteins & special chlorophyll a Converts light energy to chemical energy |
|
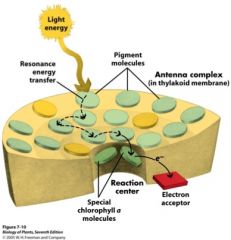
Sequence of events...
•Light energy strikes antenna pigment •Energy funneled toward reaction center •Hits special Chlorophyll a •Electron boosted & Transferred •Chlorophyll a oxidized (+) |
yo yo yo
|
|
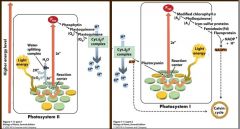
2 types of photosystems • Linked by electron transport chain
PSI = absorbs maximally at 700nm (P700) PSII = absorbs maximally at 680nm (P680) |
Yo you learn dis shit!
|
|
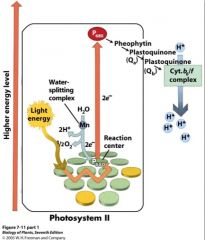
Non-cyclic electron flow
PSII •Light/ photons strike •Transfer energy to reaction center P680 •Transfer down ETC •e- from split water replace missing electrons in chlorophyll a •Proton gradient drives ATP synthesis |
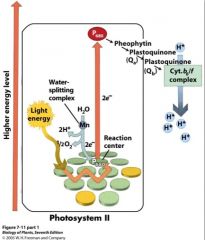
oh yeah
|

