![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the basic unit of all organisms? |
Cell |
|
|
Distinguishing characteristics of plant cells. |
Chloroplast and cell wall |
|
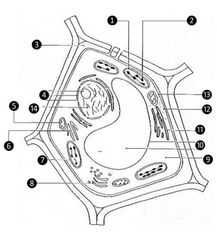
Identify the parts of a plant cell. |
1. Inner Chloroplast 2. Thylakoid 3. Cell wall 4. Nucleolus, Nuclear envelope, Nucleus 5. Mitochondria 6. Smooth er 7. Outer chloroplast 8. Golgi complex 9. Cytoplasm 10. Vacuole 11. Rough er 12. Ribosome 13. Plasma membrane 14. Chromatin |
|
|
usually composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins; functions as the boundary of the cell |
Plasma membrane |
|
|
the semi-fluid substance of a cell that is external to the nuclear membrane and internal to the cellular membrane |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
the organelle that contains the genetic information and primarily responsible for regulating the metabolism, growth, and differentiation of the cell |
Nucleus |
|
|
a double membrane-bound organelle that function in the electron transport reactions of respiration |
Mitochondria |
|
|
a double membrane-bound organelle with internal thylakoid membranes (composed of lamellae and grana in the green plants) and function mainly for photosynthesis |
Chloroplast |
|
|
a membrane-bound sac that functions in storage of compounds such as pigments, acids or ergastic substances |
Vacuole |
|
|
it is composed of interconnected phospholipid membranes and functions as the site of protein synthesis and material transport. Divided into two: |
Endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
that function as a major site of lipid synthesis and membrane assembly |
Smooth er |
|
|
which is the site of synthesis of membrane proteins and proteins to be secreted outside the cell or into the vacuoles |
Rough er |
|
|
various small bodies distributed throughout the cytoplasm; contain specialized enzymes that are bounded by a single membrane |
Microbodies |
|
|
Scientific name of onion |
Allium Cepa |
|
|
- It is the outermost layer - maintains structure - protects from mechanical damage - primarily made up of cellulose |
Cell wall |
|
|
- composed of a phospholipid bilayer - boundary |
Cell membrane |
|
|
Is the region of the cell made up of cytosol and where organelles can be found |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
Protects the genetic material and regulates the cell's function |
Nucleus |
|
|
A double membrane-bound organelle that functions in the cellular respiration |
Mitochondria |
|
|
A double membrane-bound organelle containing thylakoids that functions in photosynthesis |
Chloroplast |
|
|
Functions as storage of compounds in cells |
Vacuole |
|
|
Interconnected phospholipid membrane that functions as a site for protein and lipid synthesis |
Endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Site of protein synthesis |
Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Site of lipid synthesis |
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Various small bodies scattered around the cell containing certain enzymes. |
Microbodies |
|
|
A microbody that contains enzymes that aid in the survival of plants during hot conditions. |
Peroxisome |
|
|
A microbody that contains enzymes that aids in the breakdown of lipids to carbohydrates. |
Glyoxisome |
|
|
Sacs scattered around the cell involved in the modification of carbohydrates attached to proteins that are synthesized and packaged in the endoplasmic reticulum |
Dictyosome |
|
|
A macromolecule that synthesize proteins |
Ribosome |
|
|
depressions or thin areas of the wall |
Pits |
|
|
Is a plastid the stores starch |
Amyloplast |
|
|
is the flow of the cytoplasm inside the cell, driven by forces from the cytoskeleton. It is likely that its function is, at least in part, to speed up the transport of molecules and organelles around the cell. |
cytoplasmic streaming or cyclosis. |
|
|
represent waste products, which are solid and secondary |
Ergastic substances |
|
|
these are cells that are alive at maturity; they make up the portion of the primary plant body, characterized by having a thin-walled cell. They function in metabolic activities. |
Parenchyma cells |
|
|
parenchyma cells containing chlorophyll |
Chlorenchyma |
|
|
parenchyma cells containing air spaces produced by dissolution, separation and tearing of cortex cell wall |
Aerenchyma |
|
|
these are cells alive at maturity also and give support on young parts of the plant shoot, characterized by having elongated cells that have thicker primary walls than parenchyma cells, though the walls are unevenly thickened.They |
Collenchyma cells |
|
|
these are cells that are dead at maturity mainly function in mechanical support due to thick lignified secondary walls which contain large amounts of cellulose and lignin. |
Sclerenchyma |
|
|
are elongated cells with pitted cell walls, usually found in xylem, phloem, along leaf veins and margins, and surrounding vascular bundles in stems. |
Fibers |
|
|
are dense (lignified), short cells which may look like stones, rods, bones, stars, or branched structures. |
Sclereids |

