![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
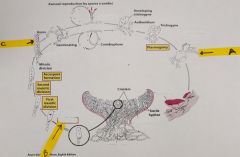
a. Whatis the ploidy of the cell labelled “A”? b. Whathas happened to prepare the cell in the circle for meiosis? (Process labelled“B”). c. Whatare the cells labelled “C” called? d. Whatis the ploidy of the cells in C above? e. Thisorganism undergoes ______?_______ meiosis. f. Thisis the life cycle of a ____?_______ |
Fungi a. n+n b. Karyogamy c. Ascospores d.1N e. Zygotic f. Ascomycete |
|
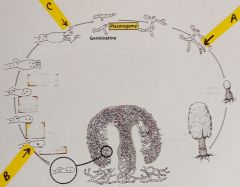
a. What termrefers to a cell with 2 nuclei as seen in the cell labelled “A”? b. Whatis the ploidy of the cell labelled “B”? c. Whatis the ploidy of the cell labelled “C”? d. Whatis the ploidy of the primary mycelium? e. Whatis the ploidy of the secondary mycelium? f. Whatis the ploidy of the tertiary mycelium? g. Thisis the life cycle of a ____?_______ |
Fungi - Mushroom a. Dikaryotic b. 2n c. 1n d. 1n e. n+n f. n+n g. Basidiomycete |
|
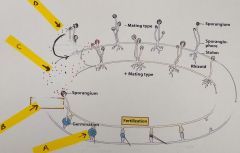
a. What is the structure labelled “A”? b. What is the ploidy of this structure? c. Is this structure involved in asexualor sexual reproduction? d. What process does arrow “B” indicate toproduce spores? e. What is the ploidy of the sporeslabelled “C”? f. Are the spores labelled “D” involvedin asexual or sexual reproduction? g. This is the life cycle of a____?_______ |
Fungi - rhizopus a. Zygospore b. 2n c. sexual d. meiosis e. 1n f. asexual g. zygomycete |
|

a. What is the structure labelled “A”? b. Is structure A male or female? What does it produce? c. What is the structure labelled “B”? d. Is structure B male or female? What does it produce? e. Are these structures part of thegametophyte or sporophyte? f. Name the organism that thesestructures belong to. |
Bryophyte- marchantia a. Archegoniophore b. Female. Eggs. c. Antheridiophore d. male. sperm. e. gametophyte f. marchantia |
|
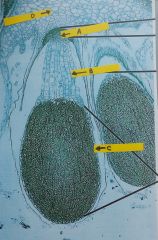
a. What is the FUNCTION of the structurelabelled “A”? b. Name the structure labelled “B”. c. Name structure “C”. What is produced in structure “C”? d. What is this entire structure? What is its ploidy? e. What is this structure growing outof? (Be specific.) f. Name this organism. |
Bryophyte- marchantia a. anchors the sporophyte to gametophyte (foot) b. seta c. capsule or sporangium. spores d. sporophyte. 2n e. archegonial tissue f. marchantia |
|

a. This organism is a: b. Identify the structure labelled “A”? c. Identify structure “B”. d. What is produced in structure “B”? What is the ploidy of structure “B”? e. Identify structure “C” (lid). f. Is this a vascular plant? g. Which is the dominant generation inthis organism?
|
Bryophyte a. moss b. Seta c. Capsule d. Spores. 1n e. operculum f. no g. gametophyte |
|
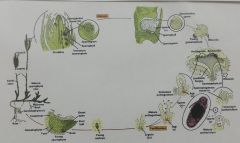
a. These are parts of a moss. Identify structure “A”. b. Identify structure “B”. c. What is structure “C”? d. What is produced in structure “D”? e. To which generation do “A” and “B”belong? |
Bryophyte - Mnium a. Archegonium b. Antheridium c. egg d. sperm e. gametophyte |
|
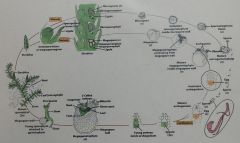
a. What is this organism? b. Is this organism homosporous orheterosporous? c. Is the gametophyte unisexual orbisexual? d. What type of stele does this organismhave? e. Does this organism have microphylls ormegaphylls?
|
Seedless vascular plants - lycopodium a. Lycopodium b. Homosporous c. Bisexual d. Protostele e. Microphylls
|
|
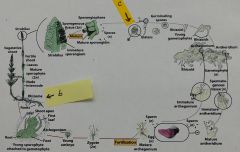
a. What is this organism? b. Is this organism homosporous orheterosporous? c. Does this organism have endosporic or exosporicgametophytes? d. Is this a vascular plant? |
Seedless vascular plants - selaginella a. Selaginella b. Heterosporous c. endosporic d. yes |
|
a. Identify this organism. b. What is a rhizome? c. What is the FUNCTION of elaters? d. What is the dominant generation? |
Seedless vascular plants - Equisetum a. equisetum b. a rhizome is an underground stem c. to ehlp disperse spores d. sporophyte |
|
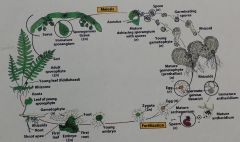
a. Does this organism have microphylls ormegaphylls? b. Does this organism have an indusium? c. Is this organism homosporous orheterosporous? d. Why are young fronds called fiddleheads? |
Seedless vascular plants - polypodium a. megaphylls b. no c. homosporous d. Because the start outcurled like a fiddle. They unfold viacircinate vernation. |
|
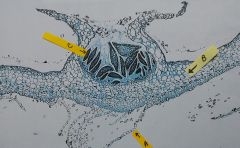
a. What is the structure labelled “A”? b. What is the structure labelled “B”? c. What is the ploidy of the tissueindicated by “B”? d. What is the function of structure “C”? e. What is the ploidy of structure “C”? f. Identify the organism. |
Bryophyte - gemma cup a. rhizoid b. thallus c. 1n d. grows into a new gametophyte e. 1n f. marchantia |
|

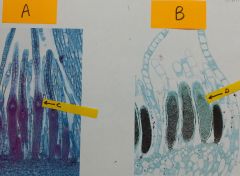
a. Whatis the ploidy of the cell labelled “A”? b. Namethe layer indicated by “B”. |
Fungi - hymenium of ascomycete a. 1n b. hymenial layer/hymenium |
|
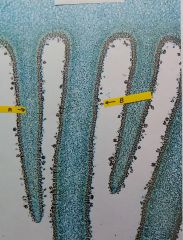
a. Name the structure labelled “A”. b. Where are this structure found? (Bespecific). c. What is the ploidy of the structurelabelled “B”? d. This is a: |
Fungi - hymenium of agaricomycotina a. gill b. underneath/underside of the pileus c. 1n d.basidiomycete
|
|

a. This is a cross section through whattype of structure? b. What is the FUNCTION of the structurelabelled “A”? c. Does this organism have leptosporangiaor eusporangia? d. What is the ploidy of the cellsindicated by “B”? e. Name the structure indicated by “C”. |
Seedless Vascular Plants - sorus a. a sorus b. To protectspores. When spores are mature, it opensand releases/expels spores c. leptosporangia d. 1n e. indusium |
|
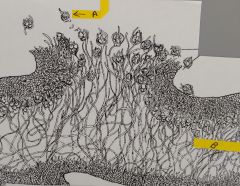
a. What is this a diagram of? b. What does structure “B” contain? c. What is the purpose of structure “A” (this should have read A, not B)? d. What is the region indicated by “B”? e. What makes up “B”? |
Fungi - lichen a. a lichen b. Soredium =Photobiont(algaor cyanobacterium) and fungal filaments. c.To produce a new lichen. d.medulla e.fungal hyphae |
|

a. What type of lichen is “A”? b. What type of lichen is “B”? c. What type of lichen is “C”? d. What tells you that “C” is the type oflichen you said it was? |
a. crutose b. foliose c. fruticose d. it has visible fruiting bodies |
|
|
Draw gametic meiosis |
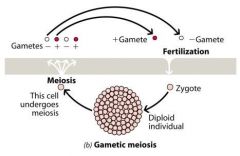
|
|
|
Draw zygotic meiosis |
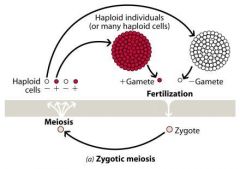
|
|
|
Draw sporic meiosis |
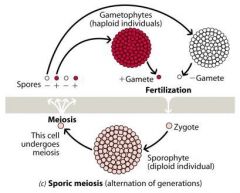
|
|
|
Haploid symbol |
N |
|
|
Diploid Symbol |
2N |
|
|
Dikaryotic symbol |
N+N |
|
|
Thecolonization of land |
big step from aquatic toterrestrial probably freshwateralgae,drying ponds problems – solutions : - support – lignin - waterloss – cuticles, stomata- gametophyte dominant – sporophyte dominant - transport – vasculartissue· why go terrestrial?: more light,CO2· bryophytes:a first step, transitional between charophytes and vascularplants· importantconcepts: macrophytic algae are in no way suited toterrestrial life, doingso changed them intoplants; bryophytescan’t stray far from their watery heritage. |
|
|
Bryophytes are a group of organisms at the transition between: |
Green algae and vascular Plants |
|
|
Which of the fallowing statements about bryophytes is FALSE? a. They lack xylem and phloem b. The cell walls of their water-conducting cells are lignified. c. they exhibit alternatiing heteromorphic generations d. the sporophyte is usually nutritionally dependent on the gametophyte e. the gametophyte is usually larger then the sporophyte. |
b. The cell walls of their water-conducting cells are lignified. |
|
|
Gemmae are multicellular structures involved in: |
Asexual reproduction |
|
|
In bryophytes, fertilization takes place in the: |
Archegonium |
|
|
Liverworts lack ______, whereas mosses and hornworts have _____. |
Stomata |
|
|
At maturity, the sporophyte of most bryophytes consists of the: |
foot, seta and capsule. |
|
|
Peat mosses belonw to the phylum______, class___________. |
Bryophyta; Sphagnidae |
|
|
What is the function of hydroids? |
Conducting water |
|
|
Which of the following is not found in the marchantia life cycle? a. thallus b. isomorphic gametes c. sporangium d. gametophyte e. zygote |
Isomorphic gametes |
|
|
The main photosynthetic pigments used in bryophytes are: |
chlorophyll a & b |
|
|
The main cell wall sugar is ____. Their main energy storage compound is ________. Bryophytes exhibit _________ meiosis, with an alternation of ___________ morphic generations |
glucose, starch, sporic meiosis, heteromorphic generations |
|
|
Which of the following statements about equisetum is FALSE? a. they produce fertile and vegetative shoots b. shoots arise from rhizomes c. the gametophyte is free-living d. they are heterosporous |
d. they are heterosporous |
|
|
In equisetum, the hollow, longitudinal channels found within the vascular bundle and formed from the disintegration of the protoxylem are called the: |
Carinal canals |
|
|
Which of the following statemetns about the fern, polypodium is false? a. the fronds are megaphylls b. it produces leptosporangia c. the gametophytes are bisexual d. sporangia are clustered in sori e. the gametophyte is the dominant generation |
e. the gametophyte is the dominant generation |
|
|
An annunus is found in? |
Ferns |
|
|
A yount fern frond is called a fiddlehead because it demonstrates circinate vernation? true of false |
True |
|
|
Which of the following has/have strobili? a. Psilotum b. Equisetum c. Polypodium d.A&B or all of the above. |
b. Equisetum |
|
|
Which of the following statements if false? Psilotum, Polypodium and equistum all; a. are homosporous b. have sori c. have bisexual gametophytes d. produce sporangia e. have rhizomes |
b. have sori |
|
|
In bryophytes the dominant generation is the __________ and in seedlesss vascular plants the dominant generation is the _________. |
Gametophyte, sporophyte |
|
|
Which of the following statements about fungi is FALSE? a. they are heterotrophic organisms b. most are multicellular c. they are more closely related to plants than to animals. d. the largest living organism may be a fungus e. only the insects have a greater number of species. |
c. they are more closely related to plants than to animals. |
|
|
By definition, an endophyte; |
lives within a plant |
|
|
coenocytic hyphae lack: |
Septa |
|
|
Karyogamy is the: |
fusion of nuclei |
|
|
Meiosis in fungi is |
Zygotic |
|
|
When two haploid nuclei do not fuse, the result is a: |
Dikaryon |
|
|
a macroscopic mass of fungal filaments is called a: |
mycelium |
|
|
In the ascomycete life cycle, meiosis takes place within a: |
Ascus. |
|
|
The layer of asci on the inner surface of an ascoma is called the: |
hymenium |
|
|
An ascoma that is open and cup-shaped is called a: |
apothecium |
|
|
mushrooms and toadstools belong to the phylum |
Basidiomycota |
|
|
The pileus is the _________ of a mushroom |
cap |
|
|
In the mushroom life cycle, karyogamy occurs in a basidium. True or false |
True |
|
|
The teleomorphic stage in fungi is the sexual stage of the life cycle True of false |
False |
|
|
A lican is formed from the mutualistic relationship between a photosynthetic member, known as the ____________, and a fungal member known as the __________. |
Photobiont, mycobiont |

