![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Function of Bones |
-Firm Framework -Protect Vital Organs -Storage for Minerals salts and fat -Blood cell production - Allows movemetn |
|
|
Diaphysis |
Shaft main Proportion |
|
|
Epipihysis |
The ends Enlarged ends Covered by a Thins layer of articular cartilage |
|
|
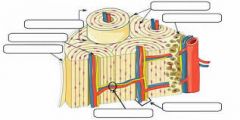
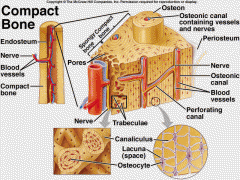
Compact bone |
hollow cylinder surrounding the cavity |
|
|
Yellow marrow storage |
cavity is used for fat strorahge of yellow marrow |
|
|
spongy bone |
more porous contain large spaces filled with red bone marrow |
|
|
Yellow Marrow |
Storage of fat |
|
|
Red bone marrow |
Blood cell production take place |
|
|
Periosteum |
Outer surface of the bone dense white fibrous covering not found in the articular cartilage |
|
|
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
cells separated from each other by large amount of non cellular material. called matrix |
|
|
matrix |
organic salt are deposited increase its rigidity and strength hardest connective tissue |
|
|
Osteons |
Units of compact bone |
|
|
Central canal |
|
|
|
Lamallae |
Surrounds the central canal concentric layers of bony matrix |
|
|
lacunae |
Between the lacunae small spaces in the martix |
|
|
canaliculi |
tiny canals that runs between lacunae |
|
|
spongy bone |
irregular arrangement of thin bony plates called trabeculae |
|
|
trabelcula |
occupied by bones cells not arrange in concentric layer |
|
|
cartilage |
connective tissue contain numerous muscle fibres made up of protein called collagen certain amount of flexibility |
|
|
chrodrin |
fibres embedded in a firm matrix of a protein- carbohydrate complex enables cartilage to function as a structural support |
|
|
Chondroblast |
firm matrix where collagen fibres are embed to spaces that contain cartilage cells gradually surrounded until trapped in a small space (lacunae) |
|
|
Chndrocytes |
Mature chondroblast when when surrounded and traped |
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage |
closely packed collagenous fibres throughout the matrix. strength and flexibility make up rings of trachea and bronchi, ends of bones |
|
|
elastic cartilage |
conspicuous elastic cartilage not closesly packed provides flexible elastic support eg outer ear |
|
|
fibrocartilage |
coarse appearance not compact can be compressed slightly intervertebral discs of the spinal column providing cushion between vertebrae |
|
|
joint |
bone to bone |
|
|
slightly movable joint |
held in place by cartilage allow slight movment joint between adjacent vertebrae |
|
|
fixed joint |
no movement occours held in place by connective tissue skull |
|
|
movable joint |
amount of movement possible is limited by ligaments, muscles, tendons and adjoining bones |
|
|
Ball-and-socket joint |
spherical heal of one bone fits into a cup like cavity of another head of humerus head of femur |
|
|
hinge joint |
elbow knee finger toes |
|
|
Pivot joint |
allows the head to rotate Radius and ulna |
|
|
gliding joint |
allows movement at any direction side to side and back and forth moveent thumb joints with palm |
|
|
condyloid |
metacarpals and phalangies |

