![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
number of cranial bones
|
8
|
|
|
|
number of facial bones
|
14
|
|
|
|
auditory ossicles
|
Malleus
Incus Stapes |
hammer
anvil stirrup |
|
|
hyoid bone
|
supports the tongue
|
|
|
|
number of cervical vertebrae
|
7
|
|
|
|
number of thoracic vertebrae
|
12
|
|
|
|
number of lumbar vertebrae
|
5
|
|
|
|
number of sacral vertebrae
|
5
|
|
|
|
number of coccygeal vertebrae
|
4 or 5
|
|
|
|
Bones of the sternum
|
manubrium
gladiolus xiphoid |
|
|
|
ribs 1-7
|
true ribs
|
|
|
|
ribs 8-12
|
false ribs
|
|
|
|
ribs 11-12
|
floating ribs
|
|
|
|
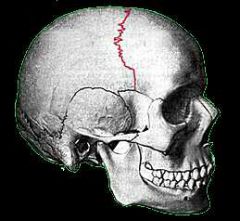
coronal suture
|
|
|
|
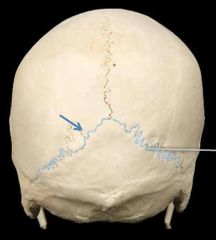
lambdoidal suture
|
|
|
|
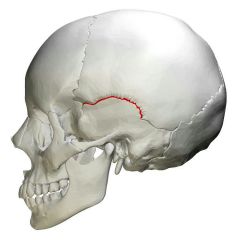
Squamosal suture
|
|
|
|
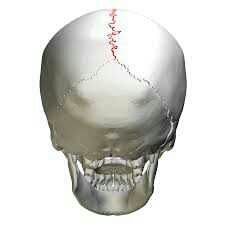
sagittal suture
|
|
|
|
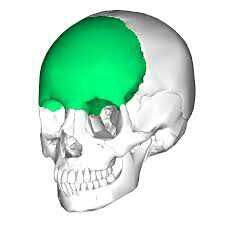
frontal
|
|
|
|
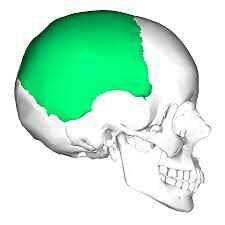
parietal
|
|
|
|
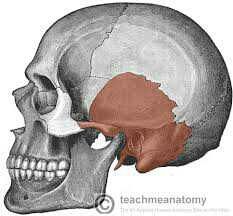
temporal
|
|
|
|
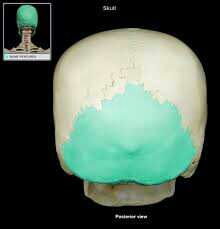
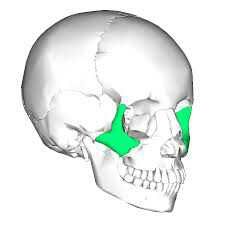
occipital bone
|
|
|
|
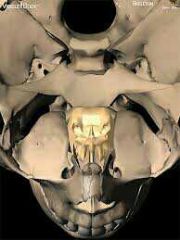
sphenoid
|
|
|
|
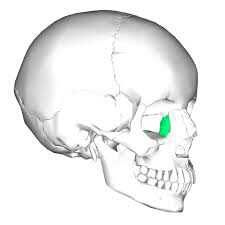
ethmoid
|
|
|
|
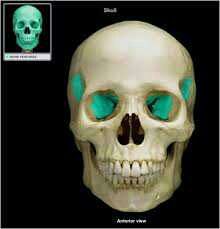
zygomatic
|
|
|
|
lacrimal
|
|
|
|
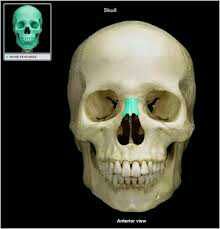
nasal bone
|
|
|
|
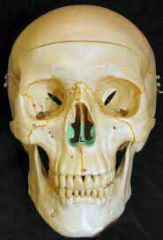
vomer
|
|
|
|
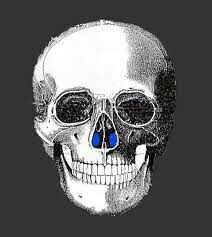
inferior nasal concha
|
|
|
|
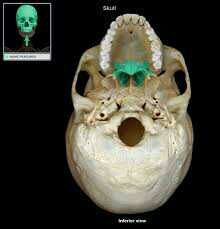
palatine
|
|
|
|
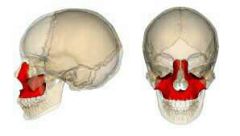
maxillae
|
|
|
|
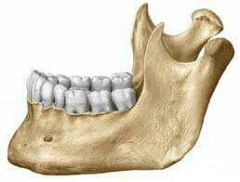
mandible
|
|
|
|
bridging bone
|
sphenoid bone
|
|
|
|
Sella turcica
|
superior landmark of sphenoid. houses pituitary gland.
|
|
|
|
optic foramen
|
allows passage of the optic nerve (cranial nerve II)
|
|
|
|
foramen rotundum
|
allows passage of the second branch of the trigeminal (cranial nerve V) conveys sensation from the teeth of maxillae.
|
|
|
|
second division road block
|
injection of anesthetic not far below foramen rotundum desensitize all of the upper teeth on one side of the maxilla.
|
|
|
|
foramen ovale
|
allows passage of the third branch of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V) that conveys sensation from the teeth of mandible.
|
|
|
|
third division nerve block
|
injection given in mandibular foramen to deaden all teeth on one side of mandible
|
|
|
|
foramen spinosum
|
opening for meningeal blood vessels
|
|
|
|
superior orbital fissure
|
allows passage of several cranial nerves
|
|
|
|
foramen lacerum
|
located between petrous portion of temporal, sphenoid, and occipital. closed off by connective tissue
|
|
|
|
crista galli
|
superior landmark of ethmoid bone, anterior attachment site for falx cerebri.
|
|
|
|
cribriform plate
|
allows passage for fibers of the olfactory nerves (cranial nerve I)
|
|
|
|
perpendicular plate
|
forms the superior part of the nasal septum
|
|
|
|
turbinates
|
nasal conchae
|
|
|
|
lacrimal groove
|
allows passage for nasolacrimal duct which drains tears into the nasal cavity
|
|
|
|
nasal septum consists of
|
perpendicular plate of ethmoid
vomer bone septal cartilage |
3 parts
|
|
|
infraorbital foramen
|
allows passage of a blood vessel and a nerve
|
|
|
|
cleft palate
|
palatine processes of the maxillae fail to join during early prenatal development.
|
|
|
|
occlude
|
align
|
|
|
|
roof of nasal complex
|
nasal bones
cribriform plates of ethmoid frontal bone sphenoid bone |
4 bones
|
|
|
floor of nasal complex
|
palatine processes of maxillae
horizontal plates of palatine bones |
2
|
|
|
walls of nasal complex
|
ethmoid
maxillae inferior nasal concha palatine bones lacrimal bones |
5
|
|
|
paranasal sinuses
|
ethmoidal
frontal sphenoidal maxillary |
lined with mucous and cilia
|
|
|
Bones of orbital complex
|
maxilla
palatine sphenoid zygomatic frontal lacrimal ethmoid |
many people see zebras falling like elephants
|
|
|
auditory ossicles
|
stapes (stirrup)
incus (anvil) malleus (hammer) |
Sims come out of your imagination
|
|
|
develop by intramembranous ossification
|
flat bones of skull
zygomatic, maxilla, mandible clavicle sesamoid bones |
|
|
|
coronal suture fuses
|
20s
|
|
|
|
sagittal and lambdoidal sutures fuse
|
40s
|
|
|
|
squamosal suture fuses
|
60s
|
|
|
|
4 spinal curves
|
cervical curvature
thoracic curvature lumbar curvature sacral curvature |
|
|
|
anulus fibrosus
|
outer fibro cartilage ring of intervertebral discs
|
|
|
|
nucleus pulposus
|
inner circular core of intervertebral discs
|
|
|
|
majority of herniated discs
|
L4/L5 or L5/S1
|
|
|
|
spinal taps
|
needle inserted into L3/L4 intervertebral space to collect spinal fluid
|
|
|
|
coccyx fuses
|
25 years
|
|
|
|
xiphoid ossification
|
age 40
|
|
|
|
rectus abdominus
|
anterior supporting muscles of the lower spine
|
|
|
|
erector spinae muscles
|
posterior supporting muscles of the spine
|
|
|
|
humerous
|
longest and largest bone of the upper extremity
|
|
|
|
funny bone
|
ulnar nerve
|
|
|
|
medial side of antebrachium
|
ulna
|
|
|
|
lateral side of antebrachium
|
radius
|
|
|
|
interosseous membrane
|
dense regular connective tissue connecting the radius and ulna
|
|
|
|
pollex
|
thumb
|
|
|
|
lateral epicondylitis
|
tennis elbow
|
|
|
|
medial epicondylitis
|
golfers elbow
|
|
|
|
colles fracture
|
fracture of distal radius resulting in silver fork deformity
|
|

