![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the functions of the skeloton |
Provide support, protect internal organs, movement, blood formation, electrolyte balance, storage of energy, detoxification |
7 |
|
|
How many bones are there In the skull |
29 |
|
|
|
How many bones In the upper limbs |
60 |
|
|
|
How many bones In the vertebral column |
26 |
|
|
|
How many bones in the thorax |
25 |
|
|
|
How many bones in the lower limbs |
60 |
|
|
|
How many bones In the pectoral girdle |
4 |
Think main regions |
|
|
How many bones in the pelvic girdle |
2 |
How many coxas are there |
|
|
Define long bone |
Hard and dense that provide strength and mobility |
Found in the arms and legs |
|
|
Where is the short bones found |
Wrist and tarsal |
|
|
|
Is there an increase In the amount of bones when there is an increase in mobility or decrease |
Increase |
When we move a lot do you need more bones or less |
|
|
Where is a flat bone found |
Between 2 layers of compact bone |
|
|
|
The pectoral girdle is an incomplete ring because it is open in the back between the |
Scapula |
|
|
|
What is the capitate apart of |
Carpals |
|
|
|
What is the capitate apart of |
Carpals |
|
|
|
Where is the trochlear notch |
Ulna |
|
|
|
The ---- divides the posterior side of the scapula into unequal portions |
Scapular spine |
|
|
|
What is your acetebelum |
The socket In your hip where the head of the femur goes |
|
|
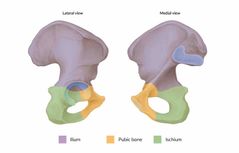
Where is the iliac crest |
The top of the ilium |
|
|
Where is the coccyx |
The blue part |
|
|
|
The pelvic girdle consists of 2 |
Hip bones |
|
|
|
Patella |
Located in a tendon over the knee |
|
|
|
Does the femur have A lateral malleolus |
No that is part of the fibula |
|
|
|
Is a cuboid part of the tarsals or the carpals |
It is one of the seven tarsal Bones |
|
|
|
Five bones that form the instep Are part of the |
Metatarsals |
Think the arch in the foot near ankle |
|
|
What is the forea Capitis apart of |
The femur |
|
|
|
What is the bone in the skull that is behind the palatine process of the maxilla and attaches to the sphenoid bone |
Palatine bone |
Roof of mouth |
|
|
What is the name of the hole in the skull called |
Foremen magnum |
|
|
|
What is the back most part of the skull called |
occipital |
|
|
|
What is a green stick fracture |
A small fracture |
|
|
|
When healing a break which comes first |
Osteoclast |
Clear |
|
|
Osteoclast |
Reobsorb broken bone |
Clear the rubble |
|
|
In healing a break what actually heals the bone |
Osteoblasts |
|
|
|
What do osteoblasts do |
They produce bone matrix to heal the bone |
|
|
|
What are the functions of foremen's |
Allow things to run through |
|
|
|
Does the Sphenoid bone have 2 bones or just 1 |
Just 1 |
|
|
|
What is the shape of a male mandible |
Broad |
|
|
|
What is the shape of the women's mandible |
Wider set |
|
|
|
Why does your vertebral column curve |
Because you are bi-pedal |
|
|
|
Is your lumbar region fused |
Not normally... Hopefully
|
|
|
|
What 2 regions In your vertebrae are fused |
Sacrum and coccyx |
The lowest regions |
|
|
How do you label your coccyx bones |
Co- 1- CO-2 |
|
|
|
What do true ribs do |
They go directly to your sternum |
|
|

What bone is this |
Atlas |
|
|
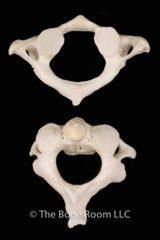
Which bone is the axis |
The bottom one |
|
|
|
Which way does the spinus process point on the vertebral bones |
Angles down |
|
|
|
Why is the Illium so broad |
because in needs to attach to a large amounts of muscles |
|
|
|
Where does the pubis Connect |
The left and right pelvis |
|
|
|
What do you sit on |
The ischium |
|
|
|
Why is the pelvic girdle wider In females |
For childbirth |
|
|
|
What are the three main regions of your foot |
The hindfoot,midfoot, and forefoot |
|
|
|
What makes our feet work |
Linear with the leg, perpendicular to the ground, No opposable Phalange, bulky heel bones underlined with fat, formation of an arch
|
Five |
|
|
What is the patella |
Forms the kneecap |
|
|
|
What age does the patella harden |
Ages 3-6 |
|
|
|
What is the pectoral girdle |
The set of bones that connect the arm on each side of the chest |
|
|
|
Which one is the pectoral Girdle a part of |
Appendicular skeleton |
|
|
|
Where is the scapula located |
Thoracic wall |
|
|
|
What is the function of scapula |
Range of motion for the shoulder at many different angles |
|
|
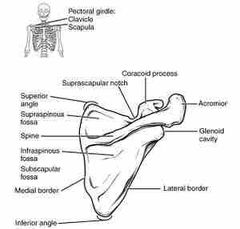
Which side and back or front |
Left scapula posterior side due the acromion clearly seen |
|
|
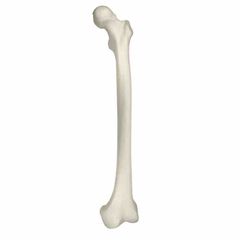
Left or right which bone and back or front |
Left femur on posterior side |
|
|
|
Which side what bone and back or front |
Right humerus and anterior view |
|
|
|
Which side on the humerus bones does the intertubicular Groove face |
Anterior side |
|
|
|
What does the ulna help p with |
Locks elbow in extension( hinge) |
|
|
|
What does the radius help with |
Circular motion how arm (twisting) |
|
|
|
On the hand which arm bone is above the pinky |
Ulna |
|
|
|
Back or front, left or right |
Posterior view of left hand |
|
|
|
What do the carpals form |
The wrist |
|
|
|
What bone have you broken when you say the medial malleoulus that directly articulates with the talus |
Tibia |
|
|
|
What metatarsal is the big toe |
#I |
|
|
|
What is the name for a small fracture |
Greenstick facture |
|
|
|
How many phalanges do you have |
56 |
|
|
|
How many phalange bones In each digit |
3 in each except for your thumbs and big toes |
|
|
|
What suture has the "lambda" shape |
The lamboloidal suture |
|
|
|
How doyou classify osteoblast when they are fully mature |
As ossified bone |
|
|
|
What is the name fora small fracture |
Greenstick facture |
|
|
|
The entire zygomatic arch is made from which 2 bones |
The temporal and zygomatic bone |
|
|
|
What is a dead giveaway you have a broken bone |
A hematoma forms ( swelling) |
|
|
|
What is a simple fracture |
The bone breaks but does not pierce the skin |
|
|
|
What is a foreman |
A hole that allows things to run through |
|
|
|
Which of the many bones in your foot create the arch |
Your metatarsal bones |
|
|
|
What is a meatus |
An opening or passageway |
|
|
|
Why are females pelvis wider |
For childbirth |
|
|
|
How many bones In Cervix and labels |
C1-C7 (7) |
|
|
|
What bone is this and why |
Coccyx because it is fused and does not have facets (tail-like) |
|
|
|
What bone is this and why |
Lumbar because of the huge body |
|
|
|
What is the pectoral girdle |
The set of bones that connect the arm on each side of the chest |
|
|
|
Where do the biceps, triceps, deltoids, and the rotator cuff attach |
To the scapula |
|
|
|
How big is the body of the cervical region |
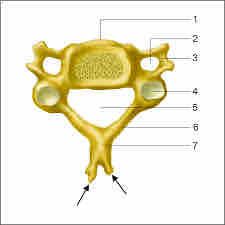
The smallest |
|
|
|
What movement |
Rotation |
|
|
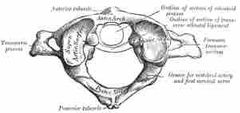
What bone is this |
The atlas |
|
|
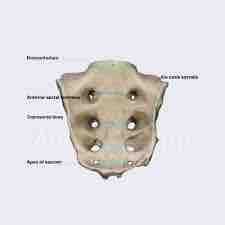
What bone is this and why |
The bones are fused so it is the sacrum also because of foremen's on the side |
|
|
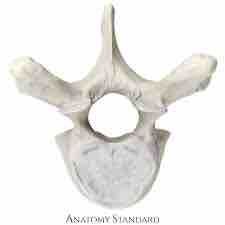
What bone and why |
Thoracic vertebrae because the larger body and facets |
|
|

What bone is this and why |
Coccyx because it is fused and does not have facets (tail-like) |
|
|
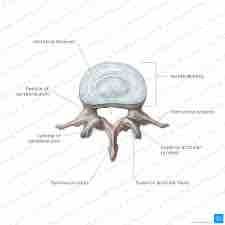
What bone is this and why |
Lumbar because of the huge body |
|
|
|
How many bones in the sacral with labels |
(5) S1-S5 |
|
|
|
How many bones In the coccyx with labels |
(4) CO1-CO4 |
|
|
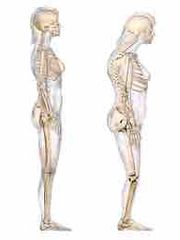
What disease is this an example of |
Kyphosis |
|
|

What movement |
Rotation |
|
|
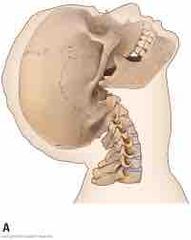
What is this |
Hyperextension |
|
|
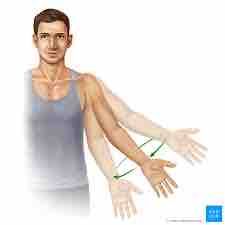
What movement is this |
Circumlocution |
|
|
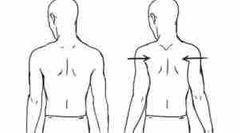
What movement is this |
Retraction |
|
|
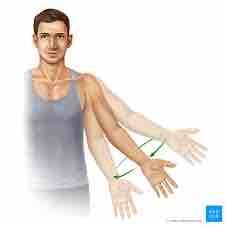
What movement is this |
circumduction |
|
|
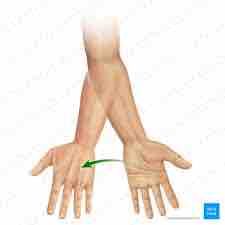
What movement is this |
Pronation |
|
|
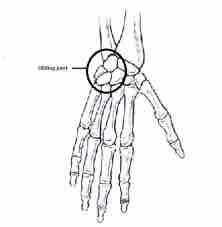
What type of joint |
Gliding |
|
|
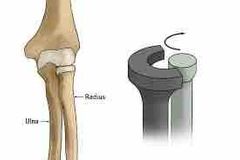
What joint |
Pivot |
|
|
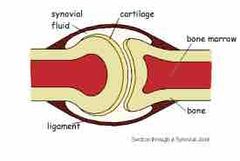
What joint |
Ball and socket |
|
|
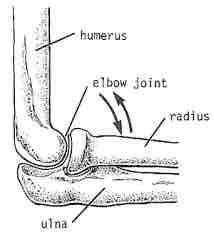
What joint |
Hinge |
|

