![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
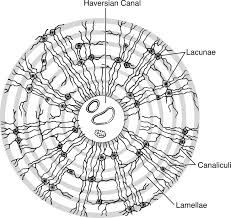
Compact Bone |
structural unit of bone = osteon
Central canal - where the blood vessels go Osteons form circular units around blood vessels. Lamella - rings of calcified extracellular matrix (like rings of a tree trunk) Lacunae - osteocytes live in spaces called lacunae between each ring of lamella Canaliculi - small canals filled with fingerlike processes (arms) of osteocytes (allows them to communicate) The canals connect lacunae with one another and with the central canal. System of interconnected canals provides routes for nutrients and oxygen to reach the osteocytes Osteons form linear to the growth of the bone. When tissue dead, central canal, lacuna, and canaliculi will be empty. |
|
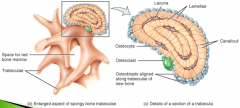
Spongy or trabecular or cancellous bone |
Does not contain osteons Trabeculae - lamella (rings of matrix) arranged in an irregular lattice of thin columns Spaces in between trabeculae are filled with red bone marrow where blood cells develop. Each trabeculae has same components of compact bone: osteocytes in lacunae, canaliculi, lamella Osteocytes recieve nourishment from surrounding bone marrow filled with blood vessels. Functions: 1. spongy bone tissue is light, reduces the overall weight of the bone 2. the trabeculae of spongy bone tissue support and protect the red bone marrow |
|
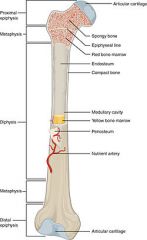
Anatomy of Long bone |
Compact bone distribution Subperiosteal bone region: covers almost outer surface of bone Subchondral bone region: at places of movement between bones (smooth and thin) Diaphysis - bones shaft or body, long cylindrical portion of the bone Epiphyses - proximal and distal ends of the bone Articular Cartilage - thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the part of the epiphysis where the bone forms an articular (joint) with another bone. (covers subchondral bone region) - Reduces friction and absorbs shock at joints. |
|
|
Anatomy of Long Bone continued... |
Spongy bone distribution: forms most of the structure of short, flat, irregular bones and the epiphyses of long bones. At ends where bones are compressed so able to shock absorb. Periosteum - Dense irregular CT that surrounds the external surface of the bone wherever it is not covered by articular cartilage. Medullary or marrow cavity - hollow, cylindrical space within the diaphysis that contains fatty yellow bone marrow. (hollow because of tension and compression strains) Nutrient foramen and canal - Near the center of the diaphysis, a large nutrient artery passes through a hole in a compact bone called the nutrient foramen. On entering the medullary cavity, the nutrient artery divides into proximal and distal branches that supply both compact bone and spongy bone. |
|
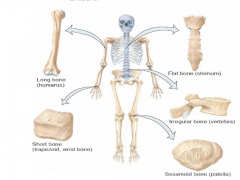
Classification of bones |
Long bone
- appendicular skeleton Short bone - cube shaped and equal in length and width Flat bone - generally thin, in cranial skull, sternum, ribs, and scapulae (shoulder blades) Irregular bone - complex shapes and can't be grouped in other categories, vertebrae, hip bones, facial bones Sesamoid bone - develop in certain tendons where considerable friction, tension, and physical stress. protect tendons from excessive wear and tear, patella (kneecaps). |
|
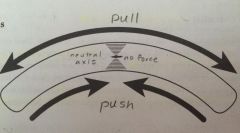
Bones in bending |
Tension and compression strains - when bending bone, pulling it apart and pushing it together at the same time It cross section a bone it will be empty because middle tissue is not necessary and better to make tissue less heavy. Bones will fail in tension (pulling) first before compression |
|
|
Bone marrow |
Red Bone Marrow - within certain bones, produces red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Yellow Bone Marrow - consists mainly of adipose cells which store triglycerides (chemical energy reserve). In newborns all bone marrow is red. With increasing age, much of the bone marrow changes from red to yellow. |

