![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
t(X;17)(p11.2;q25) - ASPL/TFE3 fusion gene
Intracytoplasmic PAS+ crystalline inclusions Spreads to lung via hematogenous route |
Alveolar soft parts sarcoma |
|
|
t(12;16)(q13;p11) - FUS-ATF1 fusion (M.C.)
t(12;22)(q13;q12) - ATF1-EWSR1 t(2;22)(q33;q12) - CREB1-ESWR1 +) Desmin, EMA, CD99, CD68 -) CD31, CD34, S100, CK |
Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma |
|
|
t(9;22)(q22;q12) - EWSR1/NR4A3 fusion
t(9;17)(q22;q11) TAF15/NRF4A3 |
Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma |
|
|
t(12;22)(q13;q12) ATF1/EWS
M.C. sarcoma of foot and ankle In aggressive cases mets to LN, liver, bone, lung in 50% +) S100, melanocytic markers |
Clear cell sarcoma |
|
|
t(11;22)(p13;q12) EWS/WT1
+) WT1 (carboxy terminus), Desmin, CK, EMA -) SMA (tumor cells, stroma +) Aggressive, most die w/in 4 yrs of dx |
Desmoplastic small round cell tumor |
|
|
t(11;22)(q24;q12) FLI1/EWS
2nd M.C. ERG/EWS Also subset with FUS (instead of EWS) |
Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET, extraosseous |
|
|
t(2;13)(q37;q14) PAX3/FOXO1 (FKHR)
t(1;13)(p36;q14) PAX7/FOXO1 (FKHR) No PAS+ crystalline inclusions Extremitites > H+N Diffuse myogenin + Worst Px |
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma |
|
|
t(X;18)(p11.23;q11) - SYT-SSX1
+) TLE1 |
Synovial sarcoma |
|
|
t(1;2)(p11;q35-37)
CSF1 rearrangements |
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor |
|
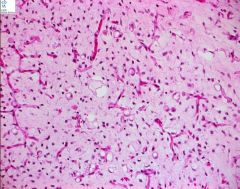
Genetic alteration? |
|
|
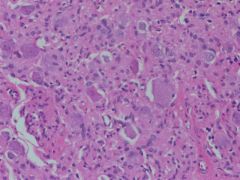
A two year old child had an abdominal mass, which was excised.
Molecular: 1p36.33 deletion, N-myc amplification, 14p deletion |
Neuroblastoma
Positive: chromogranin, synaptophysin, neurofilament and neuron-specific enolase, as well as vimentin and ALK negative: keratin, CD45, CD99 and desmin |
|
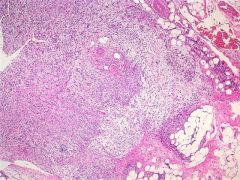
|
Nodular fasciitis
It is highly cellular and composed of plump, immature fibroblasts or myofibroblasts, with a feathery pattern due to the abundance of ground substance. The tumor cells usually have prominent nucleoli. There is often a myxoid stroma, frequent mitotic figures but no atypical forms, a lymphocytic infiltrate and red blood cell extravasation. The vasculature is usually prominent. There may be bands of collagen similar to keloid scars, or metaplastic bone. Rapid growth. |
|
The spindle cells had diffuse cytoplasmic immunoreactivity for CD68 and calponin, and were negative for S100 and pan-keratin. CD34 highlighted the blood vessels.
|
Nodular fasciitis |
|
|
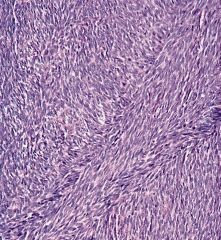
Patternless architecture of hypo- and hypercellular areas separated by thick, hyalinized collagen with cracking artifact and staghorn vesselsPerivascular sclerosis
+) CD34, CD99, EMA and Bcl-2 (1/3) -) Desmin, Keratin, S100, CD117, CD31 NAB2/STAT6 fusion |
Solitary fibrous tumor |
|
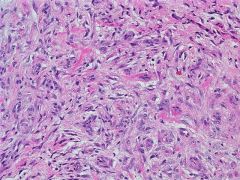
variably immunoreactive for smooth muscle actin.
|
Fibrosarcoma |
|
|
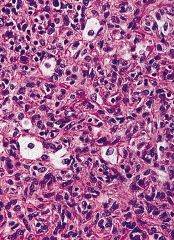
Benign fibrous histiocytoma: Polymorphous population of histiocytoid and spindled
cells, Touton giant cells and chronic inflammatory cells. |
|
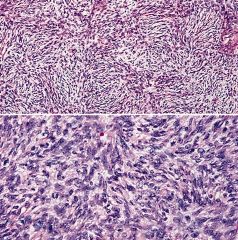
Positive stains: CD34 (strong in 95%), vimentin; also actin (focal), ApoD, bcl2, NKI-C3 (AJCP 1992;97:478), CD99
Negative stains: Factor XIIIa (usually), keratin, EMA, S100, HMB45, desmin, CD117 |
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP):
prominent storiform pattern of monomorphic fibroblast-like cells that invade into subcutis Bednar’s tumor: 5-10% of cases; pigmented variant due to dendritic cells with melanin, S100+ only in pigmented cells, HMB45 negative; associated with black patients |
|
|
Spindle cell lesion, M.C. in stomach DOG1, CD117+ KIT mutation confers sensitivity to TKi |
GIST |
|
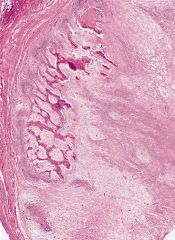
|
Myositis ossificans is a benign, ossifying soft-tissue lesion typically occurring within skeletal muscle. Patients are usually adolescents and young adults; myositis ossificans is rare in children under 10 years of age. The most frequent symptoms and signs are pain and tenderness with a soft tissue mass. Approximately 80% of cases arise in the large muscles of the extremities.
|
|
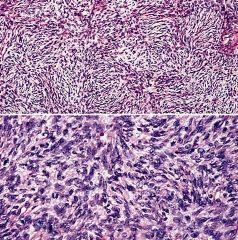
Positive stains: CD34 (strong in 95%), vimentin; also actin (focal), ApoD ,bcl2, NKI-C3 (AJCP 1992;97:478), CD99
Negative stains: Factor XIIIa (usually), keratin, EMA, S100, HMB45, desmin, CD117 |
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
|
|
|
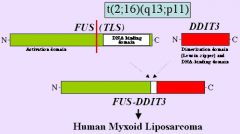
Myxoid liposarcoma
|
t(12;16)(q13;p11) FUS/DDIT3 TLS/CHOP
|
|
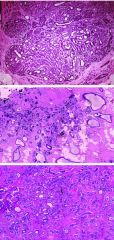
|
Paraganglioma.
Nests of polygonal tumor cells with nuclear atypia and eosinophilic cytoplasm create a Zellballen pattern. |
|
|
Spindle cell lesion Beta-catenin positive No mets potential t(17;22) CTNNB1 mutation Can be a/w FAP/Gardner's Syndrome (APC gene) |
Desmoid fibromatosis |
|
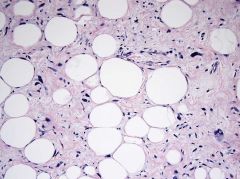
High potential for recurrence, no potential for metastasis MDM2 amplification |
Atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma |
|
|
Fibrous hamartoma of Infancy |
|
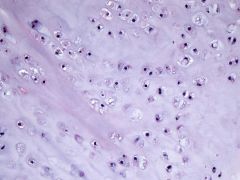
IDH1 and IDH2 |
Enchondroma/chondroma, chondrosarcoma |
|
|
Highly complex karyotype with high chromosome counts and complex structural rearrangements |
Pleomorphic liposarcoma |
|
|
Ring or giant marker chromosomes with amplification of 12q13-15 MDM2 (and freq. CDK4) |
Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma |
|
|
Abberations in chromosome 8 PLAG1 |
Lipoblastoma |
|
|
MDM2 |
ATL/WDLS Dediff Liposarc Intimal Sarcoma |
|
|
SDH-deficient A/w non-hereditary Carney Trida (this, Pulm chondroma, paraganglioma) or Carney-Stratakis syndrome (AD, this, paranganglioma) |
Epithelioid GIST (of stomach) |
|
|
M.C. soft tissue sarc. in kids and adols Primitive looking cells in various stages of development Focal to moderate myogenin IHC Anaplasia portends poor Px |
Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma |
|
|
t(11;16)(q13;p13) C11orf95/MKL2 |
Chondroid Lipoma |
|
|
ALK (2p23) with TPM3, TPM4, or CLTC Subset ROS1 instead of ALK ALK/CLTC: granular cytoplasmic ALK IHC ALK/RANBP2: paranuclear membranous ALK IHC, epithelioid morphology, poorer px (aggressive bvr and incr. mets) |
Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor |
|
|
GNAS1 |
|
|
|
Kaposi Sarcoma |
|
|
Spindle cell lesions, numberous in multiple tissue planes +) CD31, ERG, Diffuse AE1/AE3 -) CD34, EMA, Pankeratin MNF116 Retains INI1 t(7;19) SERPINE1/FOSB |
Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma |
|
|
BCOR-CCNB3 |
Round Cell Sarcoma |
|
|
USP6-CDH11 |
ABC Nodular Fasciitis |
|
|
Spindle cell lesion +) CD31, CD34, FLI1, F.VIII, ERG, CD45 t(1;3)(p36;q23-25) CAMTA-WWTR1 |
Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma |
|
|
Aka myxoid MFH one of M.C. adult sarcomas Pleomorphic spindle cells in myxoid to fibrous matrix in varying proportions Myxoid areas with curvilinear vessels |
Myxoid Fibrosarcoma |
|
|
Pathognomonic for NF1 Can undergo malignant transformation to MPNST |
Plexiform Neurofibroma |
|
|
Painful vascular/fatty lesions with fibrin thrombi |
Angiolipoma |
|
|
Types of Collagen |
I: Bone, skin II: Cartilage III: Reticular Fibers IV: Basement membrane |
|
|
Wagner-Meissner Bodies |
Diffuse Neurofibroma |
|
|
Carney Complex |
|
|
Carney Triad |
|
|
Epithelioid cells surrounded by zone of necrosis Loss of INI-1 (SMARCB-1) |
Epithelioid Sarcoma (Distal) |
|
|
t(7;16)(q34;p11) FUS/CREB3L2 MUC4 |
Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma/Evan's Tumor |
|
|
Mafucci's Syndrome |
Multiple enchondromas and (spindle cell) hemangiomas |
|
|
Ollier Disease |
Multiple enchondromas |
|
|
Epiphyseal Lesions |
|
|
|
Metaphyseal Lesions |
|
|
|
Jaw bones and ribs Biphasic tumor Hemangiopericytoma-like vascularity |
Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma |
|
|
M.C. malignant bone tumor |
Osteosarcoma |
|
|
2nd M.C. malignant bone tumor |
Chondrosarcoma |
|
|
Soap bubble appearance on imaging |
ABC Adamantinoma |
|
|
Aka Osteitis Deformans Polyostotic form: Incr. alk phos; normal ca, phos |
Paget's Disease of Bone |
|
|
Lytic metastatic bone tumors |
Kidney GI Thyroid Melanoma |
|
|
Blastic metastatic bone tumors |
Prostate |
|
|
Blastic AND lytic metastatic bone tumors |
Breast Lung |
|
|
4th M.C. primary bone tumor |
Ewing's Sarcoma |
|
|
Ossifying Fibroma |
|
|
Non-ossifying fibroma |
|
|
Giant Cell Ddx |
Non-ossifying fibroma (Metaphysis) Giant Cell Tumor (Metaphysis to Epiphysis) Brown Tumor ABC |
|
|
Herringbone pattern/cellular spindle cell ddx |
FibrosarcomaSynovial sarcomaMPNSTLeiomyosarcCellular schwannoma
|
|
|
Myxoid ddx |
Benign: Nodular fasciitis Myxoma Nerve sheath tumors: NF, NT, Schwannoma Malignant: Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarc Myxoid Fibrosarc t(9;22) Myxoid liposarc LGFMS t(7;16) CREB/FUS |
|
|
Clean geographic necrosis in sarcomas |
MPNST Ewing's/PNET t(11;22) EWS/FLI1, t(21;22) EWS/ERG Poorly diff SS |
|
|
Pseudogranulomas |
Granuloma Annulare Rheumatoid Nodule Epithelioid Sarcoma NL? |
|
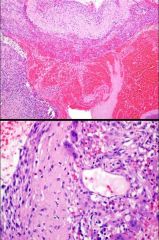
Genetic alteration?
|
USP6-CDH11 ABC |
|
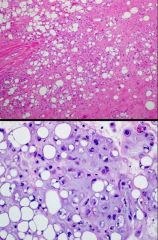
Genetic alteration?
|
C11orf95-MKL2 Chondroid lipoma |
|
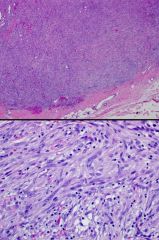
Fusion?
|
USP6/MYH9 Nodular Fasciitis |
|
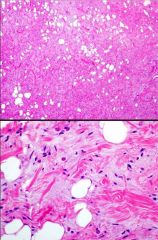
59 to M, posterior neck mass. Chromosomal abnormalities?
|
13q14 abnormalities Spindle cell/pleomorphic lipoma |
|
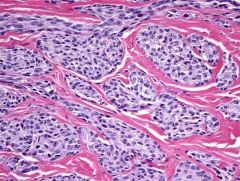
31 yo M, ankle pain. IHC + S100, HMB45; - desmin, CD34, pan-keratin, EMA. Fusion?
|
EWSR1-ATF1 Clear cell sarcoma |
|
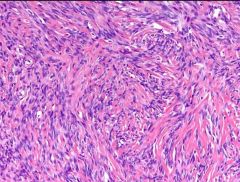
57 yo F, pleural based mass. Positive IHC?
|
STAT6 SFT |
|
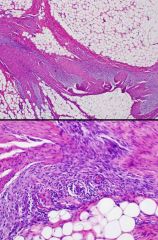
Newborn with posterior shoulder mass. |
Fibrous hamartoma of infancy |
|
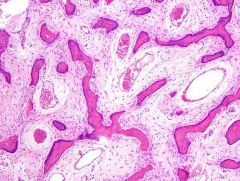
Genetic alteration?
|
GNAS |
|

|
Elastofibroma |
|
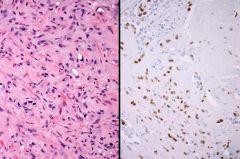
46 yo F, IHC pos for CD31 and ERG, focal CK. What is this IHC?
|
CAMTA1 Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma |
|
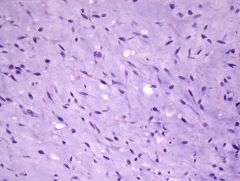
EWSR1-NR4A3 fusion
|
Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma |
|
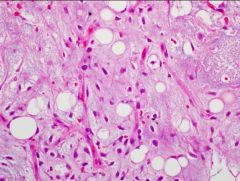
Most important predictor of unfavorable outcome?
|
Round cell compoinent >5% Myxoid liposarcoma |
|

|
Calcifying aponeurotic fibroma |
|
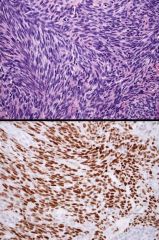
t(x;18). IHC?
|
TLE1 |
|
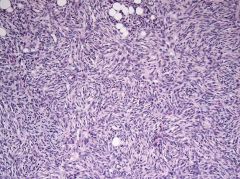
Pos for CD34. What would confirm DFSP?
|
t(17;22)(q21;q13) COL1A1-PDGFB |
|

|
Myxofibrosarcoma |
|
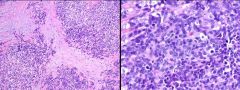
Pos for CK, Desmin. Neg for S100, CD99. EWSR1 gene rearrangement. Dx?
|
DSRCT |
|
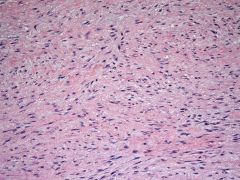
Focal pos SMA, pos nuclear B-catenin. Mutation in most sporadic tumors?
|
CTNNB1 Desmoid Fibromatosus |
|
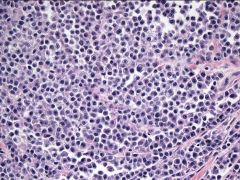
Pos for HMB45, Mart1, S100; Neg for SMA, desmin, TFE3, CD34, Pankeratin, EMA. Genetic alteration?
|
t(12;22)(q13;q12) EWSR1/ATF1 Clear cell sarcoma |
|
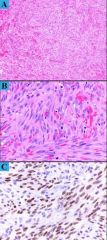
47 yo M, HIV Pos. What is IHC or ISH?
|
HHV8 Kaposi Sarcoma |
|
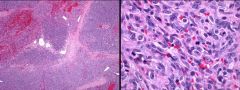
Pos CD34, CD31; Neg MDM2, HHV8, desmin, myogenin, S100, CK. Dx?
|
Angiosarcoma |
|
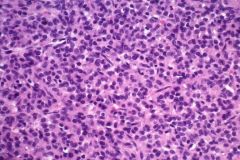
Pos KIT and DOG1; Neg CK, SMA, S100. Genetic alteration?
|
SDH-deficient, SDHB gene mutation Epithelioid GIST |
|

|
Hibernoma |
|
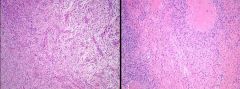
t(7;16). Confirmatory IHC?
|
MUC4 LGFMS/Evan's tumor |
|
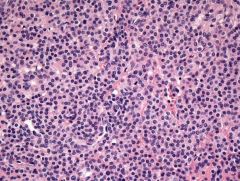
Painful nodule on digit. Pos for SMA, caldesmon; Neg for PanCK, EMA, S100, Mart1, HMB45. Dx?
|
Glomus Tumor |
|
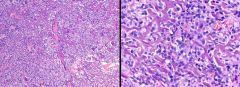
s/p chemo. Most important Px indicator?
|
>90% post-chemo necrosis Osteosarcoma |

