![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 2 main components of bone? |
Collagen fibres and Hydroxyapatite (mineral) |
|
|
What is the puroose of collagen fibres in bone? |
To hold the bone together |
|
|
What is the purpose of hydroxyapatite in bone? |
Gives the bone strength |
|
|
What are the 2 parts of long bone? |
Diaphysis and Epiphysis |
|
|
What part of the long bone is the diaphysis? |
Middle |
|
|
What part of long bone are the epiphysis? |
Ends |
|
|
What is found in the diaphysis and what is it's purpose? |
Yellow bone marrow to make the bone more bendy |
|
|
What is found in the epiphysis and what is the purpose? |
Red bone marrow to generate blood cells. |
|
|
What type of bone is the epiphysis made of and what is it's purpose? |
Spongy bone that acts as a shock absorber |
|
|
Long Bone |
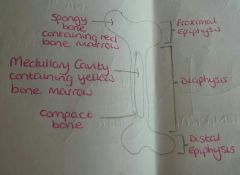
|
|
|
What is an advantage of flat bone? |
Contains lots of spongy bone so it is deformable and acts as a very good shock absorber |
|
|
What is flat bone filled with? |
Red bone marrow (in spongy bone) |
|
|
What areas of the body does flat bone cover? |
Vulnerable parts such as organs |
|
|
What is haematopoiesis? |
Production of blood cells |
|
|
Leukopoiesis occurs at a relatively constant rate. When are more white blood cells produced and released? |
When there is infection |
|
|
How does erythropoiesis increase oxygen levels? |
Low blood oxygen causes the kidneys to release erythropoietin. Erythropoietin stimulates red bone marrow to generate red blood cells. More red blood cells = more haemoglobin = increased oxygen |
|
|
What happens when an athlete injects erythropoietin? |
The erythropoietin stimulates the production of red blood cells. Blood gets thicker and blood flow slows. Causes an increased risk of DVT |
|
|
Why is cartilage different to other tissue? |
It has no blood supply or nerves |
|
|
How is the shape of cartilage maintained? |
Perichondrium. (Outer capsule made of collagen fibres) |
|
|
Name the 3 types of cartilage. |
Hyaline Elastic Fibrocartilage |
|
|
Hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage. Where is it found? |
Joints |
|
|
Where is elastic cartilage found? |
Outer part of ear |
|
|
Fibrocartilage is cartilage reinforced with collagen. Where is Fibrocartilage found? |
Makes up the discs in the back |
|
|
Name 2 types of joint. |
Fixed/Fibrous Synovial |
|
|
What is a fixed joint? |
2 bones held together by collagen fibres |
|
|
Where are fixed joints found? |
Skull |
|
|
Synovial joints |

|
|
|
What is the purpose of synovial fluid? |
To prevent friction |
|
|
What is found between 2 bones at a synovial joint? |
Articular (hyaline) cartilage |
|
|
What type of joint does arthritis affect? |
Synovial |
|
|
Osteoarthritis can be referred tp as 'wear and tear' athritis. Which parts of the body does it commonly affect? |
Back Hips |
|
|
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. What causes rheumatoid arthritis? |
Antibodies destroy articular cartilage |
|
|
Which part of the body does rheumatoid arthritis commonly affect? |
Fingers |
|
|
What causes brittle bone disease? |
Abnormalities in the genes controlling collagen production |
|
|
What causes Rickets/Osteomalacia? |
Lack of vitamin D |
|
|
Why does the body need vitamin D? |
For absorption of calcium and phosphate |
|
|
In relation to bone formation, what happens during week 8 of embryo development? |
Osteoblasts start to deposit hydroxyapatite |
|
|
Where does primary ossification occur? |
Diaphysis |
|
|
Where does secondary ossification occur? |
Epiphysis |
|
|
Where are growth plates found? |
Between diaphysis and epiphysis |
|
|
What hormone has an effect on growth plates and what effect does this have on the bone? |
Pituitary gland releases somatotropin. Increases width of growth plates = increases length of bone |
|
|
What do osteoclasts do? |
Break down bone and help give bone it's correct shape |
|
|
Is calcitonin osteo-protective or osteo-destructive? |
Osteo-protective |
|
|
Where is calcitonin produced and when is it released? |
Produced by thyroid. Released when calcium is consumed |
|
|
What effect does calcitonin have on osteoblasts? |
Causes osteoblasts to deposit calcium into bone |
|
|
Is parathyroid hormone osteo-protective or osteo-destructive? |
Osteo-destructive |
|
|
Where is parathyroid hormone produced and when is it released? |
Produced by parathyroid glands. Released when calcium levels are low |
|
|
What effect does parathyroid hormone have on osteoclasts? |
Causes osteoclasts to break down bone so calcium can be released into the blood |
|
|
There is lots of parathyroid hormone released during pregnancy. What does this cause? |
Pica - calcium craving |
|
|
What happens as a result of osteoporosis? |
Bone breaks down quicker than laid down. Bone is demineralised and more porous. |
|
|
What type of bone is most vulnerable to osteoporosis? |
Spongy bone |
|
|
Why are post menopausal women most vulnerable to osteoporosis? |
Oestrogen (osteo-protective hormone) levels plummet |

