![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe a Molecular Covalent Bond and Cmpds
|
This is a non-metal bonded to a non-metal via the sharing of electrons. The cmpds are further held tother via IMFs. These molecules will have lower MP and BPs due to weak IMFs.
|
|
|
Describe Network Solids
|
Quartz (SiO2) or Diamond (pure C) held together via covalent bonds (internally and externally - picture a lattace).
|
|
|
Describe Ionic Bonds and Ionic Cmpds
|
AKA Ionic Crystals/Crystalline Salts. A metal bonded with non-metal. Bond formed via the transfer of electrons. Very high MP and BPs. Solids don’t conduct electricity, but liquids and aq. sol’ns do.
|
|
|
Describe Metalic Bonds
|
They form metal lattices. Covalent bonds, but outer electrons are very loose. This is why metals can conduce electricity and heat. Metals are ductile (can be drawn into wires), malleable (drawn into sheets), and shiny (luster). Usually have a high MP and BP.
|
|
|
What is a Coodinate Covalent bond?
|
When one atom provides BOTH electrons for the bond. The other atom doesn’t provide any electrons. The donor is a Lewis Acid (ligand) and the receiver is a Lewis Bas (Metal Ion).
|
|
|
Which elements form diatomic gases?
|
H, N, O, F, Cl, Br, I
|
|
|
How does H violate the Octet Rule?
|
It only wants its s shell filled, it has 1 electron prefers 2 max, will make 1 bond.
|
|
|
How does Be violate the Octet Rule?
|
It only wants its s shell filled, it has 2 valance electrons which it will share to make 2 bonds.
|
|
|
How does B and Al violate the Octet Rule?
|
It has 3 valance electrons which it will share to make three bonds.
|
|
|
How do Period 3 and higher elements violate the Octet Rule?
|
They can (but don’t have to) hybrize their p with the d orbitals.
|
|
|
What specific types of molecules violate the Octet Rule?
|
Any molecule with an overall odd # of electrons (ex. NO)
|
|
|
When drawing Lewis Dot structures, which atom do you put in the center?
|
The one that can make the most bonds.
|
|
|
What is the Formal Charge and how do you calculate it?
|
Its the charge on an individual atom in a molecule. Ideally, each atom in a Lewis Dot structure should be closest to 0. Formal Charge = Normal Valence Electrons - lines and dots
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle, EDG and MG when there are _2_ Electron Domains and _0_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
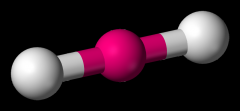
sp, 180, Linear, Linear (CO2)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _3_ Electron Domains and _0_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
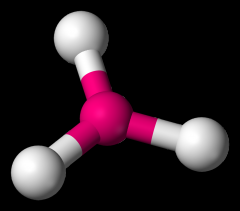
sp2, 120, trigonal planar, trigonal planar (BCl3)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _3_ Electron Domains and _1_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
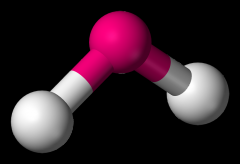
sp2, 119, trigonal planar, bent (SO2)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _4_ Electron Domains and _0_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
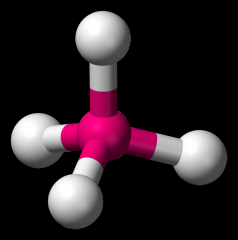
sp3, 109.5, tetrahedral, tetrahedral (CH4)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _4_ Electron Domains and _1_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
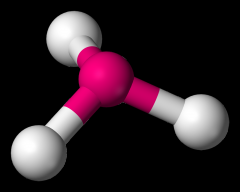
sp3, 107, tetrahedral, Trigonal pyramidal (NH3)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _4_ Electron Domains and _2_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
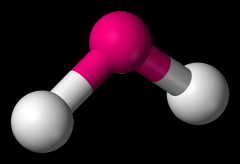
sp3, 104.5, tetrahedral, bent (H2O)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _5_ Electron Domains and _0_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
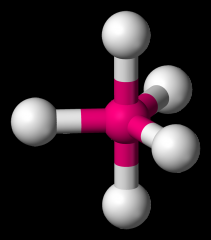
sp3d, 90/120/180, trigonal bipyramidal, trigonal bipyramidal (PCl5)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _5_ Electron Domains and _1_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
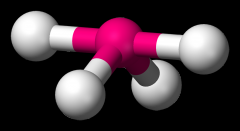
sp3d, 101.5/173, trigonal bipyramidal, see-saw (SF4)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _5_ Electron Domains and _2_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
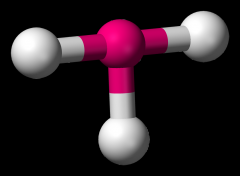
sp3d, 87.5/<180, trigonal bipyramidal, T-shaped (ClF3)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _5_ Electron Domains and _3_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
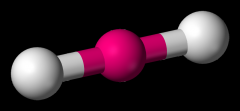
sp3d, 180, trigonal bipyramidal, linear (XeF2)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _6_ Electron Domains and _0_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
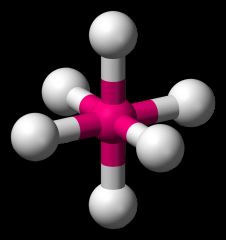
sp3d2, 90/180, octahedral, octahedral (SF6)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _6_ Electron Domains and _1_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
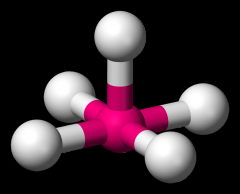
sp3d2, 85/180, octahedral, square pyramidal (BrF5)
|
|
|
Define the Hybridization, Bond Angle EDG and MG when there are _6_ Electron Domains and _2_ Non-bonding Pairs of electrons.
|
sp3d2, 90/180, octahedral, square planar (XeF4)
|
|
|
Trigonal Bipyramidal has 2 positions for electron domains. What are they and which position do lone pairs prefer to be in?
|
Axial (up and down) and Equitorial. LPs prefer to be in the Equitorial position.
|
|
|
Do bonded electron pairs or lone pairs have a greater repulsion?
|
LPs
|
|
|
What type of orbitals can be used to make a sigma bond?
|
s, p, or ANY hybrid orbital (sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d, etc.)
|
|
|
What type of orbitals can be used to make a pi bond?
|
ONLY p orbitals (sideways overlap)
|

