![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ionic Bonds |
- Metal and Nonmetal - Lattice Structure - High Melting and Boiling Points - Conducts electricity when aqueous or molten - Extremely strong Coulombic forces |
|
|
Metallic Bonds |
- High thermal and electric conductivity - Malleability - Ductility - High Melting Point |
|
|
Interstitial Alloy |
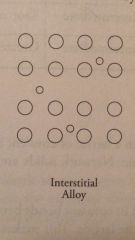
Metal atoms with two vastly different radii combine. Ex: Steel |
|
|
Substitutional Alloy |

Atoms of similar radii. Ex: Brass |
|
|
Covalent Bonds |
- Atoms share electrons Can contain single, resonance, double, and triple bonds |
|
|
Network (Covalent) Bonds |
- Lattice - Diamond and Graphite (Carbon Based) - Quartz (Silicon Based) - Poor conductors of electricity and heat - Brittle |
|
|
Coulomb's Law |
Lattice energy is inversely proportional to distance between the ion centers. Compounds with smaller ions will have stronger attractions. |

