![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epithelial Tissue |
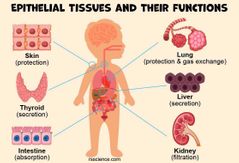
Covers surfaces or forms structures derived from body surfaces. Forms continuous sheets that contain no blood vessels. Forms: outside of the body, digestive tract, blood vessels, and other body cavities. |
|
|
Connective tissue |
Most abundant and widely distributed type of tissue in the body. Consists of cells separated from each other by the extracellular matrix. |
|
|
7 types of connective tissue |
1. Areolar - Attaches to skin and underlying tissue 2. Adipose - Fat 3. Fibrous - Tendons 4. Cartilage - Hyaline is found at on the trachea, fibro makes intervertebral disks 5. Bone - Femur 6. Blood - Vessels 7. Hematopoietic - bone marrow |
|
|
Areolar tissue |
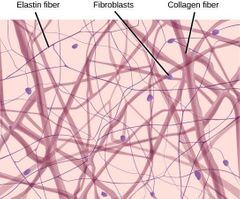
Loose tissue that consists of delicate webs of fibers and variety of cells embedded in a matrix of soft sticky gel. Contains: Protein fibers, collagen, reticulum, and elastin. |
|
|
Adipose tissue |
Fat tissue. Connective tissue that stores lipids. Insulator, protector, and energy storage. |
|
|
Fibrous connective tissue |
Made up of bundles of strong, white collagenous fibers in parallel rows. (Tendons) High strength and inelasticity. |
|
|
Cartilage |
Cartilage cells. Somewhat rigid matrix. Hyaline cartilage is found in articulating surfaces, smooth and firm. Fibrocartilage is flexible and supple. |
|
|
Bone |
Hard connective tissue that consists of living cells and mineralized matrix. Support and protect other tissues and organs |
|
|
Types of bone |
1. Long bones 2. Short bones 3. Irregular bones 4. Flat bones Cancellous bone - has spaces between the plates of the bone (spongey) Compact bone - solid |
|
|
Blood |
Matrix between the cells is liquid. Carries nutrients, oxygen, waste products, and other materials. |
|
|
Hematopoietic tissue |
Marrow cavities of bones. Also found in the spleen, tonsils, and lymph nodes. Responsible for the formation of blood cells and cells of the lymphatic system. |
|
|
Muscle tissue |
Contractile tissue. Force behind all body movement. Skeletal (voluntary, striated), cardiac (involuntary and striated), and smooth (nonstriated and involuntary). |
|
|
Nervous tissue |
Know by it's ability to conduct an electrical signal (action potential) 2 types of cells: Neurons (nerve cells) Neuroglia (support cells of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves) |

