![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomical Position: |
Erect person, arms by side, palms facing forward. |
|
|
Supine: |
Lying face up, palms up |
|
|
Prone: |
Anatomical position, face down. |
|
|
Superior (the meaning of description, and two other words for it) |
Cephalic or cranial. Towards the head.
e.g. Head superior to neck. Knees superior to ankles. |
|
|
Inferior (the meaning and other word for it) |
Caudal. Towards the tail. e.g. Pelvis inferior to stomach. |
|
|
Anterior (the meaning and other word for it) |
Ventral. Towards the front of the body. e.g. Breasts anterior to the spine. |
|
|
Posterior (the meaning and other word for it) |
Dorsal. Towards the back. e.g. Ankles are posterior to the toes. |
|
|
Proximal: |
(Usually used for limbs). Nearest from the point of attachment. e.g. the elbow is proximal to the wrist. |
|
|
Distal: |
Most distant from the point of attachment. e.g. the fingers are distal to the wrist. |
|
|
Medial: |
Towards the mid-line of the body. e.g. the nose is medial to the ears. |
|
|
Lateral: |
Away from the mid-line of the body. e.g. The ears are lateral to the lips. |
|
|
Superficial: |
Close to the surface. e.g. The skin is superficial to muscle and bone. |
|
|
Deep: |
Towards the interior/further into the body. e.g. The lungs are deeper than the ribs. |
|
|
Sagital/Median |

Runs vertically down the body, separating it into left and right parts. |
|
|
Frontal/coronal |
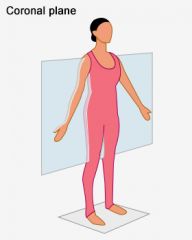
Runs vertically down the body dividing it into anterior and posterior parts. |
|
|
Transverse/Horizontal |
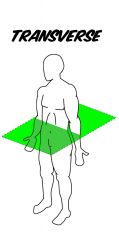
Runs parallel to the ground, dividing the body into superior and inferior portions. |
|
|
Oblique |
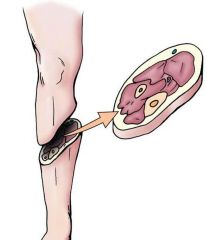
Does not run parallel to the frontal or transverse plane. |
|
|
What are the 3 cavities that the trunk of the body contains? |
1) Thoracic cavity * Diaphragm 2) Abdominal cavity 3) Pelvic cavity
Sometime cavities 2 + 3 are grouped together and called the Abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
What are the 4 subdivisions of the abdomen called? |
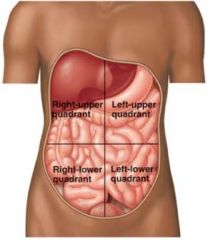
1) Right upper quadrant 2) Left upper quadrant 3) Right lower quadrant 4) Left lower quadrant
* Remember the right and left are the subjects personal right and left |
|
|
What are the 9 regions of the abdomen? |
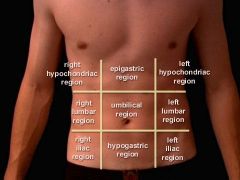
1) Right hypochondriac region 2) Epigastric 3) Left hypochondriac 4) Right lumbar 5) Umbilical 6) Left lumbar 7) Right iliac 8) Hypogastric 9) Left iliac |
|
|
Define: serous membranes |
Membranes that line the cavities in the trunk of the body, as well as covering the organs within these cavities. |
|
|
What are the 2 layers of serous membranes. |
1) Parietal - Lines trunk cavity 2) Visceral - Layer lines the organ * Serous fluid (mixture of water and proteins) fills the cavity between two layers - acting as a lubricant. |
|
|
Name 3 serous membranes - |
1) Pericardium - heart 2) Pleura - Lungs and thoracic cavity 3) Peritoneum - Abdominopelvic cavity. |

