![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cells with enlarged nuclei and perinuclear halos seen in LSIL are called what?
|
koilocytes
|
|
|
neoplasia
|
general process of new growth
|
|
|
neoplasm
|
a new growth
|
|
|
tumorigenesis
|
mechanisms underlying tumor formation
|
|
|
tumors of the squamous epithelium
|
benign - squamous papilloma
malignant - squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
tumors of the glandular epithelium
|
benign - adenoma
malignant - adenocarcinoma |
|
|
tumors of the surface epithelium
|
benign - papilloma
malignant - papillary carcinoma |
|
|
differences in benign vs malignant tumors (4)
|
differentiation, growth, local invasion, metastasis
|
|
|
What is CIN and what does it stand for?
|
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia - a ranking system for cervical cancer precursor lesions
|
|
|
what is the 3 step model of cervical carcinogenesis?
|
infection with high-risk HPV, persistence of infection with progression to a precursor lesion, invasion of surrounding tissues
|
|
|
what types of HPV are most commonly responsible for cancer?
|
16* and 18
|
|
|
describe how HPV genes extend the life of the cell
|
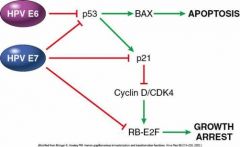
|
|
|
HPV infects what kinds of epithelial cells?
|
basal keratinocytes
|
|
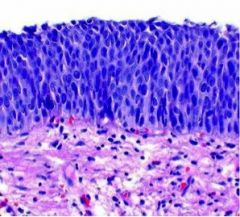
high nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio and mitotic figures are characteristic of what?
|
HSIL
|
|
|
What is the most likely outcome of any SIL
|
regression (only 1.7% progress to cancer)
|
|
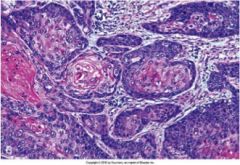
nests of tumor cells that have invaded the stroma are characteristics of what?
|
invasive squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
____________ is the most important prognostic factor in cervical cancer
|
staging
|
|
|
HSIL classifies as stage __
|
0
|

