![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
True vocal cords is covered by what cell type?
|
Stratified squamous epithelium
Small DNA viruses such as HPV can cause infxn on stratified squamous Can cause hoarseness and possible stridor |
|
|
The nose, the paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx, most of the larynx, and the tracheobronchial tree are lined with
|
pseudostratified columnar, mucus-secreting epithelium
|
|
|
in the URT stratified squamous epithelium is found?
|
in the oropharynx, laryngopharynx, anterior epiglottis, upper half of the posterior epiglottis, and vocal folds
|
|
|
The common cardinal veins of the developing embryo drain directly into?
|
The sinus venosis
|
|
|
The cardinal veins ultimately give rise to?
|
Superior Vena cava
|
|
|
The truncus arteriosis gives rise to?
|
The ascending aorta and the pulmonary trunk
|
|
|
drug intox-MI
|
Cocaine
|
|
|
drug intox-Respiratory depression
|
Benzodiazepine and barbiturates
|
|
|
drug intox-Seizures and strokes
|
Stimulants (cocaine and amphetamines)
|
|
|
drug intox-Trauma
|
PCP-induces violent behavior
|
|
|
Marker for Hodgkin's lymphoma; on Neutrophils and Reed Sternberg cells
|
CD15
|
|
|
CD16
|
surface marker found on NK cells and other cell types
|
|
|
Low levels of circulating B-cells and low levels of immunoglobulins including IgA. Predisposed to recurrent respiratory infections and persistent giardiasis
|
X-linked agammaglobulinemia
|
|
|
Number needed to harm
|
1/Attributable risk
Attributable risk=a/a+b - c/c+d |
|
|
Presentation of Neurofibromatosis type 1
Autosomal DOMINANT NF1 gene on chromosome 17 |
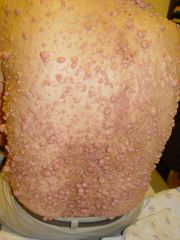
Cafe-au-lait spots
Neurfibromas (pictures) Lisch nodules in the eye Bony abnormalities-congenital pseudoarthrosis and scoliosis Associated with brain tumors |
|
|
Ectopy
|
microscopically and functionally normal cells/tissues found in an abnormal location d/t embryonic maldevelopment
|
|
|
Patchy atelectasis can be caused by?
|
Decrease in surfactant
|
|
|
Postpartum depression develops?
|
2 weeks to 12 months
|
|
|
Insulin is packaged in secretory granules with?
|
C-peptide; fromed from proinsulin in the pancreatic B-cell Golgi apparatus
|
|
|
Fetal hydronephrosis usually has a obstruction where?
|
Ureteropelvic junction; the last segment of the fetal ureter to canalize; most common site of obstruction
|
|
|
Mesonephros forms when and what are the intermediary and adult structures?
|
4th week
mesonephric (wolffian) duct Male GU components |
|
|
Metanephros forms when and what are the intermediary and adult structures?
|
5th to 6th week
forms a diverticulum call ureteric bud Collecting ducts, renal pelvis, ureters |
|
|
Glycogen degredation is coupled with skeletal muscle contraction d/t
|
Calcium mediated myophosphorylase activation. Increased calcium in the cytosol allosterically activates the phosphorylase kinase which than phosphorylates (activates) muscle phosphorylase
|
|
|
What type of test is used to determine whether there are any significant differences between the means of 2 or more independent groups
|
ANOVA (Analysis of variance)
|
|
|
Test used to check for an association between 2 categorical variables
|
Chi square
|
|
|
Pearson correlation coefficient
|
Measure of strength and direction of a linear relationship between 2 variables
|
|
|
Difference between t-test and ANOVA
|
compare the difference between the means of two groups (T-test)
ANOVA compares the difference between the means of 2 or more groups |
|
|
IL-1 function
|
secreated from macrophages; stimulates the helper T-cells to proliferate and or secrete lymphokines
|
|
|
Il-3 function
|
promotes the growth and diffenentiation of bone marrow stem cells
|
|
|
Il-5 function
|
Secreted by helper T-cells, but functions to promote B-cell IgA synthesis and eosinophil activation
|
|
|
TGF-B is involved in?
|
Tissue regeneration and repair
|
|
|
What lab value is found in Klinefelter syndrome? (male; bilateral breast enlargement, tall stature, little body hair, small testicles)
|
Increased plasma FSH also an increase in estradiol
|
|
|
What enzyme removes RNA primers during DNA replication
|
DNA polymerase I (5' to 3' exonuclease activity) which is used to excise RNA primers
|
|
|
Meconium discharge from the umbilicus
|
Persistent yolk sac
|
|
|
Incomplete obliteration of the vitelline duct
|
Meckel diverticulum
|
|
|
Hypospadias
|
urethral opening is located on the ventral surface of the penis; often associated with a downward curvature of the penis called a chordee
|
|
|
Patent urachus
|
remnant of the allantois that connects the bladder with the yolk sac during fetal development. Failure of the urachus to obliterate by birth results in a patent urachus-->urine discharge
|
|
|
What organism? HIV patient that has cough and chest pain; mucicarmine staining of bronchoalveolar fluid shows budding yeast with thick capsules
******* |
Cryptococcus neoformans (most commonly will cause meningitis-diagnosis is made by examing CSF stained with india ink)
****** |
|
|
What organism? White oral plaques
|
Candida; oral thrush is associated with diabetes, immunosupression (HIV) and tx with steroids
|
|
|
Esophagitis in an HIV patient is most commonly caused by?
|
Candida infection; presents with odynophagia (painful swallowing)
|
|
|
What bug in immunocompromised? paranasal sinusitis
|
Mucormycosis; in immnuncompromised patients and is strongly associated with diabetes mellitus and diabetic ketoacidosis
|
|
|
Double stranded DNA viruses known to be neurotropic include
|
herpesviruses and the JC papovavirus
|
|
|
Herpesvirus type-8 is associated with?
|
Kaposi sarcoma
|
|
|
During muscle contration, the labeled ATP is observed to attach to the sacromere which causes
|
myosin head detachment from the actin filament (without ATP, the muscle will be fixed in a contracted state (rigor mortis)
|
|
|
Calcium binding to troponin C...
|
shifts tropomyosin away from the myosin binding site on actin.
|
|
|
The presence of fluid in the pulmonary interstitium (possibly d/t an MI) causes...
|
Decreased lung compliance-->O2 sat is low
|
|
|
ARBs mech of action
|
Block AT-1 receptors and inhibit the effects of angiotensin II. This results in arterial vasodilation and decreased aldosterone secretion; DONT interfere with bradykinin degradation or levels; increase renin, Ag I and II
|

