![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
102 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
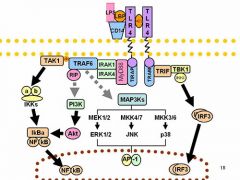
What is TLR4's signaling pathway?
|
|
|
|
Which is major IFN producing DC?
|
Plasmacytoid DC?
|
|
|
Which TLR amplify signals independently of MyD88 post PAMP recognition
|
TLR3 & 4- utilizes TBK in doing so and preferentially activates IRF 3.
|
|
|
TLR 2
|
Two TB & other mycobacteria
|
|
|
TLR4
|
CD14 (for LPS)
|
|
|
TLR5
|
Five, Flagellin, Flagellated Bacteria
|
|
|
TLR9
|
Nine, non methylated cPG
|
|
|
TLR3
|
3 is free of MyD88
|
|
|
Which are the intracellular TLR
|
3, 7, 8 and 9 and detects NA
|
|
|
What is MyD88 ?
|
An adapter protein that plays a role in TLR signalling for all TLR except TLR 3.
|
|
|
Nickel Allergy
|
Tracked to a single TLR
|
|
|
Deficiency of NEMO or IkBa results in mycobacterial susceptibility
|
Defective fn of TLR 1 & 2
|
|
|
KIR can either induce or inhibit NK fn. What is key characteristic of activating KIR
|
All activating KIR have short cytoplasmic tails.
|
|
|
TLR3 is for
|
DS RNA
|
|
|
TLR 7 & 8
|
Recognizes pharmacologics (imidiazoquinolones useful in antiviral response as well as certain ssRNA)
|
|
|
Presence of long cytoplasmic tail in a KIR receptor
|
implies presence of an ITIM motif which can facilitate inhibitory signaling.
|
|
|
In order to generate Ag receptor, developing B cells must undergo complex DNA gene rearrangements beginning with precise cutting of DNA strands and ends with imprecise joining of ends of non-homologous sequence
|
Activation induced cytidine deaminase- involved with isotype switching, otherwise RAG, surrogate light chain, and TdT are required
|
|
|
For Hyper IgM syndrome, whcih defects are AR and results in impaired somatic mutation and isotype switching
|
AID and UNG
|
|
|
In the variable domain region, three intervals of highly divergent sequences are termed..
|
CDR (separated from each other by 4 intervals of conserved framework
|
|
|
In both heavy and light chain the ____ is the direct product of VDJ joining an dlies at the center of Ag binding site
|
CDR3
|
|
|
Major source of diversity in this region is enzyme catalyzing random introduction of NT between rearranged gene semgnets
|
TdT
|
|
|
Cytokine that inducs B cellt o switch to IgE
|
IL4
|
|
|
Which Ab classes activates compliment best?
|
IgM
|
|
|
Which cannot be performed by IgA
|
binding Fc receptor on mast cells
|
|
|
What fns can IgA do?
|
Block pathogen adhesion, facilitate ADCC, mucosal transport, and neutralize toxins.
|
|
|
Which Ig has the greatest serum concentration/
|
IgG, also has longest half life and subsets
|
|
|
Largest Ig
|
Big MoMMa --IgM
|
|
|
IgA
|
invovled w/ adhesion protection, aggregates 2 units together involed in alternative complement activation
|
|
|
What are the Fc receptors for IgG
|
CD16, CD 32, and CD64
|
|
|
How do they correlate with affinity?
|
CD16, 32, and 64 a/w FcR III, FcR II, and FcR I (lowest to highest affinity)
|
|
|
What process allows same set of Ab genes to procue a soluble protein and membrane bound receptor
|
Alternative splicing
|
|
|
Which receptor downregulates IgG
|
CD32 (two-turns down) IgG
|
|
|
Stem Cell
|
CD34 +
|
|
|
Plasma Cell
|
CD 38 +
|
|
|
Interleukins HOT T BONE STEAK
|
IL-1 - pyrogen, IL-2 stimulates T cells, IL-3 Bone marrow, IL-4 simulates IgE and IL5- stimulates IgA
|
|
|
Infants are dependent on maternally derived Ab. Which immunoglobulin isotype crosses placenta during third trimester of gestation by binding to neonatar Fc receptor
|
Ig G
|
|
|
Which of the following molecules is reliably present on all developing and mature B cells and disappears only when lymphocytes terminally differentiates?
|
CD19
|
|
|
In the BM, recently arisen immature B cells express highly self-reactive Ab that may be rescued by
|
receptor editing
|
|
|
Which of the following Ig isotypes may be expressed w/o further gene rearrangement?
|
IgD
|
|
|
First gene rearrangement event in formation of Ig is joining of which two gene segments?
|
DH--> JH
|
|
|
In order for activated T cells to help B cells initiate class switching what other ligand intxn is required
|
CD40:CD40L
|
|
|
Which receptor downregulates IgG
|
CD32 (two-turns down) IgG
|
|
|
Stem Cell
|
CD34 +
|
|
|
Plasma Cell
|
CD 38 +
|
|
|
Interleukins HOT T BONE STEAK
|
IL-1 - pyrogen, IL-2 stimulates T cells, IL-3 Bone marrow, IL-4 simulates IgE and IL5- stimulates IgA
|
|
|
Infants are dependent on maternally derived Ab. Which immunoglobulin isotype crosses placenta during third trimester of gestation by binding to neonatar Fc receptor
|
Ig G
|
|
|
Which of the following molecules is reliably present on all developing and mature B cells and disappears only when lymphocytes terminally differentiates?
|
CD19
|
|
|
In the BM, recently arisen immature B cells express highly self-reactive Ab that may be rescued by
|
receptor editing
|
|
|
Which of the following Ig isotypes may be expressed w/o further gene rearrangement?
|
IgD
|
|
|
First gene rearrangement event in formation of Ig is joining of which two gene segments?
|
DH--> JH
|
|
|
In order for activated T cells to help B cells initiate class switching what other ligand intxn is required
|
CD40:CD40L
|
|
|
Which of the following Ag does not require T cell help
|
Pneumococcal polysaccharide sero3
|
|
|
XLA stops at pre-B cell
|
expression of cytoplasmic mu heavy chain
|
|
|
What unique process allows B cells to enhance specificity and affinity of Ag receptors
|
Somatic hypermutation
|
|
|
APC have PAMP recognition receptors divided into 3 groups
|
(secreted, opsonized, MASP), endocytic, and signaling/TLR
|
|
|
Mnemonic for Classic Complement
|
C1 cleaves C4 binds to bacterial surface then cleaves C2- C1C4b2aC3
|
|
|
Selectins
|
Selectins are plasma membrane carbohydrate-binding adhesion molecules that mediate an initial step of low-affinity adhesion of circulating leukocytes to endothelial cells lining postcapillary venules (Table 3-1). The extracellular domains of selectins are similar to C-type lectins, so called because they bind carbohydrate structures (the definition of lectins) in a calcium-dependent manner. Selectins and their ligands are expressed on leukocytes and endothelial cells.
Body_ID: P003006 Two types of selectins are expressed by endothelial cells, called P-selectin (CD62P) and E-selectin (CD62E). P-selectin, so called because it was first found in platelets, is stored in cytoplasmic granules of endothelial cells and is rapidly redistributed to the surface in response to microbial products, cytokines, histamine from mast cells, and thrombin generated during blood coagulation. E-selectin is synthesized and expressed on the endothelial cell surface within 1 to 2 hours in response to the cytokines interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and microbial products such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We will discuss IL-1, TNF, and LPS in our discussion of inflammation in Chapter 4. The ligands on leukocytes that bind to E-selectin and P-selectin on endothelial cells are complex sialylated carbohydrate groups related to the Lewis X or Lewis A family, present on various surface glycoproteins of granulocytes, monocytes, and some previously activated effector and memory T cells. The best defined of these is the tetrasaccharide sialyl Lewis X (sLeX). A leukocyte membrane glycoprotein called P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) is post-translationally modified to display the carbohydrate ligands for P-selectin. Several different molecules may display the carbohydrate ligands for E-selectin, including the glycoproteins PSGL-1 and E-selectin ligand 1 and some glycolipids. |
|
|
What are the two integrins?
|
In the immune system, the most important integrins are two that are expressed on leukocytes, called LFA-1 (leukocyte function-associated antigen 1, more precisely named β2αL or CD11aCD18) and VLA-4 (very late antigen 4, or β1α4, or CD49dCD29) (see Table 3-1).
|
|
|
Know the interactions of LFA-1
|
One important ligand for LFA-1 is intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1, CD54), a membrane glycoprotein expressed on cytokine-activated endothelial cells and on a variety of other cell types, including lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages, fibroblasts, and keratinocytes. The extracellular portion of ICAM-1 is composed of globular domains that share some sequence homology and tertiary structural features of domains found in immunoglobulin (Ig) molecules and are called Ig domains. (Many proteins in the immune system contain Ig domains and belong to the Ig superfamily, which is discussed in more detail in Chapter 5.) LFA-1 binding to ICAM-1 is important for leukocyte-endothelial interactions (discussed later) and T cell interactions with antigen-presenting cells (see Chapter 6). Two other Ig superfamily ligands for LFA-1 are ICAM-2, which is expressed on endothelial cells, and ICAM-3, which is expressed on lymphocytes.
|
|
|
Know interactions for VLA-4
|
VLA-4 binds to vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1, CD106), an Ig superfamily protein expressed on cytokine-activated endothelial cells in some tissues, and this interaction is important for leukocyte recruitment into inflammatory sites. Other integrins also play roles in innate and adaptive immune responses. For example, Mac-1 (β2αm, CD11bCD18) on
|
|
|
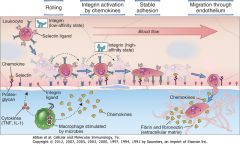
How are leukocytes recruited?"
|
SIP of wine-- selectins (L-selectins), then integrins (LFA-1 and VLA-4)
|
|
|
Which TCR hypervariable loop has greatest variability and is able to contact peptide presented in MHC
|
CDR3
|
|
|
Where do superantigens bind
|
Superantigens link to specific TCR V beta to the MHC and thus avoid need for specificity.
|
|
|
Invariant chains
|
Facilitates the loading and deliver of class II MHC
|
|
|
What transcriptional factor is used to distinguish Th1 cells?
|
Tbet
|
|
|
Which is txn factor essential in distinction of Th2 cells
|
GATA3
|
|
|
What are the CD markers that differentiate central vs effector memory cells
|
CD markers for central vs. effector memory T cells:
Central memory T cells: CD45RA-, CD27+, CCR7+, CD62L+ Effector memory T cells: CD45RA-, CD27-, CCR7-, CD62L |
|
|
What defines invariant NK cells
|
Specifically utilize Va24, Ja18, and Vb 11 to generate their T cell receptor
|
|
|
Which is the costimulatory receptor ligan that promotes the activation of T-cells
|
CD28 on T cells and CD86 on APC.
|
|
|
What represents receptor ligand pairing that results in inhibition
|
PD-1 on T cells and B7-H1 on APC. CD86 on T -cells and CTLA-4 on APC.
|
|
|
Discriminate LAD 1 and LAD 2
|
LAD type 1 is a problem of PMNs binding to integrins (LAF-1). Integration (tight adhesion) is the second phase of the PMN recruitment (see the "SIP" mnemonic above). LAD type 2 is a problem of PMNs binding to selectins. Selection ("rolling") is the first phase of the PMN recruitment (see the "SIP" mnemonic above).
|
|
|
Which TCR hypervariable loop has greatest variability and is able to contact peptide presented in MHC
|
CDR3
|
|
|
Where do superantigens bind
|
Superantigens link to specific TCR V beta to the MHC and thus avoid need for specificity.
|
|
|
Invariant chains
|
Facilitates the loading and deliver of class II MHC
|
|
|
What transcriptional factor is used to distinguish Th1 cells?
|
Tbet
|
|
|
Which is txn factor essential in distinction of Th2 cells
|
GATA3
|
|
|
What are the CD markers that differentiate central vs effector memory cells
|
CD markers for central vs. effector memory T cells:
Central memory T cells: CD45RA-, CD27+, CCR7+, CD62L+ Effector memory T cells: CD45RA-, CD27-, CCR7-, CD62L |
|
|
What defines invariant NK cells
|
Specifically utilize Va24, Ja18, and Vb 11 to generate their T cell receptor
|
|
|
Which is the costimulatory receptor ligan that promotes the activation of T-cells
|
CD28 on T cells and CD86 on APC.
|
|
|
What represents receptor ligand pairing that results in inhibition
|
PD-1 on T cells and B7-H1 on APC. CD86 on T -cells and CTLA-4 on APC.
|
|
|
Discriminate LAD 1 and LAD 2
|
LAD type 1 is a problem of PMNs binding to integrins (LAF-1). Integration (tight adhesion) is the second phase of the PMN recruitment (see the "SIP" mnemonic above). LAD type 2 is a problem of PMNs binding to selectins. Selection ("rolling") is the first phase of the PMN recruitment (see the "SIP" mnemonic above).
|
|
|
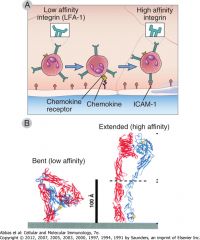
How are integrins upregulated
|
|
|
|
Describe the steps of migration
|
|
|
|
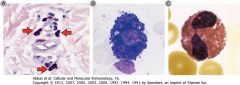
What is the morphology of mast cell,basophil and eosinophil
|
|
|
|
In a patient s/p honeybee sting, the absence of venom specific IgE indicates that..
|
this is not an IgE mediated reaction
|
|
|
Elevated b/l level of total tryptase suggests
|
systemic mastocytosis; typically mature trptase level will be low.
|
|
|
How can one distinguish between basophil and mast cell lineage
|
Notably the low levels of Kit exists before comitting to specific lineages then Kit expression stops unless they delineate to mast cells wherein expression of Kit increases as they mature.
|
|
|
How are integrins differentiated?
|
The β1-containing integrins are also called VLA molecules. VLA ("very late antigens") received their name because α1β1 and α2β1 were expressed on T cells 2 to 4 weeks after repetitive stimulation in vitro in the early experiments.
The β1 integrins are also called CD49a-fCD29. CD49a-f refers to different α chains (α1 to α6). CD29 refers to the common β1 subunit. |
|
|
What constitutes the LFA-1 family?
|
The β2 integrins are also known as the LFA-1 family or CD11a-cCD18. CD11 refers to different α chains and CD18 to the common β2 subunit. LFA-1 is also called CD11aCD18.
|
|
|
What are the other members of the b2 subunit family?
|
her members of the LFA-1 family include CD11bCD18 (Mac-1 or CR3) and CD11cCD18 (p150,95 or CR4), both of which have the same β subunit as LFA-1.
|
|
|
Describe the cell lineage of various immunocytes
|
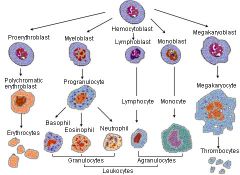
|
|
|
Describe the cell lineage of various immunocytes
|
|
|
|
Describe MBP
|
Makes 1/2 of eosinophil granule protein; cytotoxic to parasites similar to EDN and ECP. Notably capable of trigerring histamine release from mast cells and basophils
|
|
|
What are some other mediators found in eosinophil specific granulse?
|
EDN, ECP, EPO
|
|
|
What are some cytokines/chemokines produced by eosinophils
|
IL-2, IL6, IL8, GM-CSF, TNF, TGF
|
|
|
What is the most potent chemoattractant
|
Eotaxin -2
|
|
|
Eosinophils migrating to tissues respond to :
|
Eotaxin (CCL11/CCL24) and RANTES (CCL5)
|
|
|
Receptors for IL-3, IL-5 and GM-CSF shares a common ___ chain
|
beta; all stimulate eosinophil devpt
|
|
|
Describe the cell lineage of various immunocytes
|
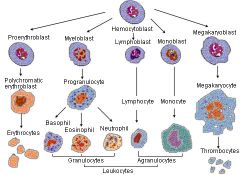
|
|
|
What are the newly generated cell mediators?
|
leukotrienes and prostaglandins (Eicosanoids are signaling molecules made from the oxygenation of 20 - C essential FA)
|
|
|
What are some preformed mediators secreted from mast cells
|
histamine, serine proteases (tryptases), TNF, proteoglycans (such as heparin) and serertonin
|
|
|
What are some important newly formed mediators
|
PGD2, LTC4, PAF, IL-4
|

