![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
196 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the Ag/Ab makeup of Blood Group A?
|
A Ag on RBC surface
B Ab in plasma |
|
|
What is the Ag/Ab makeup of Blood Group B?
|
B Ag on RBC surface
A Ab in plasma |
|
|
What is the Ag/Ab makeup of Blood Group AB?
|
A and B Ag's on RBC surface
No Ab's so "universal recipient" |
|
|
What is the Ag/Ab makeup of Blood Group O?
|
Neither A or B Ag on RBC surface
Both Antibodies in plasma "universal donor" |
|
|
What is Rh blood stuff? significance?
|
Rh+ has the Ag
Rh- doesn't have the Ag Rh- mom w/ Rh+ child: if mom is exposed to kid's blood then she can develop a anti-Rh igG that can cross placenta and cause hemolytic disease of newborn |
|
|
Why don't A and B antibodies cause fetal problems?
|
they're IgM and can't cross placenta
|
|
|
What does a spherocyte indicate?
|
Hereditary Spherocytosis
Autoimmune hemolysis |
|
|
What does an elliptocyte indicate?
|
Hereditary Elliptocytosis
|
|
|
What does a macro-ovalocyte indicate?
|
megaloblastic anemia
marrow failure |
|
|
what else is characteristic of megaloblastic anemia?
|
Hypersegmented PMN's
|
|
|
What do helmet cells and schistocytes indicate?
|
DIC
TTP/HUS Traumatic Hemolysis |
|
|
What does a bite cell indicate?
|
G6PD Def
|
|
|
What does a tear-drop cell indicate?
|
Myeloid Metaplasia w/ myelofibrosis
|
|
|
What does an Acanthocyte (spur cell) indicate?
|
Spiny appearance in liver disease and abetalipoproteinemia
|
|
|
What does a Target Cell indicate?
|
HbC disease
Asplenia Liver Disease Thalassemia |
|
|
what does a Burr Cell indicate?
|
TTP/HUS
|
|
|
What does Basophilic stippling indicate?
|
Thalassemias
Anemia of chronic disease Iron Def anemia Lead poisoning |
|
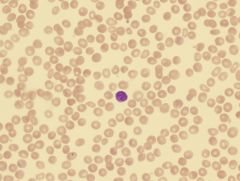
what is this?
|
Spherocytosis
sphere shaped cells, reduced pallor |
|
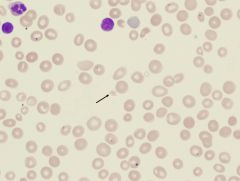
what is it
|
schistocyte
|
|
what is it
|
tear drop cell
|
|
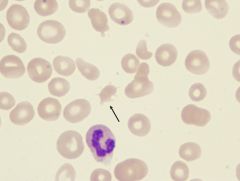
what is it
|
acanthocyte
|
|
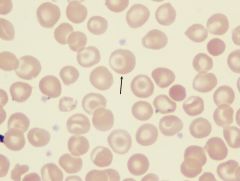
what is it
|
target cell
|
|
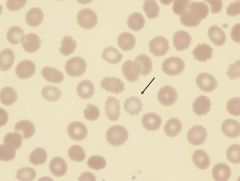
what is it
|
burr cell (echinocyte)
|
|
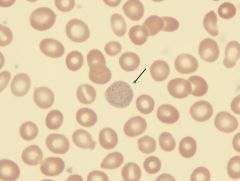
what is it
|
basophilic stippling
|
|
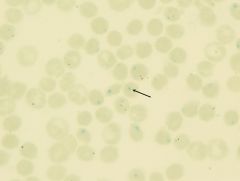
what is it
|
heinz bodies
|
|
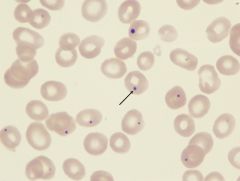
what is it
|
howell jolly body
|
|
|
What causes a Heinz body to form?
|
Oxidation of iron from ferrous to ferric form leads to denatured hemoglobin precipitation and damage to RBC membrane
|
|
|
What happens to heinz bodies?
|
bitten out by macs--->bite cells
|
|
|
When do you see Heinz bodies?
|
Alpha-Thalassemia
G6PD Def |
|
|
What are Howell Jolly bodies?
|
Basophilic nuclear remnants found in RBC's
|
|
|
When do you see Howell-Jolly Bodies?
|
hyposplenia
asplenia |
|
|
3 main types of Anemia?
|
Microcytic, hypochromic (mcv <80)
Macrocytic: mcg > 100 Normocytic, normochromic |
|
|
Causes of Microcytic, hypochromic anemia?
|
Iron Def
Thalassemias (w/ target cells) Lead Poisoning Some sideroblastic anemias |
|
|
labs w/ iron def anemia?
|
dec serum iron
Inc TIBC dec ferritin |
|
|
What causes macrocytic anemia?
|
Megaloblastic = b12/folate def
Drugs that block DNA synthesis (sulfa's, phenytoin, AZT) Marked reticulocytosis (bigger than mature RBC's) |
|
|
Which is associated w/ neurological sx's, b12 of folate def?
|
B12 def
|
|
|
Causes of Normocytic Normochromic anemia?
|
Acute Hemorrhage
Enzyme Defects RBC Membrane defects Bone marrow disorders Hemoglobinopathies Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Anemia of Chronic Disease |
|
|
what enzyme defects lead to Normocytic Normochromic anemia?
|
G6PD def (x-linked)
PK def (auto rec) |
|
|
example of a membrane defect --> Normocytic Normochromic anemia?
|
hereditary spherocytosis
|
|
|
example of bone marrow disorder --> Normocytic Normochromic anemia?
|
aplastic anemia
leukemia can present w/ macrocytic sometimes |
|
|
Lab values associated w/ Anemia of Chronic Disease?
|
Dec TIBC
Inc Ferritin Inc storage iron in marrow macrophages |
|
|
Labs that indicate RBC hemolysis?
|
dec serum haptoglobin (binds free hemoglobin)
Inc serum LDH |
|
|
Test to distinguish between immune and non-immune mediated RBC hemolysis
|
Direct Coombs
positive = immune mediated |
|
|
What do defects in the synthesis of hemoglobin lead to?
|
microcytic, hypochromic anemia
|
|
|
What are 4 etiologies that disrupt normal hemoglobin synthesis and thus lead to microcytic, hypochromic anemia? how do they screw w/ hemoglobin synthesis?
|
Iron Deficiency Anemia (dec heme sythesis)
Anemia of Chronic Disease (dec release of iron to transferrin) Thalassemias (mutations-->dec globin synthesis) Lead poisoning (inhibits ferrochelatase and ALA dehydrase) |
|
|
What are the porphyrias related by?
|
Specific enzymes needed for heme synthesis are defective--->accumulation of intermediates
|
|
|
Who are the 3 most "important" diseases affecting heme sythesis?
|
Lead Poisoning
Acute Intermittent Porphyria Porphyria cutanea tarda |
|
|
What enzyme is defective in Lead Poisoning and what does the defect cause to accumulate?
|
Ferrochelatase---> inc Coproporphyrinogen
AND ALA-dehydratase---> inc ALA |
|
|
What enzyme is defective in Acute Intermittent Porphyria and what does the defect cause to accumulate?
|
Uroporphyrinogen I Synthase---> inc Porphobilinogen and delta-ALA
|
|
|
What enzyme is defective in Porphyria Cutanea Tarda and what does the defect cause to accumulate?
|
Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase----> Inc Uroporphyrin (tea colored)
|
|
|
Sx's of heme synthesis defects?
|
the 5 P's
Painful Abdomen Pink Urine Polyneuropathy Psychological Disturbances Precipitated by drugs |
|
|
ok...so what are the steps to Hemoglobin Synthesis?
|
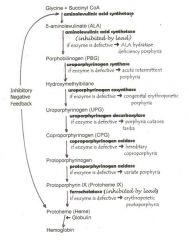
|
|
|
What is Ferritin?
|
Primary Iron Storage protein of body
|
|
|
What is Transferrin?
|
transports iron in blood
|
|
|
what is TIBC?
|
Indirectly measures transferrin
|
|
|
Lab Values for Iron Deficiency anemia?
|
Dec Serum Iron
Inc Transferrin/TIBC Dec Ferritin Dec % transferrin saturation (serum Fe/TIBC) |
|
|
Lab Values for Anemia of Chronic Disease
|
Dec Serum Iron
Dec Transferrin/ TIBC*** Inc Ferritin |
|
|
Lab Values for Hemochromatosis?
|
Inc serum iron
Dec Transferrin (TIBC) Inc Ferritin Way Inc % Transferrin (serum Fe/TIBC) |
|
|
Lab Values for Pregnancy/OCP use?
|
Normal Serum Fe
Inc Transferrin/TIBC Dec % Transferrin saturation |
|
|
What is Aplastic Anemia? general cause?
|
Pancytopenia (severe anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
Caused by failure/destruction of multipotent myeloid stem cells--->decreased production/release of mature cell lines |
|
|
Etiologies of Aplastic Anemia?
|
Radiation
Benzene Chloramphenicol Alkylating Agents Antimetabolites Viral agents Fanconi's Idiopathic |
|
|
What viruses can cause Aplastic Anemia?
|
Parvovirus B19
EBV HIV |
|
|
Sx's of Aplastic Anemia?
|
Fatigue
Malaise Pallor purpura mucosal bleeding Petechiae Infection |
|
|
Dx of aplastic anemia?
|
Bone marrow Bx showing hypocellular BM w/ fatty infiltration
|
|
|
Rx of Aplastic Anemia
|
Remove offending agent
Immunosuppression Allogenic BM Transplant RBC and Platelet Transfusions G-CSF and GM-CSF |
|
|
What are G-CSF and GM-CSF?
|
Granulocyte and Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
|
|
|
Main 3 Blood dyscrasias?
|
Sickle Cell Anemia
alpha-Thalassemia beta-Thalassemia |
|
|
Etiology of Sickle Cell Anemia?
|
HbS mutation in Beta chain of glutamic acid--->valine
|
|
|
Hetero vs Homo-zygote Sickle Cell pts?
|
Hetero = sickle cell trait
homo = Sickle cell anemia |
|
|
Benefit of sickle cell trait?
|
malaria resistance
|
|
|
Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia?
|
Aplastic Crisis
Autosplenectomy INc risk of encapsulated organism infection Salmonella osteomyelitis Painful crisis (vaso-occlusive) Renal Papillary Necrosis Splenic sequestration crisis |
|
|
What causes aplastic crises in sickle cell pts?
|
Low O2
Dehydration |
|
|
2 conditions that precipitate sickling?
|
Low O2
Dehydration |
|
|
Rx for Sickle Cell anemia?
|
Hydroxyurea---> inc HbF
Bone Marrow Transplant |
|
|
How does HbC come in to play w/ Sickle Cell?
|
HbC is a different beta-chain mutation---> milder disease than an HbSS pt
|
|
|
Cause of alpha-Thalassemia?
|
We should have 4 alpha-globin genes. alpha-thalassemias have between 1 and 4 alpha-gene mutations
|
|
|
2 main types of alpha-thalassemias?
|
beta4-tetramers have 3 alpha-chain mutations
gamma4 tetramers has 4 alpha chain mutations (all of them) |
|
|
What does gamma4 alpha-thalassemia result in?
|
Hydrops Fetalis
Intrauterine Fetal Death |
|
|
What is beta-thalassemia? types? causes?
|
Mutations in splicing sites and promoter sequences
in Minor (hetero), the beta chain is underproduced in Major (homo), the beta chain is absent in both cases HbF is increased, but not enough |
|
|
Sx's of beta-Thalassemia Major?
|
Severe Anemia requiring blood transfusions
Cardiac Failure due to secondary hemochromatosis Marrow expansion---> skeletal deformities (skull) |
|
|
alpha/beta thalassemias and ethnicities?
|
Alpha: asia and africe
Beta: meditteranean |
|
|
General findings w/ hemolytic anemias?
|
Inc bilirubin---> jaundice, pigment gallstones
Inc reticulocytes (marrow compensating) |
|
|
General findings in intra vs extra-vascular hemolysis?
|
Intra---> hemoglobinuria
extra---> jaundice |
|
|
3 Types of Autoimmune Hemolyic Anemia?
|
Warm Agglutinin
Cold Agglutinin Erythroblastosis fetalis |
|
|
Warm vs Cold Agglutinin
antibody type? |
Warm = IgG
Cold = IgM |
|
|
Warm vs Cold Agglutinin
chronic or acute? |
Warm: chronic
Cold: acute (triggered by cold) |
|
|
Warm vs Cold Agglutinin Associated conditions?
|
Warm: SLE, CLL, w/ certain drugs (methyldopa)
Cold: Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection, infectious mono |
|
|
Where does hemolysis occur in Warm Agglutinin?
|
Mostly extravascular
Accelerated by RBC destruction in liver Kupffer cells and spleen |
|
|
Difference between Direct and Indirect Coombs test?
|
Direct: anti-Ig antibodies are added to pt's blood. If RBC's are coated w/ Ig, the they agglutinate
Indirect: Normal RBC's are added to pt's serum. If the pt has anti-RBC surface Ig, then the new RBC's will aggulinate |
|
|
Confirmatory test for Aggultination?
|
Osmotic fragility test
|
|
|
What is Hereditary Spherocytosis? cause?
|
Intrinsic, extravascular hemolysis due to ankyrin, band 3.1, or spectrin defect
|
|
|
Clinical findings w/ Hereditary Spherocytosis?
|
Small, round RBC's with no central pallor (less membrane)
Inc MCHC Inc RDW |
|
|
Associations for Hereditary Spherocytosis?
|
Splenomegaly
Aplastic crisis (B19 infection) |
|
|
What do you seen in a Hereditary Spherocytosis pt after splenectomy?
|
Howell-Jolly Bodies
|
|
|
What is Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hematuria? cause?
|
Intravascular hemolysis due to membrane defect---> inc sensitivity of RBC's to lytic activity of C'
defect=impaired synthesis of GPI anchor/decay accelerating factor |
|
|
Urinalysis finding w/ PNH?
|
inc urine hemosiderin
|
|
|
What is Microangiopathic
anemia? when do we see it? |
Intravascular hemolysis
Seen in DIC, TTP/HUS, SLE, or malignant HTN |
|
|
Blood smear findings w/ Microangiopathic Anemia?
|
Schistocytes (helmet cells too) due to mechanical destruction from passing through obstructed/narrowed vessels
|
|
|
What is DIC?
|
Activation of coagulation cascade--> microthrombi and global consumption of platelets, fibrin, and coag factors
|
|
|
Causes of DIC?
|
sepsis (gram neg)
Trauma Obstetric complications acute Pancreatitis Malignancy Nephrotic syndrome Transfusion |
|
|
Lab findings w/ DIC?
|
Inc PT
inc PTT inc fibrin split products (d-dimers) dec platelet count helmet cells and schistocytes |
|
|
2 general causes of bleeding disorders?
|
platelet abnormalities
coagulation factor defects |
|
|
5 conditions leading to abnormal platelets?
|
ITP
TTP DIC Aplastic Anemia Drugs |
|
|
What is ITP?
|
Idiopathic Thrombocyopenic Purpura
|
|
|
Clinical Findings w/ ITP?
|
peripheral platelet destruction
anti-GpIIb/IIIa antibodies Inc megakaryocytes its immune destruction of platelets |
|
|
What is TTP?
|
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
|
|
|
What causes TTP?
|
deficiency in vWF-cleaving metalloproteinase--->excess large vWF multimers--->inc platelet aggregation,
|
|
|
clinical findings w/ TTP
|
thrombosis
schistocyte formation inc LDH Neuro and renal Sx's fever |
|
|
What types of hemorrhage do abnormal platelet disorders vs coag factor defects lead to?
|
Platelet Disorders: microhemorrhages
Coag factor defects: macrohemorrhages |
|
|
how do microhemorrhages present?
|
Mucous membrane bleeding
epistaxis petechiae purpura inc bleeding time |
|
|
How do macrohemorrhages present?
|
hemarthroses (bleeding into joints)
easy bruising Inc PT and/or PTT |
|
|
3 types of coagulation factor defects?
|
Hemophilia A
Hemophilia B von Willebrand disorder |
|
|
What is the most common bleeding disorder?
|
von Willebrand disorder
|
|
|
cause of Hemophilia A vs B?
|
A: factor VIII def
B: factor IX def |
|
|
cause of von Willebrand disease? effect?
|
vWF def--->defective platelet adhesion and dec factor VIII survival
|
|
|
What does PT test? PTT?
|
PT (extrinsic): factors I, II, V, VII, and X
PTT (intrinsic): all factors except factors VII and XIII |
|
|
What are two other conditions leading to defective platelet plugs?
|
Glanzmann's Thrombastenia
Bernard-Soulier Disease |
|
|
What is Glanzmann's Thrombastenia?
|
dec GpIIb/IIIa---> defective platelet-to-platelet aggregation
|
|
|
What is bernard-soulier's disease?
|
Dec Gp1b--->defective platelet-to-collagen adhesion
|
|
|
PT and PTT times for Hemophilia A and B?
|
both in PTT (intrinsic)
|
|
|
PT and PTT times for vW disease?
|
normal or increased PTT (since vWF protects factor 8)
|
|
|
Vitamin K ---> what factor issues?
|
dec synthesis of factors II, VII, IX, X, protein C, and protein S
|
|
|
bleeding times for Vitamin K def?
|
Inc PT and PTT
|
|
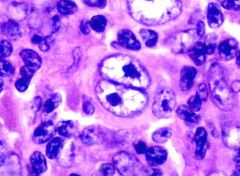
what is it?
|
Reed-Sternberg Cell
|
|
|
What are and when do you see Reed-Sternberg Cells?
|
Tumor Giant cell seen in Hodgkin's disease
binucleate/bilobed cell w/ 2 halves (mirror images) "owl's eyes" |
|
|
What markers are on Reed-Sternberg Cells?
|
CD30+
CD15+ B-cell origin |
|
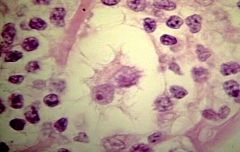
who is this guy? when do you see him?
|
Lacunar Cell
Reed-sternberg variant in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's |
|
|
Hodgkin's vs Non-Hodgkin's
nodal involvement and spread? |
H: localized, single group of nodes (rare extranodal)
spread is contiguous NH: multiple peripheral nodes extranodal common noncontiguous spread |
|
|
Hodgkin's vs Non-Hodgkin's
Sx's? |
H: constitutional (B) sx's:
fever, night sweats, wt. loss mediastinal lymphadenopathy NH: fewer constitutional sx's |
|
|
Hodgkin's vs Non-Hodgkin's
associations? |
H: EBV
NH: HIV, immunosuppression |
|
|
Hodgkin's vs Non-Hodgkin's
age and gender? |
H: bimodal (young and old)
men, except Nodular sclerosing NH: some types 20-40 yo's |
|
|
Px for Hodgkins?
|
Good prognosis = inc lymphocytes and dec RS cells
|
|
|
Types of Hodgkin's Lymphoma and prevalence?
|
Nodular Sclerosing (65-75%)
Mixed cellularity (25%) Lymphocyte predominant (6%) Lymphocyte depleted (rare) |
|
|
RS and Lymphocyte levels for each type of Hodgkin's?
|
NS
RS: + L's: +++ Mixed RS: ++++ L's: +++ Lymphocyte Predominant RS: + L's: ++++ Lymphocyte depleted RS: high in relation to lymphocytes L's: + |
|
|
Px for each type of Hodgkin's?
|
NS: excellent
Mixed: intermediate L-predominant: excellent L-depleted: poor correlates well w/ lymphocyte:RA ratio (the higher the better) |
|
|
Who typically gets NS Hodgkin's?
|
young women
|
|
|
Who typically gets L-predominant Hodgkin's?
|
young (< 35) males
|
|
|
who typically gets L-depleted Hodgkin's?
|
Old guys w/ disseminated disease
|
|
|
What do the plasma cells produce in Multiple Myeloma?
|
IgG (55%)
IgA (25%) |
|
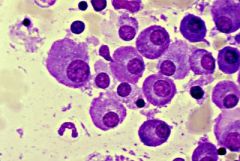
what are these cells characteristic of
|
Plasma cells in multiple myeloma (fried egg appearance)
|
|
|
Sx's of Multiple Myeloma?
|
Destructive Bone Lesions
Consequent hyperCa Renal insufficiency Inc susceptibility to infections Anemia primary amyloidosis |
|
|
Imaging and test results characteristic of Multiple Myeloma?
|
Punched-out lytic bone lesions on x-ray
M spike on (monoclonal Ig spike) serum protein electrophoresis Bence Jones Proteins in pee (Ig light chains) Rouleaux formation on blood smear |
|
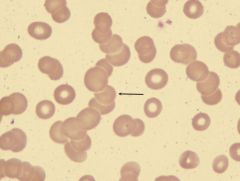
what is this?
|
rouleaux formation characteristic of Multiple Myeloma
|
|
|
How does Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia compare Multiple Myeloma?
|
Waldernstrom's has an M spike representing inc IgM---> hyperviscosity syndromes
No lytic bone lesions |
|
|
What is MGUS?
|
Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance
ASYMPTOMATIC |
|
|
6 types of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma?
|
Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
Follicular Lymphoma (small cleaved cell) Diffuse Large Cell Lymphoma Mantle Cell Lymphoma Lymphoblastic Lymphoma Burkitt's Lymphoma |
|
|
Age group for each type?
|
Small Lymphocytic: Adults
Follicular: adults Mantle Cell: adults Diffuse large cell: older adults usually, but 20% in kids Lymphoblastic: kids Burkitt's: kids |
|
|
Cell Typs for each type of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma?
|
Small Lymphocytic: B
Follicular: B Mantle Cell: B Burkitt's: B Diffuse Large Cell: 80% B, 20% T Lymphoblastic: T (immature) |
|
|
Genetic Factors predisposing to certain types of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
|
Follicular Lymphoma: t(14;18)-->bcl-2 expression
Mantle cell Lymphoma: t(11;14) Burkitt's: t(8:14)--> c-myc moves to Ig heavy chain gene on 14 |
|
|
Which type of NHL is most common?
|
Adults: Diffuse Large Cell
Kids: Lymphoblastic |
|
|
Which type of NHL is most common in kids?
|
Lymphoblastic Lymphoma
|
|
|
Aggressiveness/Prognosis for each type of NHL?
|
Small Lymphocytic: low grade
Follicular: indolent, difficult to cure Diffuse Large Cell: aggressive, but curable Mantle cell: poor px Lymphoblastic: very aggressive |
|
|
Marker for Mantle Cell Lymphoma?
|
CD5+
|
|
|
How does Lymphoblastic Lymphoma normally present?
|
w/ ALL and mediastinal mass
|
|
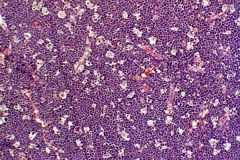
what is this characteristic of? what is going on in the image?
|
Burkitt's Lymphoma
Starry Sky = sheets of lymphocytes interspersed w/ macrophages |
|
|
What is Burkitt's associated w/?
|
EBV infection
|
|
|
How do Endemic Burkitt's and the sporadic form differ?
|
Endemic: africa and jaw lesion
Sporadic: elsewhere and pelvis or abdomen |
|
|
what does the translocation lead to?
t(9:22)? |
Philadelphia chromosome---> CML (bcr-abl hybrid)
|
|
|
what does the translocation lead to?
t(8;14) |
Burkitt's Lymphoma (c-myc activation)
|
|
|
what does the translocation lead to?
t(14;18)? |
Follicular lymphoma (bcl-2)
|
|
|
what does the translocation lead to?
t(15;17) |
M3 type of AML
|
|
|
what does the translocation lead to?
t(11;22) |
Ewing's Sarcoma
|
|
|
what does the translocation lead to?
t(11:14) |
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
|
|
|
what indicates a Leukemoid Rxn
|
Inc WBC count w/ left shift (80% bands)
Inc leukocyte alkaline phosphatase |
|
|
Who gets ALL?
|
kids
|
|
|
BM in ALL?
|
big time replacement by lymphoblasts
|
|
|
marker for ALL?
|
TdT+ (marker for pre-B and pre-T's?
|
|
|
Px for ALL?
|
most responsive to therapy
|
|
|
where can ALL spread?
|
CNS
Testes |
|
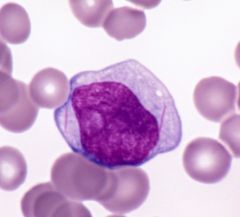
what is in the cytoplasm of this guy? indicative of?
|
auer rod
AML |
|
|
Other blood smear findings w/ AML?
|
inc circulating myeloblasts
|
|
|
who gets AML?
|
adults
|
|
|
Rx for M3 AML?
|
all-trans retinoic acid (Vit A)--->differentiation
|
|
|
Who gets CLL?
|
older (> 60) adults
|
|
|
Sx's of CLL?
|
Lymphadenopathy
Hepatosplenomegaly indolent course |
|
|
Clincal findings for CLL?
|
Inc smudge cells on smear
warm Ab autoimmune hemolytic anemia very similar to SLL |
|
|
Characteristics of CML
|
Philadelphia Ch (t(9;22))
Left Shift w/ Inc neutrophils, metamyelocytes, basophils Splenomegaly Very low alkaline phosphatase |
|
|
How can CML evolve?
|
into AML (2/3)
or ALL (1/3) = blast crisis |
|
|
Rx for CML?
|
imatinib (anti-bcr-abl)
|
|
|
What is Hairy cell Leukemia? who gets it? why hairy? stain?
|
Mature B-cell tumor in elderly
cells have hair-like projections. Stains Tartrate-resistant acid phophatase (TRAP) positive |
|
|
what is an auer rod?
|
Peroxidase+ cytoplasmic inclusions in granulocytes and myeloblasts
|
|
|
When do we see auer rods? possible complication?
|
Seen in M3 AML
Rx for AML M3 can lead to release of Auer Rods--->DIC |
|
|
What is Histiocytosis X?
|
AKA: Langerhans cell Histiocytes
Proliferative disorder of dendritic (langerhans) cells from monocyte lineage |
|
|
Markers for defective cells in Histiocytosis X?
|
S-100
CD1a |
|
|
EM and Histiocytosis X??
|
Birbeck granules (tennis rackets)
|
|
|
4 Myeloproliferative disorders?
|
Polycythemia vera
Essential thrombocytosis Myelofibrosis CML |
|
|
RBC, WBC, and Platelet counts for Polycythemia vera?
|
All increased
|
|
|
RBC, WBC, and Platelet counts for Essential Thrombocytosis?
|
Just the platelets are increased
|
|
|
RBC, WBC, and Platelet counts for Myelofibrosis?
|
RBC's are down
WBC's and platelet levels are variable |
|
|
RBC, WBC, and Platelet counts for CML?
|
RBC's are down
WBC and Platelet levels are increased |
|
|
Type of mutations common to Polycythemia vera
Essential Thrombocytosis Myelofibrosis? |
JAK2 Mutations
positive in 30-50% of essential thrombocytosis and myelofibrosis |
|
|
Classic findings for Polycythemia vera?
|
abnormal clone of hematopoietic stem cells has increasing susceptibility to GF's
|
|
|
Classic findings for Essential thrombocytosis?
|
similar to Polycythemia vera, but specifc for megakaryocytes
|
|
|
Classic findings for Myelofibrosis?
|
fibrotic obliteration of bone marrow
|
|
|
Classic findings for CML?
|
t(9:22) transforms bcr-abl--->inc cell division and inhibition of apoptosis
|
|
|
What is JAK2 normally involved in?
|
Hematopoietic growth factor signaling...hence why a mutation can lead to increased sensitivity
|

