![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the keys to Prolactin Regulation?
|
PRL stimulates an inc in dopamine synthesis and secretion from hypothalamus
Dopamine negatively feedbacks on PRL (i.e. inhibits PRL secretion) So Dopamine agonists (bromocriptine) inhibit PRL secretion and Dopamine Antagonists (antipsychotics) stimulate PRL secretion |
|
|
How come Increases in PRL lead to amenorrhea?
|
PRL inhibits GnRH synthesis and release, which inhibits ovulation
|
|
|
What does the hypothalamus secrete that exerts effects on the Pituitary Gland? what does each hormone do?
|
TRH---> inc TSH and PRL
Dopamine---> dec PRL CRH---> inc ACTH GHRH---> inc GH Somatostatin---> dec GH and dec TSH GnRH---> inc FSH and LH |
|
|
OK...how do you make Aldosterone, Cortisol, Testosterone, DHT, and Estrogens from Cholesterol...geez
|
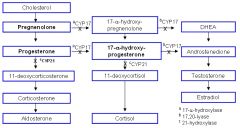
|
|
|
Who is responsible for turning Cholesterol into Pregnenolone and what can regulate this enzyme?
|
Desmolase
ACTH stimulates it Ketoconazole inhibits it |
|
|
What is responsible for the last step in the conversion of Cholesterol to Aldosterone? what regulates this enzyme?
|
Aldosterone Synthase
Angiotensin II stimulates it |
|
|
What 3 congenital deficiencies affect steroid synthesis?
|
17alpha-hydroxylase Deficiency
21alpha-hydroxylase def 11beta-hydroxylase def |
|
|
What are the hormone levels w/ 17alpha hydroxylase deficiency?
|
Dec sex hormones
Dec cortisol Inc Mineralcorticoids (aldo) |
|
|
What are the general Sx's of 17alpha hydroxylase deficiency?
|
HTN
HypoKalemia |
|
|
What are the Sx's of 17alpha hydroxylase deficiency in men?
|
Dec DHT---> pseudohermaphroditism (externally female, but MIF stops any internal female organ dev)
|
|
|
What are the Sx's of 17alpha hydroxylase deficiency in females?
|
Externally Female w/ normal internal sex organs, but lacking secondary sex characteristics
|
|
|
Which one of the Congenital steroid synthesis deficiencies is most common?
|
21alpha-hydroxylase def
|
|
|
Hormone levels for 21alpha-hydroxylase deficiency?
|
Inc Sex hormones
Dec Cortisol (inc ACTH) Dec Mineralcorticoids |
|
|
Sx's of 21alpha-hydroxylase deficiency?
|
Maculinization
Female Pseudohermaphroditism HYPOtension HYPERKalemia Inc plasma renin activity Volume Depletion |
|
|
What can happens to newborns w/ 21alpha-hydroxylase deficiency?
|
Salt wasting can lead to hypovolemic shock
|
|
|
Hormone levels in 11beta-hydroxylase deficiency?
|
Dec Cortisol
Dec Mineralcorticoids Inc Sex hormones |
|
|
Sx's for 11beta-hydroxylase deficiency?
|
Masculinization
HYPERTENSION |
|
|
Why HTN for 11beta-hydroxylase deficiency?
|
11-deoxycorticosterone is a mineralcorticoid. It builds up big time and is secreted in excess
|
|
|
What do all three congenital adrenal enzyme deficiencies have in common?
|
Enlargement of Adrenal Glands due to Increased ACTH in response to dec cortisol
|
|
|
Source of Cortisol?
|
Adrenal Zona Fasciculata
|
|
|
Cortisol Fxns
|
Anti-Inflammatory
Inc Gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, proteolysis Dec Immune Fxn Maintains BP Dec Bone Formation |
|
|
How does Cortisol get around in the blood stream?
|
Bound to Corticosteroid Binding Globulin (CBG)
|
|
|
What can induce prolonged cortisol secretion?
|
Chronic Stress
|
|
|
Source of PTH?
|
Chief Cells from the parathyroid glands
|
|
|
Fxns of PTH?
|
1. Inc Bone Resorption of Ca and Phosphate
2. Inc Kidney resorption of Ca in DCT 3. Dec Kidney resorption of phosphate 4. Inc 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D (calcitriol) production by Stimulating kidney 1alpha-hydroxylase 5. Inc Intestinal Absorption of Ca |
|
|
what does PTH do to serum and urine levels of stuff?
|
Inc serum Ca
Dec serum Phosphate Inc urine Phosphate |
|
|
PTH activity on specific bone cells?
|
Stimulates both osteoclasts and osteoblasts
|
|
|
How is PTH level regulated?
|
dec free serum Ca---> inc PTH
dec free serum Mg---> dec PTH |
|
|
What are some common causes of Decreased Mg (which dec PTH secretion)
|
Diarrhea
Aminoglycosides Diuretics Alcohol |
|
|
How does the body respond to Low Serum Phosphate?
|
Stimulates Kidney to increase conversion of vitamin D to 1,25 vit D--->
Stimulates release of phosphate from bone matrix AND Increases Intestinal absorption of Ca and Phosphate |
|
|
How do we get Vitamin D? how do we activate it?
|
D3 from Sun
D2 from plants Both converted to 25-OH Vit D by liver Converted to 1,25-(OH)2 Vit D by kidneys |
|
|
Fxns of Vitamin D?
|
Inc absorption of dietary Ca
Inc Absorption of dietary Phosphate Inc Bone Resorption of Ca and Phosphate |
|
|
Regulation of Vitamin D?
|
Inc PTH--->Inc 1,25 D
Dec Ca---> Inc 1,25 D Dec Phosphate--->Inc 1,25 D 1,25 D negatively feeds back on itself |
|
|
What happens if you don't get enough Vit D?
|
Rickets in kids
Osteomalacia in adults |
|
|
What is 24,25-(OH)2 Vitamin D?
|
Inactive form of D
|
|
|
How do PTH and D differ in their affects on Ca and Phosphate?
|
PTH---> Inc Ca and Dec Phosphate reabsorption
D---> Inc Ca and Inc Phosphate reabsorption |
|
|
Source of Calcitonin?
|
Parafollicular Cells (C Cells) of Thyroid
|
|
|
Fxn of Calcitonin?
|
Dec Bone Resorption of Calcium
|
|
|
Regulation of Calcitonin?
|
Inc Serum Ca---> Calcitonin secretion
|
|
|
Generally speaking, how do steroids and thyroid hormones elicit their actions?
|
They get into cells
Bind to a receptor in the cytoplasm or on the nucleus The receptor-steroid complex undergoes a conformational change exposing a DNA-binding site This binds to DNA and causes transcription and translation leading to a protein that will create the desire response |
|
|
Who are the main Steroid/Thyroid hormones?
|
Progesterone
Estrogen Testosterone Cortisol Aldosterone Thyroxine and T3 PET CAT |
|
|
What is the Testosterone binder and its significance in men and women?
|
Sex-Hormone Binding Globulin
an increase in SHBG in men --> dec free testosterone --> man boobs in women, a dec in SHBG ---> inc free testosterone--->hirsutism |
|
|
What are some pharmacokinetic/dynamic characteristics of steroid hormones?
|
They're lipophilic = insoluble in plasma, so they need binding globulins---> inc solubility AND allow for inc delivery to target organs
|
|
|
Source of Thyroid Hormones?
|
Follicles of Thyroid
Most of T3 is formed in the blood |
|
|
Fxns of Thyroid Hormones?
|
1. Bone Growth (synergism w/ GH)
2. CNS maturation 3. Inc Beta1-receptors in Heart---> Inc CO, HR, SV, contractility 4. Inc BMR 5. Inc Glycogenolysis, Gluconeogenesis, Lipolysis (Free up fuel) |
|
|
How do thyroid hormones in BMR?
|
via Na/K ATPase activity = Inc O2 consumption, RR, and body temp
|
|
|
How are Thyroid Hormones Regulated?
|
TRH stimulates TSH, which stimulates Follicular Cells
Free T3 negatively feeds back to Ant. Pituitary to decrease sensitivity to TRH Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin (TSI) also stimulates follicular cells (Graves') |
|
|
How are Thyroid Hormones synthesized?
|
Follicular cells make Thyroglobulin and ship it into the lumen.
Follicular cells actively transport Iodine into lumen while oxidizing it. The I2 + TG combine to for MIT and DIT. DIT + DIT = T4 MIT + DIT = T3 MIT + MIT = inactive Peroxidase does all this coupling T3/T4 are then shipped back across the follicular cell (with some proteolysis) and secreted into the blood. |
|
|
Difference between T3 and T4?
|
T3 has higher affinity for thyroid hormone receptors
|
|
|
How do T3/T4 get around in the blood? key?
|
Bound to Thyroxine-Binding Globulin (TBG)
but only free hormone is active |
|
|
When do TBG levels change?
|
Dec TBG in liver failure
Inc TBG in pregnancy (estrogen --> Inc TBG) |
|
|
Which Endocrine Hormones use the cAMP signaling pathway?
|
FSH
LH ACTH TSH CRH hCG ADH (V2 receptor) MSH PTH FLAT CHAMP Calcitonin Glucagon |
|
|
Which Endocrine Hormones use the cGMP signaling pathway?
|
ANP
EDRF NO |
|
|
Which Endocrine Hormones use the IP3 pathway?
|
GnRH
GHRH Oxytocin ADH (V1 receptor) TRH "GGOAT" |
|
|
Which Endocrine Hormones use the Steroid Receptor pathway?
|
Glucocorticoid
Estrogen Progesterone Progesterone Testosterone Aldosterone Vitamin D T3/T4 |
|
|
Which Endocrine Hormones use the Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Pathway?
|
Insulin
IGF-1 FGF PDGF Prolactin GH |

