![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the structure of artery ? |
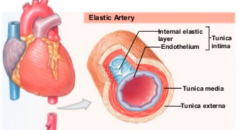
- smooth muscle is the tunica media - tunica adventitia : connective tissue and external elastic lamina |
|
|
what is the structure of vein ? |
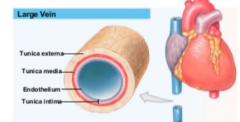
- tunica adventitia : is only connective tissue - tunica intima includes internal elastic lamina and endothelial - smooth muscle is tunica media - valves are present |
|
|
what are the difference between artery and vein ? |
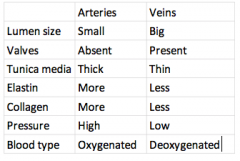
|
|
|
What are the 3 major functions of artery ? |
1. withstand high pressure - many collagen and elastin fibres in tunica adventitia to strengthen the wall 2. Expand and recoil during heart contraction (peristalsis) - keep a smooth flow of blood - elastin stretches during systole and stores energy - during diastole, energy is released into the blood by squeezing it and pushing it forward 3. adjusting diameter (resistance to flow) - smooth muscle in tunica media contracts to cause vasoconstriction - endothelial cells release endothelin to cause contraction - "resistance vessel" |
|
|
What is the major function of vein ? |
1. able to accumulate blood - ability to stretch and store blood - doesn't have much muscle layer, thus is able to stretch - "capacitance vessels" 2. prevent black flow of blood - smooth muscle contracts to propel blood - valves are present to prevent back flow |
|
|
What is venous return ? |
- blood returning in the vein to the heart - against gravity - depend on skeletal muscles around vein to contract - large veins has smooth muscles to contract and pushes blood |
|
|
What is the disease " Deep vein thrombosis" (DVT)? |
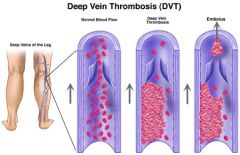
- "economic class syndrome" - blood clot (thrombosis) forming in a deep vein - causing blood to accumulate in the vein of the lower body - usually during resting blood pool and decrease flow rate due to immobility in the vein venous thrombosis |
|
|
What is the structure capillaries ? |
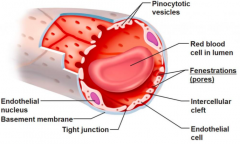
- receives blood from arterioles under high pressure - single layer of endothelial cells - have fenestrations |
|
|
what are the functions of capillary and those special features that allows capillaries to carry out its function ? |
1, large surface area - it is a network of capillaries in the capillary bed - maximised gases and material exchange -large cross-sectional area 2. high pressure - blood arrive at high pressure but it is slightly reduced due to the extensive branching - still high enough for water and small solutes to squeeze out of the capillary into interstitial fluid 3. very thin wall - reduce diffusion and osmosis distance -maximise gaseous exchange 4. Have fenestrations - allow small proteins and ions to leak out - water leaked out through aquaporine |
|
|
what is starling's forces and give an example of them ? |
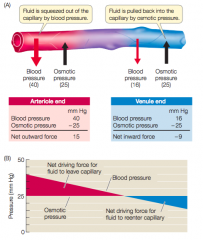
- starling forces are 2 opposing forces that maintains water balance in the capillary 1. osmotic pressure : pulls water back into the capillary (as large proteins are still in the capillary creating gradient) 2. blood pressure : forces water and small solutes out - BP<OP water moves in - BP>OP water moves out |
|
|
How does "oedema" happen ? |
- it is the accumulation of fluid - due to unbalanced starling's forces - when there are high BP and low OP continuously |
|
|
what can Aspirin do for coronary heart disease ? |
- coronary heart disease is the narrowing of the small blood vessels that supply blood and O2 to the heart - aspirin prevents blood clot formation in the arteries - thus reduces the risk of heart attack |
|
|
what can nitrates like Nitroglycerin of for coronary heart diseases? |
- it stops chest pain and improve blood supply to heart |
|
|
What can statins do to coronary heart diseases? |
- it lower cholesterol - reduce the chance of fatty substances building in the arteries |
|
|
what is "atherosclerosis" ? |
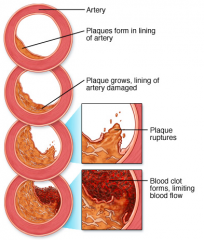
- it is the formation of "plague", fatty substance lining the inner wall of arteries. - narrowing the artery, affecting blood flow - often later cause the accumulation of "thrombus", blood clots, due to rupture of plague - endothelial cells are damaged - smooth muscles secretes fibrous connective tissue making artery "harden" |
|
|
What is "Rosuvastin" ? |
- a drug developed to lower cholesterol and improve cardiovascular morphology and function - lower plaque progression |
|
|
what kind of mouse is used for research, particularly in the field of cardiovascular disease related to atherosclerosis.Explain why. |
- Apolipoprotein E- deficient (APOE-deficient) mice - as they develop all phases of atherosclerosis lesions |
|
|
what is "arteriosclerosis" ? |
-is the stiffening and hardening of the arterial wall |

