![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
HCT is the transfer of _____ and ____ for therapeutic purpose |
hematopoietic progenitor and Stem cells |
|
|
What is a syngeneic transplant and is it auto or allo |
transplant from identical twin Treate like auto, but is officially Allo |
|
|
4 Steps in Auto HCT |
|
|
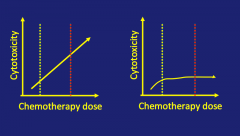
Which pt should get auto transplant |
Left; no benefit from HD chemo so no need for auto |
|
|
*When is AutoHCT indicated |
When Cytoreduction is effective (via chemo) like:
|
|
|
Steps in Allo |
Chemo to kill cancer HD chemo Donor cells added Wait |
|
|
*Indications for allo |
Replacement of hematopoiesis Graft vs Tumor effect Prevent Relapse |
|
|
What is an allo transplant really: |
A bet against the future; must decide after being told they are disease free to do allo transplant to prevent relapse (35% vs 5% for allo vs no BMT) |
|
|
T/F NPM1+ it is best to do allo transplant as 1st line therapy |
F |
|
|
MUD = what type of transplant |
Matched unrelated donor; Allo |
|
|
T/F is is best to do MUD transplant in relapsed pts with unfavorable genotype |
T |
|
|
What are the 2 immunological effects of allogeneic grafts |
GVHD GV tumor |
|
|
6 Steps in reduced intensity AlloBMT |
|
|
|
T/F All auto are myeloablative |
T |
|
|
What cell type does Bu, Mel and TBI destroy |
HSC |
|
|
What cell type does Fludarabine destroy |
CLP |
|
|
What cell type does Cyclophosphamide destroy |
CLP CMP |
|
|
T/F Giving HD of cells --> increased survival |
T |
|
|
What is responsible for GVHD and Graft Rejection |
MHC (HLA) |
|
|
*Chance of matched sibling = |
1 - (3/4)^# of siblings |
|
|
Billingham criteria * |
|
|
|
What is acute GVHD |
Rxn between Donor cells against Host cells 20-50% develop it |
|
|
What can be given prophylactically to prevent Acute GVHD (3) |
|
|
|
How does cyclophosphamide, post-graft, protect against GVHD |
T t cells that react against host start to proliferate and Cy attacks those cells keeping GVHD at bay |
|
|
How does billingham's hypothesis explain how post-transplant cyclophos prevents acute GVHD |
Billingham's criteria state that the donor cells must be reactive against host. As these cells start to proliferate after activation of reactive cells, cy is able to target the rapidly expaning cells, keeping GVHD at bay |
|
|
What is the major cause of log term mortality other than relapse |
cGVHD |

