![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
FSH
|
Stimulate development of follicle
AND Stimulates follicles in the ovaries to produces OESTROGEN |
|
|
LH
|
Causes OVULATION to occur
AND Stimulates the overay to produce progesterone from the corpus luteum |
|
|
Oestrogen
|
Causes rebuilding of the uterus lining after menstruation
AND Stimulates pituitary gland to produce LH |
|
|
Progesterone
|
Maintains lining of uterus - ready to receive fertilised egg
AND Inhibits production of FSH from the pituitary gland |
|
|
Where are hormones produced?
|
In glands, which secrete the hormone directly into the blood (endocrine glands)
|
|
|
What are the cells called that hormones act on?
|
Target cells
|
|
|
How does the second messenger model of hormone action work?
|
Hormone is the first messenger
It binds to specific receptors on the cell-surface membrane of target cells This forms a hormone-receptor complex that activates an enzyme inside the cell This produces a chemical which acts as a second messenger This second messenger causes chemical changes that produce the required response Keep going :) |
|
|
The pancreas is mainly constituted by enzyme secreting cells, however there are cells known as ______ __ __________, and ____ cells produce insulin
|
Islets of Langerhans, Beta cells produce Insulin
|
|
|
Beta cells of the IoL detect a rise in blood glucose level and so _______ is secreted into the blood plasma
|
insulin
|
|
|
When insulin combines with cell receptors:
|
More glucose is allowed into cells
Moer carrier molecules in the cell-surface membrane Activation of the enzymes that convert glucose to glycogen and fat |
|
|
Insulin reduces the blood glucose level by:
|
Increasing the rate of absorption of glucose into the cells (esp. muscle)
Increasing the respiratory rate of the cells Increasing the rate of conversinon of glucose into glycogen Increasing the rate of conversion of glucose to fat |
|
|
When physical changes take place, mass is ________
|
Conserved
|
|
|
Solids become more/less soluble in liquids as the temperature is increased to ~100*C?
|
more
|
|
|
How are igneous rocks formed?
|
Cooling of Magma
|
|
|
How are sedimentary rocks formed?
|
Decomposition of rock fragments or organic material, or evaporation
|
|
|
How are metamorphic rocks fromed?
|
By the action of heat and pressure on existing rocks
|
|
|
What are the effects of burning fossil fuels?
|
Production of acid rain, Co", solid particles
|
|
|
i)Acid + carbonate
ii) Acid + base/alkali iii) Metal + acid |
i) Salt + CO2 + H2O
ii) Salt + water iii) Salt + Hydrogen |
|
|
What are everyday applications of neutralisation?
|
Treatment of indigestion, treatment of acidic soil and manufacture of fertiliser
|
|
|
What is the atomic number?
What is the mass number? |
Number of protons
Protons and Neutrons |
|
|
How is the periodic table ordered?
|
By atomic number
|
|
|
Bond breaking is an exo/endothermic process?
|
Endothermic
|
|
|
What are the stages of the reflex arc?
|
Stumulus --> Receptor --> Sensory neurone --> Co-ordinator (CNS) --> Motor Neurone --> Effector --> Response
|
|
|
Current in series =
|
Same all the way round
|
|
|
Voltage in series =
|
Voltages across each component adds up to the total voltage supplied by the battery. Higher resistances will need more of the voltage
|
|
|
Voltage in parallel =
|
All voltages are the same
|
|
|
Current in parallel =
|
Current is shared out between the branches, but it recombines near the battery
|
|
|
Energy/Charge
|
Voltage
|
|
|
Energy transferred/time
|
Power
|
|
|
Charge/Time
(think) |
Current
|
|
|
I²R
|
Power
|
|
|
V²/R
|
Power
|
|
|
Mass/Volume
|
Density
|
|
|
Force/Area
|
Pressure
|
|
|
V2/V1 =
|
2 turns/1 turns
|
|
|
(f * d)/t
|
Power
|
|
|
energy/time
|
Power
|
|
|
frequency (Hz) * wavelength (m)
|
wavespeed
|
|
|
Potential energy lost =
|
Kinetic energy gained
|
|
|
Energy transformed (kWh) =
|
Power (kW) * time (h)
|
|
|
Force (mg) * distance (vertical)
|
GPE gained
|
|
|
Unbalanced forces change the speed or direction of movement of objects, balanced forces...
|
Produce no change in the movement of an object
|
|
|
In a uniform medium, light travels in a ________ line
|
straight
|
|
|
Shorter wavelengths are refracted more/less
|
More
|
|
|
What's the difference between heat and temperature?
|
Heat is thermal energy.
Temperature is the measurement of average kinetic energy of the particles which compose the matter being tested. |
|
|
What is conduction?
|
In heat transfer, conduction (or heat conduction) is the transfer of thermal energy between neighboring molecules in a substance due to a temperature gradien
|
|
|
What is convection?
|
The transfer of heat through a fluid (liquid or gas) caused by molecular motion
|
|
|
What is radiation?
|
Energy that is radiated or transmitted in the form of rays or waves or particles. ENERGY IS DIRECTLY TRANSFERRED BY RADIATION
|
|
|
Energy is conserved, but it may be dissipated as it changes to another form
|
.
|
|
|
What happens to resistors when charge flows through them?
|
They heat up
|
|
|
Voltage is the energy transferred per unit of ______
|
charge
|
|
|
Define electric current
|
The flow of charge carried by free electrons in metals or ions during electrolysis
|
|
|
Balanced forces do/do not alter the velocity of a moving object
|
do not
|
|
|
When two forces interact, the forces they exert on each other are...
|
equal and opposite
|
|
|
What is the frequency of a wave?
|
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time
|
|
|
What does a low frequency look like compared to a high frequency?
|
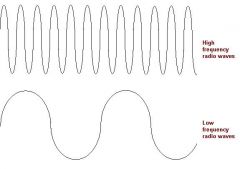
|
|
|
What does a high wavelength look like compared to a small wavelength?
|
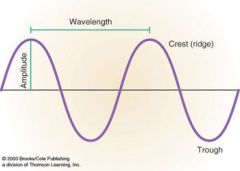
|
|
|
What does a high amplitude look like in comparison to a low amplitude?
|
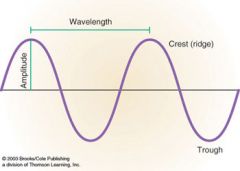
|
|
|
Waves transfer energy without transferring...
|
matter
|
|
|
Radio waves, microwaves, infrared an d visible light carry information over large and small distances, including global transmission via satellites
|
.
|
|
|
How is a voltage induced?
|
When a conductor cuts magnetic field lines and when the magnetic field though a coil changes
|

