![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Primary Hemostasis (cessation of bleeding) |
Accomplished by formation of a platelet plug |
|
|
How is a platelet plug formed? |
Following a vascular endothelial injury, platelets adhere to exposed collagen fibers and are activated; activated platelets release ADP and serotonin |
|
|
Role of ADP in blood clotting
|
Released by activated platelets
Cause platelet swelling and makes the PM sticky, resulting in the formation of a platelet plug |
|
|
Role of serotonin in blood clotting |
Increases activity of PM phospholipase, which cleaves arachidonic acid from PL's
Arachidonic acid is converted to thromboxane A2, which causes vasoconstriction |
|
|
Plavix |
Inhibits blood clotting by interfering with the effects of ADP |
|
|
How does vitamin C deficiency lead to increased coagulation time? |
Low vitamin C affects collagen synthesis, which interferes with coagulation |
|
|
How does aspirin affect blood clotting? |
It prevents formation of thromboxane A2 from arachidonic acid, preventing vasoconstriction |
|
|
Fibrinogen |
Synthesized by liver
Comprises 7% of all plasma proteins
Composed of 6 identical polypeptide chains
A rodlike protein with lots of Asp and Glu residues (negatively charged) at its N and C termini |
|
|
Thrombin
|
Cleaves fibrinogen to form fibrin and fibrinopeptides
|
|
|
Formation of a soft clot |
After thrombin cleaves fibrinogen to form fibrin, fibrin monomers spontaneously organize into fibrin polymers (insoluble, red clot; held together by weak, non-covalent bonds)
*Red because the clot traps RBC's |
|
|
Formation of a hard clot |
Thrombin cleaves Factor XIII to Factor XIIIa (Transglutaminase), which catalyzes formation of covalent crosslinks between fibrin monomers (forms an amide bond between a lysine residue and a glutamine residue) |
|
|
Prothrombin |
A zymogen containing several γ-carboxyglutamates on the N-terminal end |
|
|
What is required for conversion of prothrombin to thrombin? |
Phospholipids Calcium Factor V Factor Xa |
|
|
Why doesn't prothrombin adhere to RBC's or endothelial cells of the vascular system?
|
Prothrombin only binds to surfaces with net negatively-charged phospholipids derived from platelets or damaged tissues
These PL's are found exclusively on the cytoplasmic side of lipid bilayers |
|
|
Why does prothrombin need γ-carboxyglutamates? |
They chelate calcium ions, bringing prothrombin in close proximity to Factor V and Factor Xa |
|
|
Extrinsic Coagulation Pathway |
Tissue factor (thromboplastin) and Factor VII convert Factor X to Factor Xa, which is involved in the activation of thrombin from prothrombin
Occurs in about 12 seconds |
|
|
Thromboplastin (Tissue Factor) |
A protein released from severed tissue that begins the extrinsic coagulation cascade
Along with Factor VII, it converts Factor X to Factor Xa
|
|
|
Prothrombin Time (PT) |
A lab test measuring clotting time after thromboplastin is added to blood |
|
|
Intrinsic Coagulation Pathway |
Factor XII binds to exposed collagen and is converted to Factor XIIa, which cleaves Factor XI to Factor XIa; Factor XIa cleaves Factor IX to Factor IXa; Factor IXa, along with Factor VIII, calcium, and PL's, converts Factor X to Factor Xa
Takes 2-3 minutes |
|
|
Classic Hemophilia |
X-linked recessive inheritance
Caused by missing/defective Factor VIII, which is required for the activation of Factor X to Factor Xa |
|
|
How is intravascular coagulation prevented? |
1. Natural clotting inhibitors in blood (ex. antithrombin III)
2. Some clotting factors bind tightly to the blood clot
3. The half-life of some factors is very short, and removal of activated factors by hepatocytes is rapid
4. The concentration of activated factors decreases by dilution of flowing blood |
|
|
γ-glutamyl Carboxylase
|
Located in liver only (ER network; co-translational modification)
Catalyzes the addition of the γ-carboxyl group on Glu γ-Carboxyglutamates are present on prothrombin and Factors X, IX, and VII Requires Vitamin K as a cofactor |
|
|
Effect of Vitamin K defficiency on coagulation |
Prothrombin and Factors X, IX, and VII are made, but cannot bind calcium, leading to an increase in coagulation time |
|
|
In vitro anticoagulants for the collection of blood |
Primarily agents that chelate calcium
EDTA, citrate, F, oxalate (all negatively charged) |
|
|
In vivo anticoagulants for limiting coagulation |
Reduce clot tendency over extended periods by interfering vitamin K action
Dicumarol and Warfarin (analogs of vitamin K; competitive inhibition of γ-glutamyl carboxylase) |
|
|
Dicumarol |
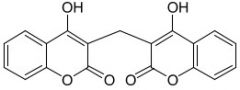
|
|
|
Warfarin |
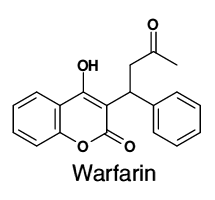
|
|
|
Heparin |
High molecular weight polysaccharide
Highly negatively charged due to large amounts of sulfate and carboxyl groups (uronic acids)
Found in mast cells
Activates anti-thrombin III |

