![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
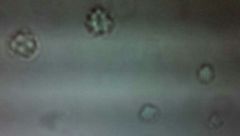
|
Bloods cells in hypertonic solution
|
|

|
Bloc cells in isotonic solution
|
|

|
left side: isotonic
right side: hypertonic |
|
|
what stains did we use in biological molecules Lab?
|
1) benedicts
2) iodine 3) Ninhydrin |
|
|
what did the biological molecule stain for?
|
1) Benedict's stains sugar
2) iodine stained starch 3) ninhydrin stains protein |
|
|
an example of our negative control is
a) starch b) water c) glucose |
negative : neutral
b) water |
|
|
one postive control example is:
a) glucose b) water |
a) glucose is an example
|
|
|
ninhydrin stains for
protein, starch, or sugar? |
protein
|
|
|
sugar will be stained by
Benedict iodine ninhydrin |
Benedict
|
|
|
soda was postive for
a) protein b) sugar c) starch d) all |
sugar only
|
|
|
chicken was postive for :
a) protein b) sugar c) starch d) all |
protein only
|
|
|
fries and buns was postive for:
a) protein b) sugar c) starch d) all |
all of them protein, sugar, starch
|
|
|
what are the organelles that store starch ?
|
Amyloplasts
|
|
|
what type of carbohydrate are stored in plant cells?
|
starch
|
|
|
in hypertonic solution the cell will:
|
expel water and shrivel up
|
|
|
when water enters the cell then this means it is :
a) hypotonic b) hypertonic c) isotonic |
a) hypotonic
|
|
|
the definition of isotonic is:
|
an isotonic solution is when two solutions have the same osmotic pressure
|
|
|
define HYPERTONIC
|
the concentrations of a solution is higher outside of the cell, the cell shrivels. (water diffuses)
|
|
|
define HYPOTONIC
|
the concentration of a solution OUTSIDE the cell is lower so water diffuses into the cell
|

