![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the blood brain barrier? |
It is a highly selective permeability barrier that separates the circulating blood from the brain extracellular fluid (BECF) in the central nervous system (CNS). The blood–brain barrier is formed by capillary endothelial cells, which are connected by tight junctions |
|
|
What is the ECF? |
Extracellular fluid (ECF) usually denotes all body fluid outside of cells. |
|
|
What is the central nervous system? |
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. |
|
|
What are tight junctions? |
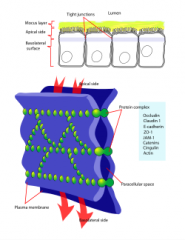
Tight junctions are the closely associated areas of two cells whose membranes join together forming a virtually impermeable barrier to fluid. |
|
|
What are astrocytes? |

Astrocytes are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They are the most abundant cell of the human brain. They perform many functions, including biochemical support of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue and maintenance of extracellular ion balance. |
|
|
What are circumventicular organs? |
Circumventricular organs (CVOs) are structures in the brain that are characterized by their extensive vasculature and lack of a normal blood brain barrier (BBB). The CVOs allow for the linkage between the central nervous system and peripheral blood flow. The lack of a blood brain barrier allows the CVOs to act as an alternative route for peptides and hormones in the neural tissue to the peripheral blood stream, while still protecting it from toxic substances. |
|
|
What are brain endothelial cells? |
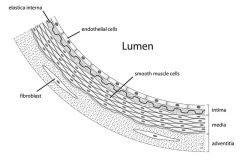
The endothelium is the thin layer of cells that lines the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels, forming an interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. The cells that form the endothelium are called endothelial cells. |
|
|
What is cerebral spinal fluid? |
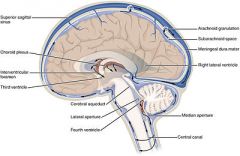
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear colorless bodily fluid found in the brain and spine. It is produced in the choroid plexus of the brain. It acts as a cushion or buffer for the brain's cortex, providing a basic mechanical and immunological protection to the brain inside the skull, and it serves a vital function in cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. |
|
|
What is the basement membrane? |
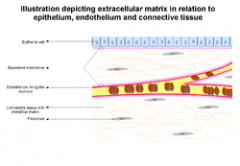
The basement membrane is a thin sheet of fibers that underlies the endothelium in the brain which lines the interior surface of blood vessels. |
|
|
What is the choroid plexus? |
The choroid plexus is a plexus in the ventricles of the brain where cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is produced. There are four choroid plexuses in the brain, one in each of the ventricles. |
|
|
What is a pericyte? |
Pericytes are contractile cells that wrap around the endothelial cells of capillaries throughout the body. Pericytes are embedded in basement membrane where they communicate with endothelial cells. In the brain, pericytes help sustain the blood–brain barrier as well as several other homeostatic functions. Pericytes regulate capillary blood flow, the clearance and phagocytosis of cellular debris, and the permeability of the blood–brain barrier. They also stabilize and monitor the maturation of endothelial cells. |

