![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
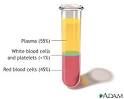
Formed Elements |
|
|

Erythrocytes |
RBC, anucleated, bioconcave disc, most numerous cell type, transports oxygen. |
|

Platelets |
Aids with Blood Clotting, cell fragments of megakaryocytes. |
|
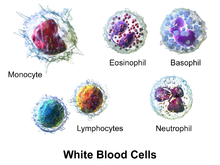
Leukocytes |
WBC, uses Amoeboid movement, divided into 2 groups: Granulocytes and Agranulocytes |
|
|
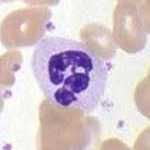
Neutrophils- Most Numerous WBC, 3-4 nuclei, non-specific defenses, 1st on site of injury, specialized in phagocytizing, and is a Granulocytes. |
|
|
Eosinophil- Granules stain dark with eosin, attack objects coated with antibodies, phagocytic cells, attacks parasitic worms like flukes, granulocyte. |
|
|
Basophil- Least occuring, granules stain purple, nonspecific, granules of histamine or heparin, attracts more basophils and eosinophils, granulocyte. |
|

|
Monocyte- Nonspecific, phagocytic, Macrophages in tissue, release chemicals to attract other WBC. |
|

|
Lymphocyte- Specific defense, immune response- direct cell attack, T-cells (protect against viruses) and B-cells (produce antibodies against bacteria and toxins) and NK (natural killer) cells. |
|
|
Anemia |
Decreased Oxygen carrying capacity |
|
|
Sickle Cell Anemia |
Not enough oxygen is available since the hemoglobin in the RBC is sickle shaped. |
|
|
Leukopenia |
Low WBC Count |
|
|
Leukocytosis |
High WBC cound |
|
|
Polycythemia |
High RBC Count |
|
|
Type A Blood |
Has A-antigens, has B-antibodies, can recieve A&O |
|
|
Type B Blood |
Has B-antigens, has A-antibodies, receives B & O |
|
|
Type AB Blood |
Has A and B antigens, no antibodies, and receives all types of blood. Universal recipient. |
|
|
Type O Blood |
Has no antigens, has both A and B antibodies, and can only receive type O blood. Universal Donor. |
|
|
Hematocrit |
Estimates RBC percentage, may indicate anemia or polycythemia |
|
|
Hemoglobin Concentration |
Low Hb may mean anemia |
|
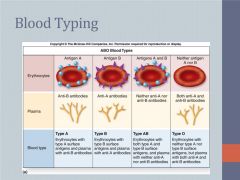
ABO Blood Typing |
Determines the presence of surface proteins on RBCs |
|
|
Rh Typing |
Determines the presence of Rh antigen |
|
|
Total WBC Count |
may indicate an infection |
|
|
Differential WBC count |
May suggest a type of infection |

