![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Are islet autoantibodies involved in the destructive process of beta cells in T1DM?
|
Islet autoantibodies are not thought to be involved in the destructive process, but rather are formed as a result of β-cell destruction, and serve as immunologic markers.
|
|
|
When is tight glycemic control used and not used?
|
Use it to slow progression to renal dz and other macrovascular disease
Once CAD begins = don't |
|
|
Amylin vs Incretin effects?
|
Amylin deficiency in T1DM
Actions: Inhibition of gastric emptying, inhibition of glucagon secretion (glucagon --> hepatic effects, MSK glycogen production) Incretin deficiency in T2DM Actions: Augment glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, suppress hepatic glucose output, slow gastric emptying, act centrally to enhance satiety vs Amylin: not as broad effect vs glucagon, but acts directly to affect satiety |
|
|
What are the interplays between the cortisol axis and the RAAS system?
|
ACTH, a pituitary peptide, also has some stimulating effect on aldosterone probably by stimulating the formation of deoxycorticosterone, a precursor of aldosterone.[16]
MR: The receptor is activated by mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone and deoxycorticosterone as well as glucocorticoids, like cortisol. In intact animals, the mineralocorticoid receptor is "protected" from glucocorticoids by co-localization of an enzyme, 11ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (11ß-HSD2), that converts cortisol to inactive cortisone. |
|
|
How is aldosterone synthesis induced?
|
1) increase in the plasma concentration of Angiotensin III, a metabolite of Angiotensin II
2) increase in plasma angiotensin II, ACTH, or potassium levels, which are present in proportion to plasma sodium deficiencies (The increased potassium level works to regulate aldosterone synthesis by depolarizing the cells in the zona glomerulosa, which opens the voltage-dependent calcium channels.) The level of angiotensin II is regulated by angiotensin I, which is in turn regulated by the hormone renin. Potassium levels are the most sensitive stimulator of aldosterone. 3) the ACTH stimulation test, which is sometimes used to stimulate the production of aldosterone along with cortisol to determine whether primary or secondary adrenal insufficiency is present (However, ACTH has only a minor role in regulating aldosterone production; with hypopituitarism there is no atrophy of the zona glomerulosa.) 4) plasma acidosis 5) the stretch receptors located in the atria of the heart. If decreased blood pressure is detected, the adrenal gland is stimulated by these stretch receptors to release aldosterone, which increases sodium reabsorption from the urine, sweat, and the gut. This causes increased osmolarity in the extracellular fluid, which will eventually return blood pressure toward normal. 6) adrenoglomerulotropin, a lipid factor, obtained from pineal extracts. It selectively stimulates secretion of aldosterone |
|
|
How do you test for medullary carcinoma? What can't you use, unlike other thyroid cancers?
|
Serum calcitonin. Can't use iodine and TSH b/c it doesn't express NIS.
|
|
|
Why can't you use midnight plasma cortisol to test for Pseudo Cushings?
|
It follows circadian rhythm and is below 7.5mg/dL or normal at midnight.
|
|
|
What does 11beta-hydroxysteroid DH do and where is it located?
|
They turn cortisol into cortisone, inactivating it.
It is located in the skin, liver, and kidneys. It is also located in the colon, sweat glands, salivary glands, placenta, adipose tissue, and CNS. |
|
|
What is a sestimibe scan?
|
Technetium (99mTc) sestamibi (trade name Cardiolite) is a pharmaceutical agent used in nuclear medicine imaging.
Sestamibi imaging is correlated with the number and activity of the mitochondria within the parathyroid cells, such that oxyphil parathyroid adenomas have a very high avidity for sestamibi, |
|
|
What constitutes polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type 2?
|
Addison's, Hashimoto's, T1DM
|
|
|
What constitutes polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type 1?
|
Addison's, Hypopara, asplenism --> candidasis
|
|
|
What glandular problem causes anovulation?
|
Hypothyroidism
|
|
|
How does Cushing's Syndrome cause elevation in androgen?
|
ACTH-secreting tumor (pituitary): ACTH increases cortisol and androgens and aldosterone.
|
|
|
How does FFA inc blood pressure?
|
The infusion of FFAs into the portal vein activates the sympathetic nervous system and elevates blood pressure in the animal model.
|
|
|
How does EE help the endometrium? What is it found in?
|
It provides staiblity. It is synthetic estrogen found in COC's.
|
|
|
Why is EE added to COC?
|
It has the best
|
|
|
How does COC prevent ovulation?
|
It acts on the central players, estrogen inh FSH and progestin inh LH.
|
|
|
What are some of the useful benefits of COC?
|
Regularizes oligomennorhea
helps dysmenorhea dec acne dec PID dec anemia for heavy bleeders dec ovarian and endometrial CA dec perimenopausal symptoms |
|
|
Where do the risks of stroke in <35ug EE COC come from?
|
Progestin
|
|
|
What should the pt do if they missed 3 pills or started 3 days late on the OC?
|
They should use contraception for 7 days, continue on with the packs. If it is in the third week, they should ignore the placebo and start new pack.
If this occurs in the first week w/ unprotected sex, emergency contraception should be considered. |
|
|
What is the definition of menopause?
|
Cessation of menstruation for 12 months.
|
|
|
What is the def of early perimenopause? What is considered late menopause and postmenopause?
|
2-8 years before menopause. Late peri = 1 year after FMP. Postmenopause = period 1 year after menopause until death.
|
|
|
What are the risks of giving estrogen HRT alone?
|
Pancreatitis
Endometrial hyperplasia/CA Ovarian CA? Kidney stones Breast/bleeding SEs Stroke Dementia DVT |
|
|
What are the risks of giving estrogen+progestin HRT?
|
Brst CA
Total CA Pancreatitis Kidney stones Breast/bleeding SEs CHD Stroke Dementia DVT/PE Gallbladder dz |
|
|
What are the benefits of giving estrogen HRT alone?
|
Improves:
Vasomotor symptoms Vaginal Atrophy Breast CA incidence if stop after 5 yrs MI Osteoporosis |
|
|
What are the benefits of giving estrogen+progestin HRT?
|
Improves:
Vasomotor symptoms Vaginal Atrophy Osteoporosis Colon CA |
|
|
What cardiovascular changes occur during pregnancy?
|
Inc total BV
Inc CO Dec SVR (sys and dias) //easier placental blood delivery |
|
|
What CV SS during pregnancy mimic heart disease?
|
Dyspnea
Reduced exercise tolerance JV distension Displaced PMI to left Peripheral edema S3 gallop Systolic flow murmur Cardiomegaly |
|
|
What respiratory changes occur during pregnancy?
|
Inc O2 consumption
Inc tidal volume Inc minute ventilation //driven by progesterone |
|
|
What respiratory SS during pregnancy mimic heart disease?
|
Dyspnea
Respiratory alkalosis |
|
|
What renal changes occur during pregnancy?
|
Inc renal plasma flow
Inc GFR |
|
|
What renal SS during pregnancy mimic respiratory dz?
|
Urinary frequency
Dilation of urinary collecting system //susceptible to UTI Dec BUN/Creat Dec serum osmol Dec Na, K, Ca |
|
|
What happens to the GI physiology during pregnancy?
|
Dec peristalsis and GERD //progesterone relaxing SM
Dec gastric emptying and intestinal motility Inc water resorption, portal venous pressure, constipation, hemorrhoids //GI mechanically obstructed by enlarging uterus Impaired gallbladder emptying //inc biliary chol and cholelithiasis |
|
|
What are SS of GI physiology during pregnancy that may mimic liver dz?
|
Spider angiomata
Palmer erythema Dec serum albumin Inc serum alkaline phosphatase (AST, ALT unchanged) Inc serum cholesterol |
|
|
What hapens to hematologic physiology during pregnancy?
|
Physiologic anemia //more plasma volume
Iron-def anemia //inc RBC volume Hypercoagulability |
|
|
Which progesterone receptor is stronger and is an activator for progesterone? What happens to this ratio during pregnancy?
|
PR-B. PR-A suppresses progesterone activity. More PR-A is expressed during pregnancy.
|
|
|
What are the stages in normal parturition?
|
Phase 0: Quiescence
Lack of gap junctions, progesterone Phase 1: Activation Uterine stretch, activation of fetal HPA axis Phase 2: Stimulation CRH expression Functional progesterone withdrawal Estrogen activation Oxytocin Prostaglandins Common pathway: cervical ripening, uterine contractility, fetal/decidual membrane activation Phase 3: Involution Oxytocin |
|
|
What is the most common type of pituitary tumor (adenoma)?
|
Prolactinoma
|
|
|
HGPIN is a likely precursor of what type of CaP?
|
Intermediate and high grade, but not low grade.
|
|
|
What are the target actions of Testosterone?
|
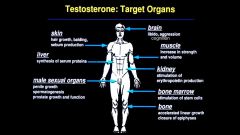
|
|
|
What tissue resemblance is observed in Meckel's diverticulum?
|
pancreatic, gastric, or small intestine
|
|
|
What can be a complication of Meckel?
|
B12 deficiency:
from Bacterial overgrowth, leads to ~pernicious anemia |
|
|
What do GI muscles have a tendency to do?
|
Constrict, i.e. LES when there is achalasia (esp. primary in the absence of NO producing neurons--myenteric plexus) or HD (lack of myenteric plexus or submucosal neurons)
|
|
|
What is the genetic defect in Hirschsprung disease?
|
Absence of RET genes or ligand.
|
|
|
Where is colonic diverticulosis more likely to occur?
|
Left colon/sigmoid
|
|
|
What part of the anatomy does ulcerative colitis affect?
|
Less the right side, more the left side. Inflammation extends into mucosa and maybe submucosa with superficial ulcers.
|
|
|
What part does Crohn's disease affect?
|
Any part of GI tract, >% ileum. Lesions can skip; inflammation is transmural (through mucosa/submucosa) with non-necrotizing granulomas, ulcerations and fissures.
|
|
|
Difference between Crohn's and UC?
|
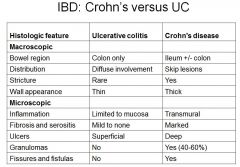
|
|
|
Which GI cancer's prognosis is related to size?
|
Pancreatic
|
|
|
Which GI cancer uses T as a rating of invasion rather than size?
|
Colon Ca
|
|
|
Can you get odynophagia with ESCCa? What is the more common symptom associated with ESCCa?
|
Yes, but dysphagia is more common.
|
|
|
Which Gastric malignancy is the most aggressive?
|
Diffuse-type (Bormann grade IV).
|
|
|
What is defined as preterm? Very preterm?
|
preterm = <37 wks, very preterm = <32 wks
|
|
|
What does follicle development (including putting up LH-R) respond to?
|
E2 and FSH
|

