![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
renal corpuscle, or AKA =
malpighian corpuscle, consists of: Bowmans capsule glomerulus (a capillary tuft) Bowman has two layers: = |
visceral layer
parietal layer The visceral layer is lined by podocytes parietal layer is simple squamous ------ glomerular capillaries, lined by fenestrated endothelial cells. mesangium, mesangial cells mesangial matrix. podocytes, ------ (Bowman's space/capsular space) contains the = plasma ultrafiltrate (primary urine) exists between visceral & parietal layers . |
urinary pole
the gate the plasma ultrafiltrate flows into the PCT The opposite pole, the site of entry and exit of the = afferent glomerular arterioles efferent glomerular arterioles is the = vascular pole. |
|
|
renal corpuscle, or AKA =
|
malpighian corpuscle,
|
|
|
|
renal corpuscle
or malpighian corpuscle, consists of the capsule of Bowman investing a capillary tuft, the = |
glomerulus
|
|
|
|
capsule of Bowman has two layers: =
|
visceral layer
parietal layer |
attached to the capillary glomerulus
associated with the connective tissue stroma. |
|
|
Nephron
The visceral layer is lined by epithelial cells called |
podocytes
reinforced by a = |
basal lamina
|
|
|
Nephron
parietal layer is covered by a basal lamina supported by what kind of epith. = |
simple squamous epithelium
|
|
|
|
Nephron
A urinary space (Bowman's space/capsular space) contains the = |
plasma ultrafiltrate (primary urine)
exists between the visceral and parietal layers of the capsule. |
|
|
|
The urinary space is continuous with the lumen of the ______ ______ _______ at the urinary pole, the gate through which the plasma ultrafiltrate flows into the proximal convoluted tubule.
|
proximal convoluted tubule
The opposite pole, the site of entry and exit of the = |
afferent and efferent glomerular arterioles
, is called the = vascular pole. |
|
|
glomerulus consists of 3 components: =
|
glomerular capillaries,
lined by fenestrated endothelial cells. mesangium, formed by mesangial cells embedded in the mesangial matrix. podocytes, constituents of the _______ layer of the capsule of Bowman |
visceral
|
|
|
glomerular capillaries are lined by ? epith. =
|
fenestrated endothelial cells.
|
|
|
|
mesangium is =
|
formed by mesangial cells embedded in the mesangial matrix.
|
|
|
|
podocytes are constituents of the =
|
visceral layer of the =
|
capsule of Bowman.
|
|
|
_________ constituents of the visceral layer of the capsule of Bowman.
|
podocytes
|
|
|
|
__________ is formed by
mesangial cells embedded in the mesangial matrix. |
mesangium
|
|
|
|
__________ are lined by fenestrated endothelial cells.
|
glomerular capillaries
|
|
|
|
glomerular filtration barrier is made up with both =
|
Both podocytes and fenestrated endothelial cells and their corresponding basal laminae constitute the ____ ____ _____.
|
glomerular filtration barrier
|
|
|
Both podocytes and fenestrated endothelial cells and their corresponding basal laminae constitute the =
|
glomerular filtration barrier.
|
|
|
|
The endings of the cell processes, the pedicels, from the same podocyte or adjacent podocytes, =
|
interdigitate to cover the basal lamina and are separated by gaps, the filtration slits.
|
|
|
|
The podocyte filtration slit diaphragm consists of the substance =
|
protein nephrin.
|
|
|
|
In addition to the components of the glomerular filtration barrier, other limiting factors controlling the passage of molecules in the plasma ultrafiltrate are =
2ct |
size
electric charge. |
|
|
|
Molecules with a
size less than 3.5 nm and positively charged or neutral are filtered more readily ie = |
Albumin
filters poorly 3.6 nm and anionic |
|
|
|
Nephron
Filtration slits are bridged by a membranous material, the filtration slit diaphragm. Pedicels are attached to the basal lamina by = |
integrin
|
|
|
|
The podocyte filtration slit diaphragm has the substance =
|
protein nephrin.
|
|
|
|
The fenestrated endothelial cells of the glomerular capillaries are covered by a
|
basal lamina
which the foot processes of the podocytes attach. |
|
|
|
Podocytes produce a substance glomerular
GEGF |
endothelial growth factor
to stimulate the development of the ___________ & maintenance of its _________= |
endothelium
fenestrations. |
|
|
fenestrated endothelial cells
endothelium is permeable to = 4ct H+ |
water
urea glucose small proteins |
WUGS
|
|
|
fenestrated endothelial cells
The surface endothelial cells is coated with |
negatively charged glycoproteins
that block the passage of large anionic proteins. |
|
|
|
The endothelial cell basal lamina, closely associated with the basal lamina produced by podocytes, contains =
4ct |
type IV collagen
fibronectin laminin heparan sulfate |
|
|
|
____ ____ ____
is caused by a mutation in the _______ gene leading to the absence or malfunction of the podocyte slit filtration diaphragm. |
Congenital nephrotic syndrome
nephrin |
|
|
|
Congenital nephrotic syndrome is caused by a mutation in the _____ gene leading to the absence or malfunction of the ________ slit filtration diaphragm.
|
nephrin
podocyte |
|
|
|
Congenital nephrotic syndrome is caused by a mutation in the nephrin gene leading to the absence or malfunction of the =
|
podocyte slit filtration diaphragm.
|
|
|
|
Congenital nephrotic syndrome
Affected children have massive proteinuria even in utero and the nephrotic syndrome develops soon after birth. Infants display = 4ct |
abdominal distention,
hypoalbuminemia hyperlipidemia edema |
|
|
|
Congenital nephrotic syndrome, is particularly common where =
|
Finland, is lethal.
|
|
|
|
diabetes mellitus and glomerulonephritis (characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli), the glomerular filter is altered
becomes = |
permeable to proteins
release of protein into the urine proteinuria |
|
|
|
_________ is an intraglomerular structure interposed between the glomerular capillaries, consisting of two components: =
|
Mesangium
mesangial cells mesangial matrix. |
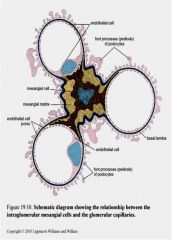
|
|
|
Mesangial cells are specialized pericytes with characteristics of
|
smooth muscle cells
macrophages |
|
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome
aka = |
anasarca
or dropsy |
|
|
|
hypoalbuminemia causes hyperlipidemia =
|
Hypoproteinemia stimulates protein synthesis in the liver, resulting in lipoprotein overproduction.
Lipid catabolism is decreased due to lower levels of lipoprotein lipase, causing lipoprotein breakdown. Cofactors, such as Apolipoprotein C2 may also be lost by increased filtration of proteins. |
|
|
|
Nephrotic
vs Nephritic podocytes are degraded & large enough to permit proteinuria thus hypoalbuminemia... |
albumin allowed to pass from blood to the urine
but podocytes are not large enough to allow hematuria. By contrast = |
nephritic syndrome RBCs can pass thru pores, causing hematuria.
|

