![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Slide 34
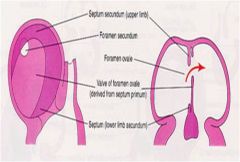
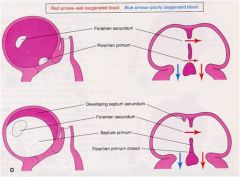
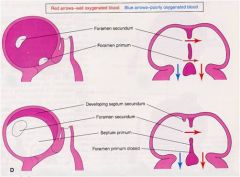
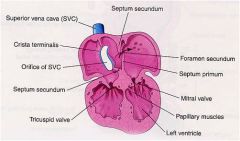
Development of the Atrial Septum Formation: composed of = |
septum primum
septum secundum foramen primum foramen secundum |
|
|
|
The crescent-shaped ______ _____ forms in the roof of the primitive atrium and grows toward the atrioventricular (AV) cushions in the AV canal.
|
septum primum
|
|
|
|
The foramen secundum forms in the center of the =
|
septum primum
The crescent-shaped septum secundum forms to the |
right of the septum primum.
|
|
|
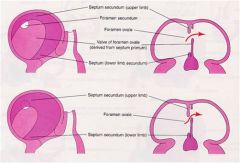
The______ -______ is the opening between the upper and lower limbs of the _______ ______
|
foramen ovale
septum secundum. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Before birth the foramen ovale allows blood to pass from the
|
right atrium into the left atrium
Reflux of blood is prevented by the valve |
|
|
|
After birth the foramen ovale normally closes by fusion of the ____ ______ and the ______ _______
|
septum primum
septum secundum. |
|
|
|
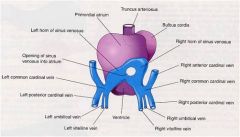
DEVELOPMENT OF RIGHT ATRIUM
Develops from: |
right horn of the sinus venosus
primitive atrium. |
|
|
|
right horn of the sinus venosus
& the primitive atrium Develops the = |
RIGHT ATRIUM
|
|
|
|
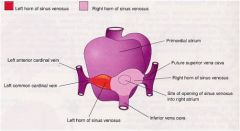
DEVELOPMENT OF RIGHT ATRIUM
sinus venosus develops a left horn which becomes the ____ _____ and a right horn which will be incorporated into the_____ ______ |
coronary sinus
right atrium. |
|
|
|
_____ _____ develops a left horn which becomes the coronary sinus and a ____ ____ which will be incorporated into the right atrium.
|
sinus venosus
right horn |
|
|
DEVELOPMENT OF RIGHT ATRIUM
The smooth part of the right atrium, the sinus venarum, is derived from the = |
sinus venosus
whereas the muscular part, the auricle, is derived from the = |
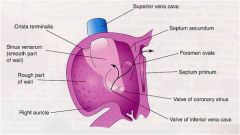
primitive atrium.
|
|
|
DEVELOPMENT OF RIGHT ATRIUM
The smooth part of the right atrium, the____ _______ , is derived from the sinus venosus whereas the____ _____ of the auricle, is derived from the primitive atrium. |
sinus venarum
muscular part, The 2 portions are separated internally by the = and externally by the = |
crista terminalis
sulcus terminalis. |
|
|
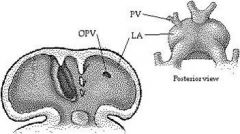
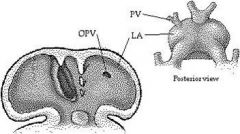
DEVELOPMENT OF LEFT ATRIUM
Development of the left atrium occurs concurrently with that of the |
right atrium.
L atrium develops from: 2ct |
pulmonary veins
Primordial atrium |
|
|
DEVELOPMENT OF LEFT ATRIUM
pulmonary veins Primordial atrium develope what = |
L atrium develops from:
|
|
|
|
DEVELOPMENT OF LEFT ATRIUM
L atrium develops from: 2ct |
pulmonary veins
Primordial atrium |
|
|
|
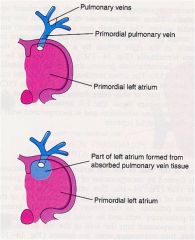
DEVELOPMENT OF LEFT ATRIUM
During the early part of the _____ week an outgrowth of the pulmonary veins appear from the left atrium. |
4th wk
As the atrium expands, the primordial pulmonary vein and its main branches are gradually incorporated into the wall of the____ ____ |
left atrium.
|
|
|
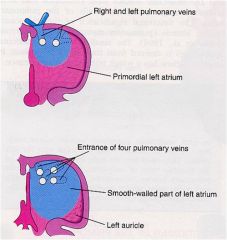
As a result 4 pulmonary veins are formed. Molecular studies have confirmed that atrial myoblasts migrate into the walls of the pulmonary veins.
The small left auricle is derived from the primordial atrium. Its internal surface has a rough trabeculated appearance |
.During ___ week an outgrowth of the pulmonary veins appear
|
4th
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Interventricular (IV) Septum
Formation: has 3 parts: |
muscular part
membranous part IV foramen |
|
|
|
The Interventricular (IV) Septum
***The muscular ___ _____ develops in the midline on the floor of the primitive ventricle and grows toward the fused AV cushions. |
IV septum
|
|
|
|
IV foramen
This foramen is closed by the membranous IV septum, which forms by the proliferation and fusion of tissue from three sources: the |
***right bulbar ridge,
***left bulbar ridge, AV cushions. |
|
|
|
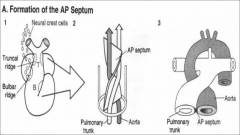
Formation of the Aorticopulmonary (AP) Septum
Neural crest cells migrate from the = |
hindbrain region
through pharyngeal arches 3, 4, 6 and invade both the truncal ridges and bulbar ridges. |
|
|
|
The_______ & ____ ridges grow and twist around each other in a _____ fashion and eventually fuse to form the
_____ ___________ |
truncal and bulbar
spiral AP septum. |
|
|
|
Formation of the Aorticopulmonary (AP) Septum
The AP septum divides the___________ __________ into the aorta and pulmonary trunk. |
truncus arteriosus and bulbus cordis
|
|
|
|
Formation of the Aorticopulmonary (AP) Septum
The AP septum divides the truncus arteriosus and bulbus cordis into the ________ _________ |
aorta and pulmonary trunk.
|
|

