![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name two classes of drugs that inhibit cell wall biosynthesis and one class of drugs that inhibits membrane potential
|
glycopeptide
beta lactams lipopeptide antibiotics |
|
|
name two glycopeptide antibiotics
|
vancomycin
teicoplanin |
|
|
glycopeptides are ___ against gram positive cocci and ___ against gram positive rods; they are ___ against gram negatives
|
bacteriostatic- gram pos cocci
bactericidal- gram pos rods non effective- gram negatives |
|
|
Where is vancomycin's site and mechanism of action
|
binds D-ALA-D-ALA terminus of murine monomer
--> inhibits murine polymer synthesis by blocking attachment of repeating disaccharide subunits to pre-existing cell wall |
|
|
name four reasons/conditions to use vancomycin
|
1. antibiotic resistant pseudomembranous colitis
2. antibiotic resistant staphylococcal enterocolitis 3. staph infection in beta-lactam sensitive patients- or when infection is resistant 4. strep infections in beta lactam sensitive patients, or when infection is resistant |
|
|
how do bugs become resistant to vancomycin
|
acquire the ability to replace the terminal D-ala with D-lactate (acquire the van HAX gene)
|
|
|
name three benefits of teicoplanin over vancomycin
|
1. extened half-life
2. once daily dosing 3. no pain or tissue necrosis after IM injection |
|
|
beta lactams are type ___ antibiotics
|
type 2:
bacteriocidal time-dependent no PAE |
|
|
name three classes of beta lactams
|
1. penicillins
2. cephalosporins 3. carbapenems |
|
|
where do penicillins come from
|
made by strains of the fungus penicillium
|
|
|
what is the common structural feature of penicillins
|
6-aminopenicillanic acid nucleus composed of a thiazolidine ring (pentagon) fused to a beta lactam ring (square)
|
|
|
why are penicllins provided as their Na or K salts
|
because they are strong acids, the salt improves their solubility
|
|
|
where is the active center of penicillins, the site of action of penicillinases, and the site of formation of the major antigenic determinants of penicillins
|
beta lactam ring
|
|
|
name four things that changing the R-group can do to the penicillin molecule
|
acid stability
sensitivity to penicllinase antibacterial spectrum potency |
|
|
penicillin MOA
|
inhibit the formation of peptidoglycan crosslinks in the cell wall.
beta-lactam moiety of penicillin -> binds enzyme that links peptidoglycan molecules in the bacteria (prevents polymerization of subunits)-> prevents bacteria from multiplying by causing lysis when bacteria tries to divide |
|
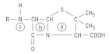
Where is the site of action for penicillinase?
for amidase? |
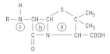
penicillinase- between the C-N bond of the beta lactam ring
amidase- between the C-N bond of the C=O to the left of the lactam ring |
|
|
penicillin G is acid/base labile.
__ of an oral dose is absorbed good distribution except ___ in renal failure, half life ___ |
acid labile
1/3 absorbed good distribution except CSF renal failure- t1/2 INCREASES |
|
|
What plays a role in hypersensitivity to penicillin G- renal secretion of unmetabolized, yet active, drug or hepatic metabolites, although inactive?
|
inactive hepatic metabolites
|
|
|
how do you delay absorption of penicillin G from intramuscular sites
|
add organic bases like procaine or benzathine
|
|
|
what is the drug of choice of syphillis
|
penicillin G + benzathine
|
|
|
What does delaying absorption of penicillin G do to the maximum blood level achieved
|
it is considerably lower for an equivalent dose
|
|
|
how do you delay elimination of penicillin G
|
administer probenecid- a competitive blocker of tubular secretion of organic acids
|
|
|
most active of the penicillins against Gram positive bacteria (non-penicillinase producers), acid labile
|
penicillin G
|
|
|
acid stable penicillin form with better absorption after oral administration
|
penicillin V
|
|
|
name four mechanisms of beta-lactam resistance
|
1. decreased affinity of penicillin binding proteins through mutation and recomb
2. decreased cell wall permeability 3. increased activity of penicillinases (beta-lactamases) 4. energy- dependent efflux pumps |
|
|
methicillin
nafcillin cloxacillin |
penicillinase resistant penicillins
|
|
|
name two bugs that make exocellular beta-lactamase
|
staph aureus and s. epidermis
|
|
|
is methacillin given orally
|
no
|
|
|
what is methicillin resistance related to
|
failure to bind to penicillin binding proteins; organisms resistant are likely to be resistant to other penicillins and cephalosporins
|
|
|
ampicillin
amoxicillin |
extended range penicillins
|
|
|
how do ampicillin and amoxicillin increase spectrum
|
better penetration of gram negative outer membrane and/or decreased susceptibility to gram negative penicillinases (but more susceptible to gram pos penicillinases)
|
|
|
which is more completely absorbed after oral administration- amoxicillin or ampicillin
|
amoxicillin
|
|
|
name 6 bugs that ampicillin and amoxicillin are good for
|
e. coli
p. mirabilis h. influenza salmonella shigella neisseria |
|
|
carbenicillin
ticarcillin |
anti-pseudomonal penicillins
|
|
|
name three bugs that are susceptible to carbenicillin and ticarcillin
|
p. aeruginosa
indole pos proteus indole pos enterobacter |
|
|
name an N-acyl derivative anti-pseudomonal penicillin (ureidopenicillin)
|
pipericillin
|
|
|
amoxicillin plus clavulanate
|
augmentin (add penicillin with a suicide inhibitor of beta-lactamase)
|
|
|
ticarcillin plus clavulanate
|
timentin (add penicillin with a suicide inhibitor of beta-lactamase)
|
|
|
ampicillin plus sulbactam
|
unasyn (add penicillin with a suicide inhibitor of beta-lactamase)
|
|
|
pipericillin plus tazobactam
|
Zosyn (add penicillin with a suicide inhibitor of beta-lactamase)
|
|
|
is penicillin itself antigenic
|
no- its polymers and metabolites can react with bacterial or tissue proteins to form antigenic conjugates
|
|
|
what is the major class of metabolites which act as antigenic determinants of penicillin
|
penicillinic acids
|
|
|
name five adverse effects of penicillins
|
1. allergic
2. diarrhea in kids 3. CV fluid overload 4. CNS effects in lg doses or renal failure 5. coag defects from inhibition of platelet activation and conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin |
|
|
does a negative skin test for penicillin hypersensitivity guarantee the absence of an anaphylactic response
|
no- it only predicts 95% of IgE mediated hypersensitivity
|
|
|
What is used to detect penicilloyl-specific IgE antibodies without skin testing
|
Rast- radioimmunoassay testing
|
|
|
cephalosporin MOA
new cephalosporins have a wider range of activity because of resistance to... |
type II bactericidal- time dependent, no PAE
gram negative penicillinases |
|
|
cefadroxil
cephalexin cefazolin cephadrine |
first generation (narrow spectrum) cephalosporin
|
|
|
first generation cephalosporins have...
___ against gram pos's ___ against gram neg's ___ against methicillin-resistant S. aureus |
good activity- gram pos
moderate activity- gram neg not effective- methicillin resistant S. aureus |
|
|
1st gen cephalosporins may not be drug of choice for active infection because they...
but may be drugs of choice for... |
don't penetrate CSF
surgical prophylaxis |
|
|
cefotetan
cefoxitin cefuroxime cefuroxime axetil carbacephem |
second generation (increased activity against gram neg, decreased activity against gram pos) cephalosporins
|
|
|
good activity against B. fragilis, and anaerobic organisms
|
cefotetan
|
|
|
similar spectrum of action to cefotetan; both used for prophylaxis during intra-abdominal surgery
|
cefoxitin
|
|
|
effective against h. influenzae and k. penumoniae; used to treat community acquired pneumonia
|
cefuroxime
|
|
|
orally active prodrug axetil form of cefuroxime
|
cefuroxime axetil
|
|
|
cephalosporin derivative with spectrum of activity comparable to that of cefaclor or amoxicillin/clavulanate
|
carbacephem
|
|
|
cefotaxime
cefpodoxime ceftazidime ceftriaxone |
3rd gen (good penetration to CNS) cephalosporin
|
|
|
high activity against many gram negative enteric bacteria
|
cefotaxime
|
|
|
orally active with wide spectrum of action; useful for URTI and UTI
|
cefpodoxime
|
|
|
indicated primarily for multidrug resistant gram negative infections; particularly those caused by pseudomonas
|
ceftazidime
|
|
|
similar spectrum to cefotaxime, 8 hr serum half life instead of 1 hr, drug of choice for n. gonorrhea and b. burgdorferi with CNS involvement
|
ceftriaxone
|
|
|
cefepime
|
4th generation cephalosporin
|
|
|
similar to ceftazidime in activity against pseudomonas and other gram negative organisms;
better than 3rd generation cephalosporins against gram pos organisms because of its resistance to chromosomally-encoded beta-lactamase; orally active |
cefepime
|
|
|
name 6 adverse effects of cephalosporins
|
1. diarrhea and GI upset
2. vit K def 3. nephrotoxicity 4. suprainfection 5. hypersensitivity reax 6. disulfiram-alcohol reax |
|
|
imipenem
meropenem ertapenem monobactam |
carbapenems (also beta-lactam antibiotics --> type II bactericidal, time-dependent; no PAE)
|
|
|
extremely broad anti-bacterial spectrum;
resistant to beta-lactamase not resistant to metallo-beta-lactamase cross-allergenicity with penicillin |
imipenem
|
|
|
imipenem with cilastatin
|
primaxin- because imipenem alone is rapidly hydrolyzed by renal tubule dipeptidase
|
|
|
structurally related to imipenem, but less susceptible to hydrolysis by renal tubule dipeptidase
|
meropenem
|
|
|
longer plasma half life than meropenem -> permitting once-daily dosing
|
ertapenem
|
|
|
excellent activity against gram neg
poor activity against gram pos little cross-allergenicity with other beta-lactam drugs |
monobactam
|
|
|
daptomycin
|
lipopeptide antibiotic- inhibits cell membrane potential
|
|
|
used for tx of complicated skin infections by aerobic, gram pos's
|
daptomycin
|
|
|
daptomycin MOA
|
bactericidal type I
concentration dependent, significant PAE binds to bacterial membranes and forms channels in a calcium-dependent manner leading to rapid membrane depolarization -> inhibiting protein, DNA, and RNA synthesis |
|
|
bactericidal against vancomycin resistant enterococci
|
daptomycin
|
|
|
how do you give daptomycin and does it cross the BBB
|
injection only
no |
|
|
how do bugs get daptomycin resistance
|
so far, they haven't
|
|
|
combinations of beta lactams with inhbitors of bacterial beta lactamases, such as ___ improves the effectiveness of the antibiotic
|
clavulanate
|
|
|
imipenem, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, is rapidly degraded by the renal ___, however, a related carbapenem, ___, is resistant to this degradation
|
renal tubule dipeptidase
meropenem |

